24.11.25 Mybatis1
1.Mybatis介绍
1.封装JDBC 减少重复性代码
2.ORM(实体关系映射框架) 通过框架 实体类 <--> 数据表 自动封装对象
3.半自动的ORM框架 还需要写sql语句 2.使用mybatis连接数据库(调通一遍 记住需要哪些文件)
1.创建全局配置文件 mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--
* jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
-->
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
2.创建与数据库表对应的实体类
package com.javasm.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
}
3.创建与数据库表对应的sql操作文件(sql映射文件)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="aa.bb">
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.javasm.entity.User" >
select * from user where id = 1
</select>
</mapper>
4.通过mybatis提供的jar包功能 启动mybatis 并调用sql语句
@Test
public void getUserByIDTest(){
//启动mybaitis框架
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//mybatis中 连接 封装在了SqlSession sql会话中
//在一定程度上简化代码
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User getUserById =(User) sqlSession.selectOne("aa.bb.getUserById");
System.out.println(getUserById);
//把连接归还mybatis
sqlSession.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}3mybatis-config.xml 配置文件(了解即可)
mybatis核心配置文件 配置mybatis启动运行使用的基本参数

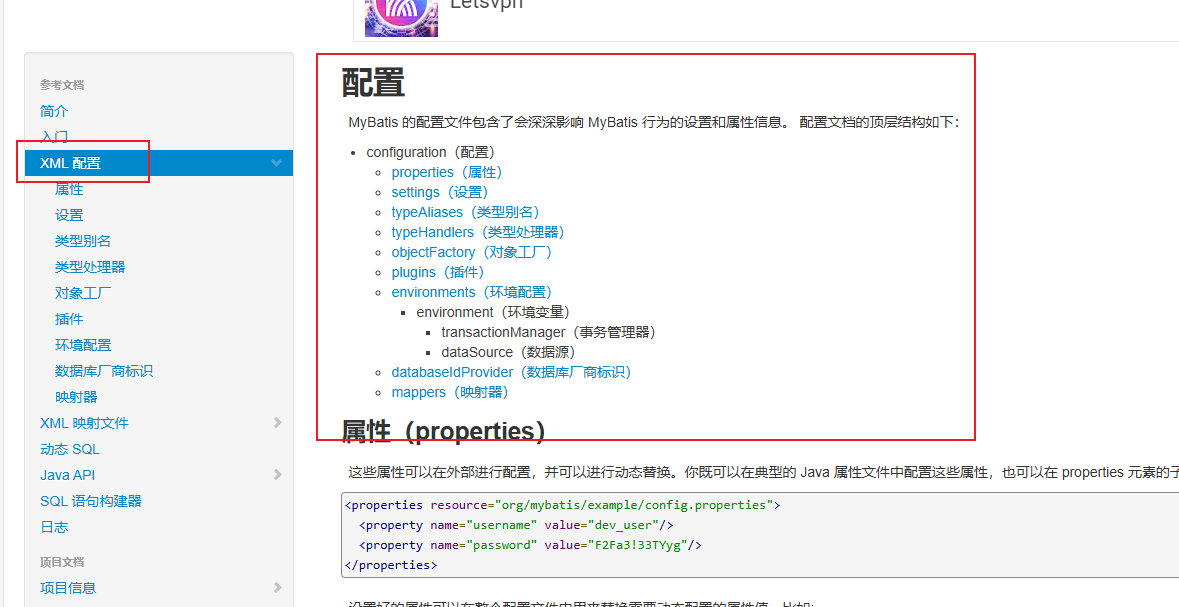


3.1properties
用来引入单独的jdbc配置文件 一般直接放在根下
<!-- <properties resource="编译的根 "> -->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties">
<!-- 自定义属性 -->
<!-- <property name="username" value="dev_user"/>-->
<!-- <property name="password" value="F2Fa3!33TYyg"/>-->
</properties>

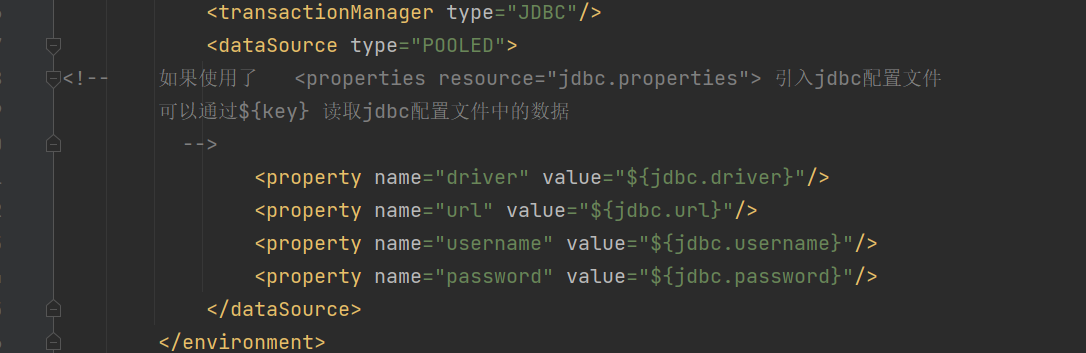
3.2 settings
运行参数设置
必须要开的设置
<settings>
<!-- 开启mybatis日志 方便调试 -->
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
<!-- 开启驼峰转换 数据库用下划线 java类用驼峰命名 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
日期类型需要注意:
//实体类一般不用date类型
//如果日期只显示 不做日期计算
//String 数据库 dateTime
//如果需要日期计算 毫秒数
//double 数据库 double
//long
private String createTime;3.3 typeAliases(在settings后面写)
