Spring 配置绑定原理分析
Spring 配置绑定原理分析
前言
Spring 应用中存在诸多配置,有的是系统配置,有的命令行启动参数配置,有的是yaml配置,有的是分布式配置中心配置,但对使用者而言总是可以通过@ConfigurationProperties将它关联到一个JavaBean当中或者使用@Value绑定,使得获取这这些来自不同地方的配置就像获取一个对象属性那么简单,那么它是如何来完成这个工作的呢?
结构层次
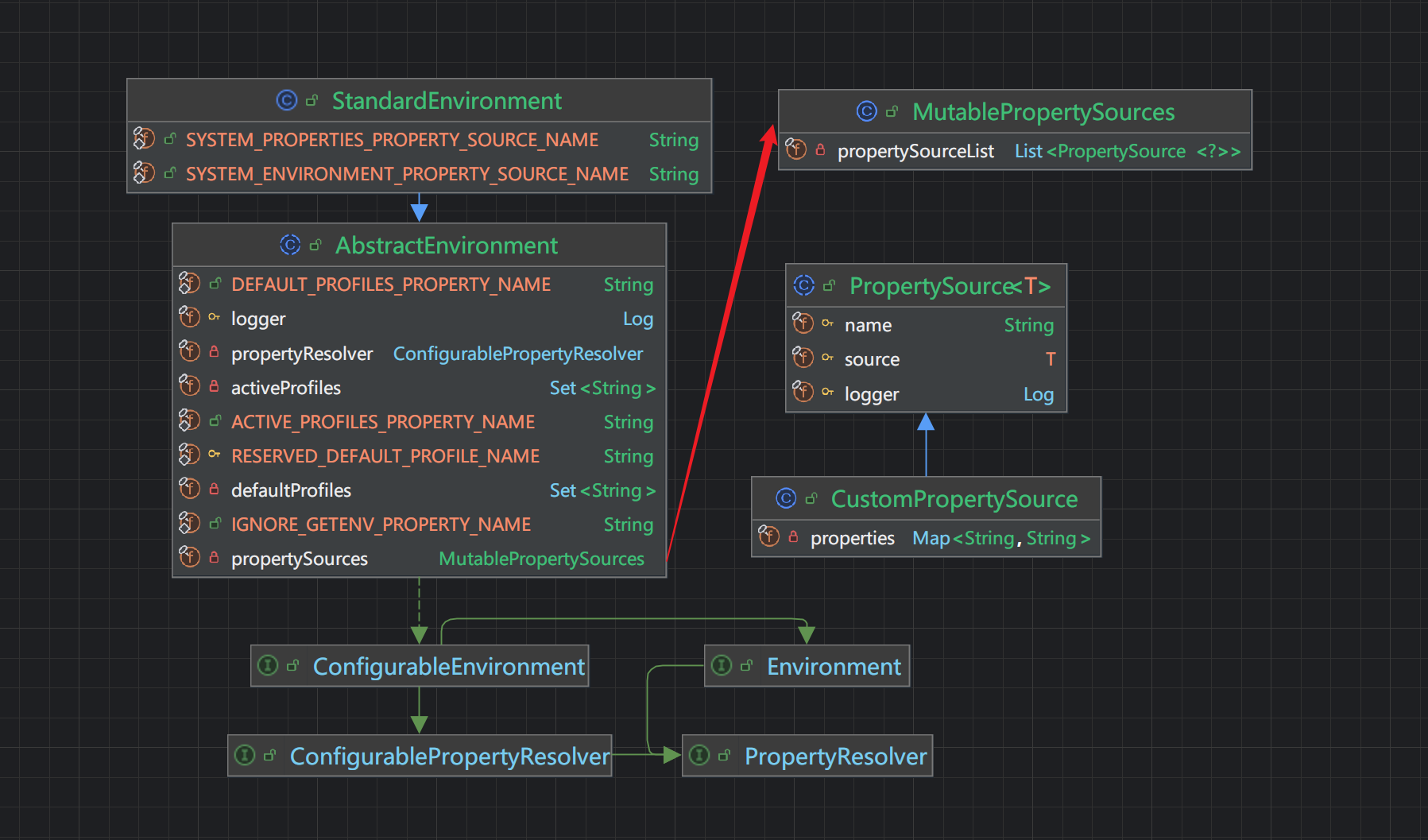
AbstractEnvironment是Spring环境的抽象实体,它存在一个MutablePropertySources类型(意为可变的配置源)的变量 propertySources,后者维护了系统中所有的配置源,系统环境变量可以是一个配置源,启动参数可以是一个配置源,application.yaml可以是一个配置源,甚至我们可以自定义一个配置源
数据源之间的冲突
我们定义了这么一个配置,我们指定了hk.name的默认值
@Data
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties("hk")
public class HkConfig {
private String name = "default";
}
我们在application.yaml做出如下配置
hk:
name: huakai
然后在启动参数也做出配置
--hk.name=hualuo
那么最终我们获取到的hk.name应该是哪一个呢?
答案是这是一个约定,原则是通常遵循着"靠近应用优先原则",通常情况下,
优先级顺序一般如下(从高到低):
- 命令行参数
application.properties或application.yml- 操作系统环境变量
- JNDI 属性
- JVM 系统属性
@PropertySource注解配置的属性文件- 默认值(在代码中指定的默认值)
实现上是如何做的呢
我们可以看到MutablePropertySources自身维护着一个List<PropertySource<?>>而配置的优先级别决定于配置源在list中的位置,配置源所处的位置越靠前那么它的优先级越高,后者又是因为Spring的策略是遍历配置源如果找到立即返回,这在Binder的实现中可见一斑
private ConfigurationProperty findProperty(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Context context) {
if (name.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
for (ConfigurationPropertySource source : context.getSources()) {
ConfigurationProperty property = source.getConfigurationProperty(name);
if (property != null) {
return property;
}
}
return null;
}
MutablePropertySources
这个可变的数据源,提供了一些添加数据源的方法,包括以下两个
addFirst()
这意味着被添加的数据源将最高的优先级
addLast()
这意味着被添加的数据源将最低的优先级
public void addFirst(PropertySource<?> propertySource) {
synchronized (this.propertySourceList) {
removeIfPresent(propertySource);
this.propertySourceList.add(0, propertySource);
}
}
public void addLast(PropertySource<?> propertySource) {
synchronized (this.propertySourceList) {
removeIfPresent(propertySource);
this.propertySourceList.add(propertySource);
}
}
自定义PropertySources
我们定义一个指定的数据源并且期望它的优先级最高
CustomPropertySource
package com.huakai.springenv.config;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CustomPropertySource extends PropertySource<Object> {
private final Map<String, String> properties = new HashMap<>();
public CustomPropertySource(String name) {
super(name);
// 在此添加您自定义的属性
properties.put("hk.name", "customValue");
}
@Override
public Object getProperty(String name) {
return properties.get(name);
}
}
CustomPropertySourcePostProcessor
package com.huakai.springenv.config;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.env.MutablePropertySources;
public class CustomPropertySourcePostProcessor implements EnvironmentPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
CustomPropertySource customPropertySource = new CustomPropertySource("customPropertySource");
propertySources.addFirst(customPropertySource);
}
}
spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=com.huakai.springenv.config.CustomPropertySourcePostProcessor
ps:EnvironmentPostProcessor 在 Spring 应用上下文初始化之前就被加载和执行所以只能通过该方式配置
测试
@Resource
private HkConfig hkConfig;
@RequestMapping("testGetConfig")
public String test2() {
return hkConfig.getName();
}

原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43779268/article/details/143580714
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