<typeAliases>
<!-- 给类型指定别名 简化类型的编写
自定义别名
内置别名 80多种
-->
<typeAlias alias="User" type="com.javasm.entity.User"/>
</typeAliases>
语句使用时 可以直接使用别名

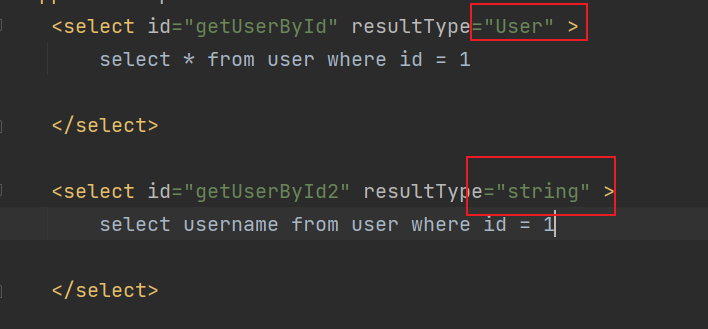
内置别名规则:
string java.lang.String
基本数据类型
_int int
包装类型
int java.lang.Integer
3.4 environments

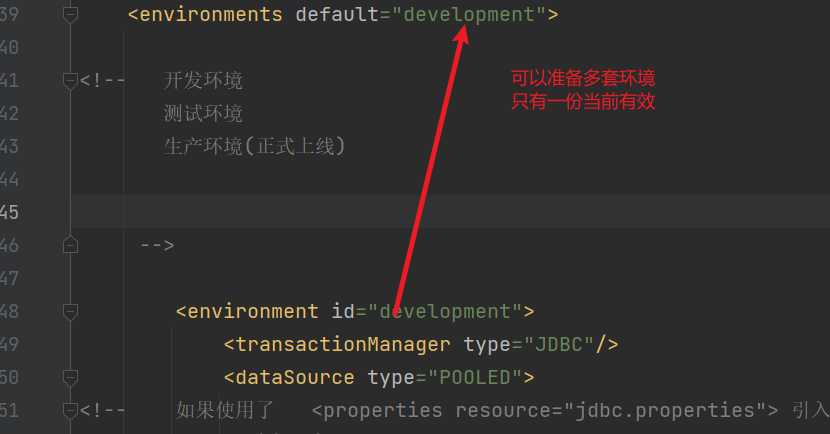
<environment id="development">
<!-- 使用jdbc事务控制 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!-- 使用数据库连接池 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 如果使用了 <properties resource="jdbc.properties"> 引入jdbc配置文件
可以通过${key} 读取jdbc配置文件中的数据
-->
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
提交回滚代码

3.5mappers
<!-- 把sql映射文件 注册给mybatis 不然无法使用 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
4.mybatis启动过程(了解即可)
mybatis启动过程中 会根据mybatis-config.xml 加载各种参数配置
1.根据连接环境 创建数据库连接池
2.读取注册别名(自定义别名 内置别名)
3.读取sql映射文件 加载sql标签 nameSpace+id (全局唯一 不能重复)
4.操作sql语句时 从数据库连接池取到连接对象
从mappedStatements 找到sql标签 传给数据库
5.数据库返回执行结果 mybatis根据 resultType="User" 配置的类型 把结果封装到对象中
需要数据库列 与实体对象一一对应(开启驼峰 应对 下划线对驼峰)
6.使用完mybatis 归还连接给数据库连接池
import com.javasm.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class MyBatisTest {
@Test
public void getUserByIDTest(){
//启动mybaitis框架
//从编译的根查找配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
//Resources 加载配置文件 读取到数据流
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 使用了构建器的模式(构建大对象) mybatis核心配置 configuration 配置mybaits的所有信息
// new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// SqlSessionFactory 核心对象(配置参数中的各种数据 别名 启动setting设置 注册的sql语句 数据库连接池 )
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//工厂模式
//按照模板创建指定对象
//从数据库连接池取一个可用连接 配置上mybatis需要的参数
//SqlSession 连接会话 (包含了connection 连接对象 被数据库连接池维护的对象)
//数据库连接池
/*
* 池化技术(复用对象)
* 线程池 代码执行器 线程对象是通用的 开多线程 会更多消耗cpu和内存
* 为了满足长时间大量使用 会预先创建好对象 使用时不需要再创建和销毁
* 数据库连接池 复用数据库连接 TCP连接 三次握手 4次挥手
* 预先创建好连接对象
* 传输数据的通道
* 每次创建多少 占满之后如何处理
* 根据实际数据量选择
*
* druid
* */
//mybatis中 连接 封装在了SqlSession sql会话中
//在一定程度上简化代码
//sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); 自动提交 不要用
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//找到注册的语句 nameSpace+id
User getUserById =(User) sqlSession.selectOne("aa.bb.getUserById");
System.out.println(getUserById);
//String getUserById2 =(String) sqlSession.selectOne("aa.bb.getUserById2");
//System.out.println(getUserById2);
// sqlSession.commit();
// sqlSession.rollback();
//把连接归还mybatis
sqlSession.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
5.sql映射标签(***)
5.1select标签
用于标记查询语句 通常需要搭配动态参数使用
<select id="getUserById" resultType="User" >
select * from user where id = 1
</select>
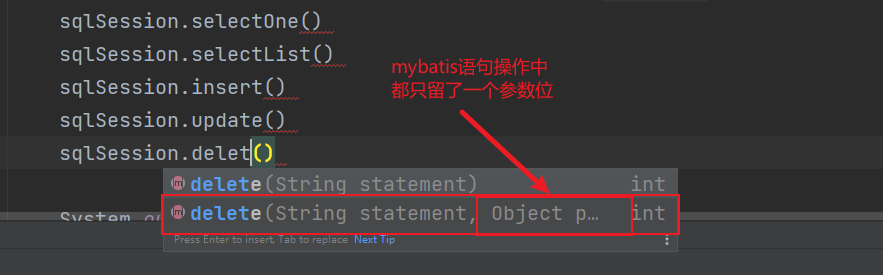
selectOne() 查单条
selectList() 查多条
select标签
id 语句标签的唯一标记 当前文件中 id不能重复 全局namespace+id不能重复
resultType 返回数据的类型(单条数据类型)(根据查询语句使用的格式不同 返回不同的数据类型)
1返回对象(实际数据对应) (多列数据)
2单个字段(某个字段) (单列数据)
3map格式(某些字段) (少用)5.2insert标签
用于插入数据 通常需要搭配动态参数使用
<insert id="addUser" >
insert into user(id,username,`password`,age)
VALUES (#{id},#{username},#{password},#{age})
</insert>
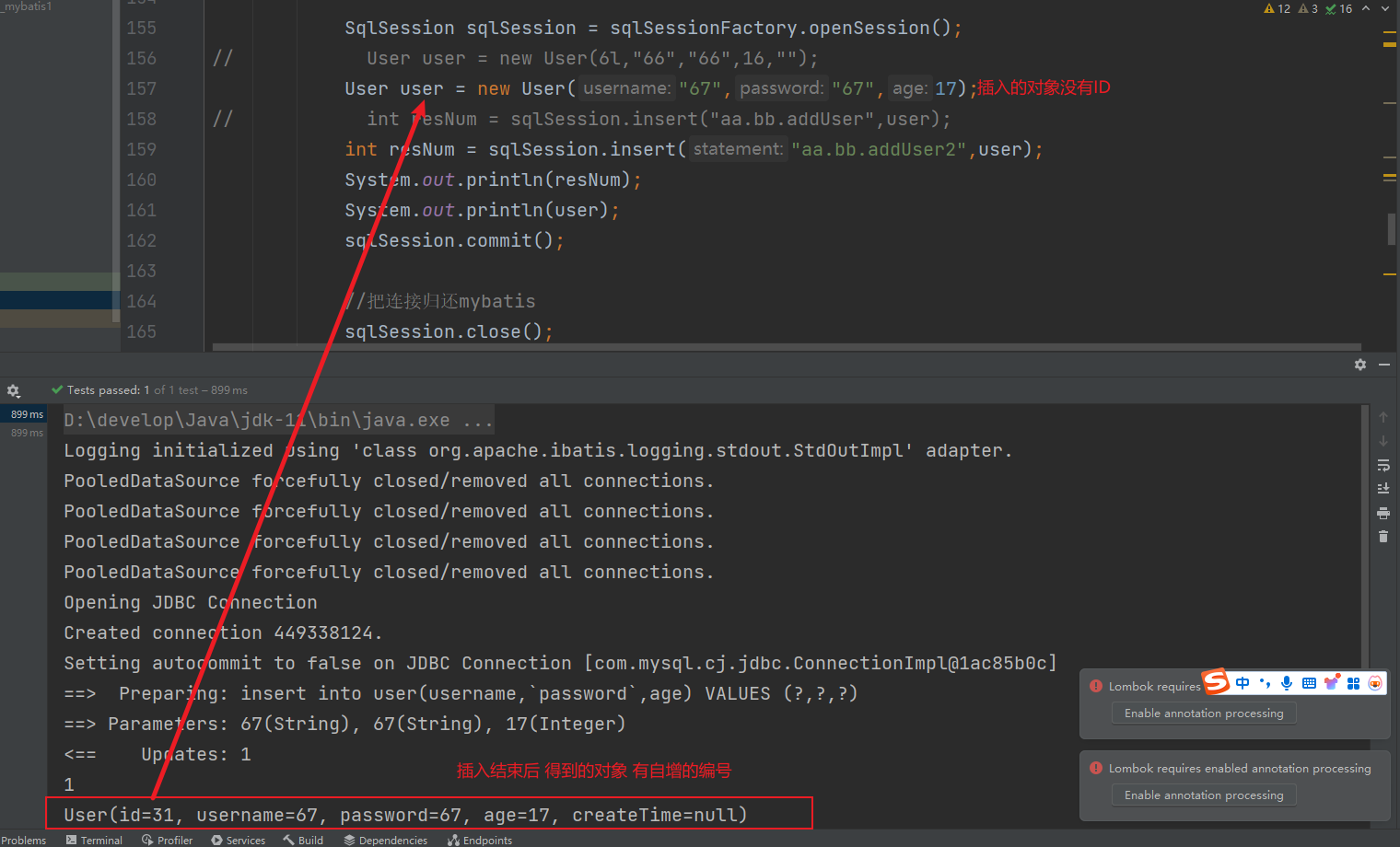
主键自增例子:
语句中不要指定id 根据jdbc的GeneratedKeys得到自增编号
<insert id="addUser2" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into user(username,`password`,age)
VALUES (#{username},#{password},#{age})
</insert>

insert 标签
id 语句的唯一标记
parameterType 可以省略不写
不需要标记返回值类型 返回的是执行成功的记录数
如果需要使用主键自增的编号
useGeneratedKeys="true" 激活jdbc获取自增主键
keyProperty="id" 获取的自增主键 设置给插入对象的哪个属性
注意:如果设置自动提交false 需要手动提交
sqlSession.commit(); @Test
public void addUserTest(){
//启动mybaitis框架
//从编译的根查找配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
//Resources 加载配置文件 读取到数据流
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 使用了构建器的模式(构建大对象) mybatis核心配置 configuration 配置mybaits的所有信息
// new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// SqlSessionFactory 核心对象(配置参数中的各种数据 别名 启动setting设置 注册的sql语句 数据库连接池 )
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// User user = new User(6l,"66","66",16,"");
User user = new User("67","67",17);
// int resNum = sqlSession.insert("aa.bb.addUser",user);
int resNum = sqlSession.insert("aa.bb.addUser2",user);
System.out.println(resNum);
System.out.println(user);
sqlSession.commit();
//把连接归还mybatis
sqlSession.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}5.3update标签
用于修改数据
<update id="editUser">
update user set username=#{username}, `password` = #{password} where id = #{id}
</update>
update 修改标签
id 语句唯一标记
parameterType 可以省略不写
不需要标记返回值类型 返回的是执行成功的记录数 @Test
public void updateUserTest(){
//启动mybaitis框架
//从编译的根查找配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
//Resources 加载配置文件 读取到数据流
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 使用了构建器的模式(构建大对象) mybatis核心配置 configuration 配置mybaits的所有信息
// new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// SqlSessionFactory 核心对象(配置参数中的各种数据 别名 启动setting设置 注册的sql语句 数据库连接池 )
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User user = new User();
user.setId(3l);
user.setUsername("aaa");
user.setPassword("aaa");
int resNum = sqlSession.update("aa.bb.editUser",user);
System.out.println(resNum);
System.out.println(user);
sqlSession.commit();
//把连接归还mybatis
sqlSession.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}5.4delete标签
用于删除数据
<delete id="deleteUser">
delete from user where id = #{id}
</delete>
<!--
delete 修改标签
id 语句唯一标记
parameterType 可以省略不写
不需要标记返回值类型 返回的是执行成功的记录数
--> @Test
public void deleteUserTest(){
//启动mybaitis框架
//从编译的根查找配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
//Resources 加载配置文件 读取到数据流
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 使用了构建器的模式(构建大对象) mybatis核心配置 configuration 配置mybaits的所有信息
// new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// SqlSessionFactory 核心对象(配置参数中的各种数据 别名 启动setting设置 注册的sql语句 数据库连接池 )
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
int resNum = sqlSession.delete("aa.bb.deleteUser",6);
System.out.println(resNum);
sqlSession.commit();
//把连接归还mybatis
sqlSession.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}5.5动态参数
mybatis传参时 需要使用动态参数标记 传入参数

所以传入参数时 不同的参数对象类型 要对应不同的取值方式
动态参数
#{} preparestatement 使用占位符 传参
${} 没使用占位符 sql硬拼接 (少用)
传参时 mybatis只接受一个参数
动态传参的几种对应方式
1.只有一个参数时 key可以任意定义 但是最好使用成查询的字段属性(可读性)
java代码
List<Object> objects = sqlSession.selectList("aa.bb.listUserById",1); xml映射文件
<select id="listUserById" resultType="com.javasm.entity.User" >
select * from user where age = #{xxxx}
</select>
2.多个参数时 a.实体对象 使用实体对象的属性名 注意多检查属性名
java代码
User inputUser = new User();
inputUser.setUsername("gxy");
inputUser.setPassword("abc123");
List<Object> objects = sqlSession.selectList("aa.bb.listUserByNameAndPwd",inputUser);xml代码
<select id="listUserByNameAndPwd" resultType="com.javasm.entity.User" >
select * from user where
username = #{username} and `password` = #{username}
</select>
2.多个参数时 b.通过map封装自定义对象 与mapkey对应 多检查key key不存在不报错 值是null
java代码
Map<String,Object> paramap = new HashMap<>();
paramap.put("myName","jack");
paramap.put("myPWD","abc123");
List<Object> objects = sqlSession.selectList("aa.bb.listUserByNameAndPwd",paramap);xml代码
select * from user where username = #{myName1} and `password` = #{myPWD}2.多个参数时 c.通过list封装参数结合 与list索引对应 (知道即可 可读性较差 使用不便)
java代码
List<Object> paramList = new ArrayList<>();
paramList.add("jack");
paramList.add("abc123");
List<Object> objects = sqlSession.selectList("aa.bb.listUserByNameAndPwd",paramList);xml代码
select * from user where username = #{list[0]} and `password` = #{list[1]}2.多个参数时 d.组合使用 多个实体对象 map中嵌套实体对象 先与mapkey对应 再跟当前对象的属性名对应
Java代码
Map<String,Object> paramap = new HashMap<>();
paramap.put("user1",new User(1l,"jack","abc123",15,""));
paramap.put("user2",new User(2l,"rose","aaaaa",17,""));
List<Object> objects = sqlSession.selectList("aa.bb.listUserByNameAndPwd",paramap);
xml代码
select * from user where username = #{user1.username} and `password` = #{user2.password}6.mybatis接口映射(主要掌握)
通过mybatis框架 运行时自动生成dao实现类的代码(dao层代码不需要写 通过配置配置文件
指定给mybatis生成)
1.写dao接口
package com.dao;
import com.javasm.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserDao {
//添加用户的接口
int addUser(User inputUser);
//查询用户信息列表
List<User> listUser();
//查询用户信息列表
User getUserById(Long id);
//查询用户信息
User getUserByNameAndPwd(User inputUser);
//@Param 把参数存入一个map 可以传递多参数
User getUserByNameAndPwd2(@Param("myname") String username,@Param("mypwd") String password);
User getUserByNameAndPwd3(@Param("user1")User user1,@Param("user2") User user2);
}
2.配置接口映射(xml文件 关联dao文件)

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
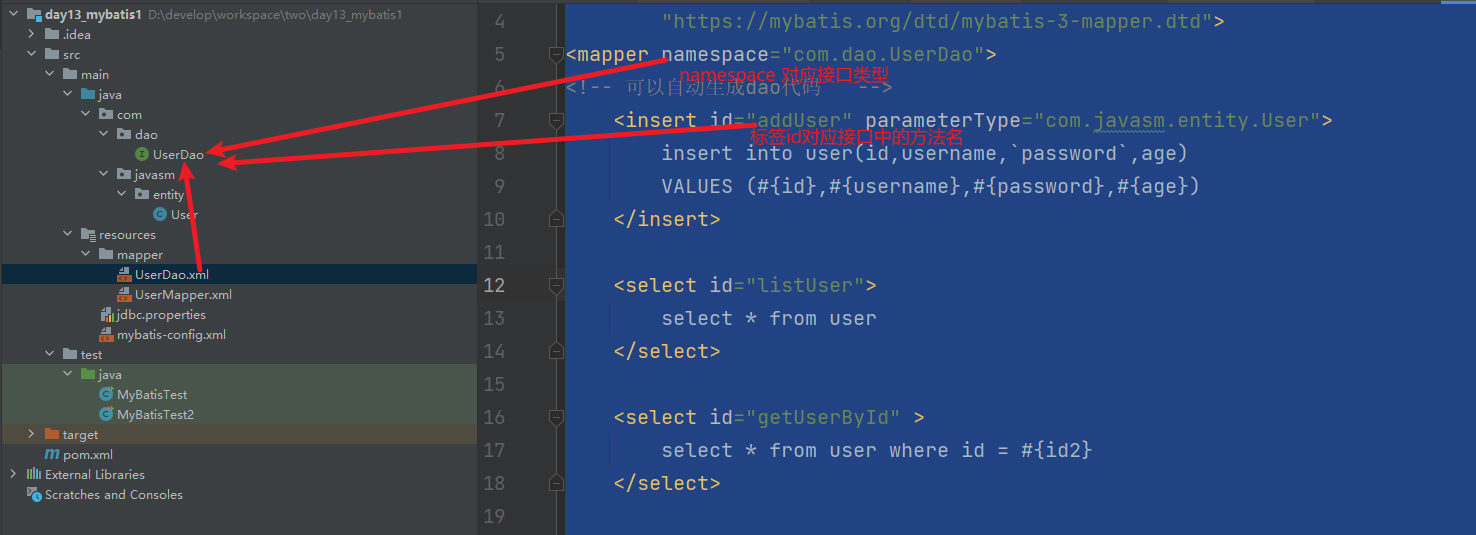
<mapper namespace="com.dao.UserDao">
<!-- 可以自动生成dao代码 -->
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.javasm.entity.User">
insert into user(id,username,`password`,age)
VALUES (#{id},#{username},#{password},#{age})
</insert>
<select id="listUser">
select * from user
</select>
<select id="getUserById" >
select * from user where id = #{id2}
</select>
<select id="getUserByNameAndPwd" >
select * from user where username = #{username} and `password` = #{password}
</select>
<select id="getUserByNameAndPwd2" >
select * from user where username = #{myname} and `password` = #{mypwd}
</select>
<select id="getUserByNameAndPwd3" >
select * from user where username = #{user1.username} and `password` = #{user2.password}
</select>
</mapper>
注意 mybatis基于的还是
selectOne
selectList
insert
update
delete
这些方法
参数类型上默认不支持多参数
多参数时 是封装为了map传参
3.获取接口实现类 执行方法
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserDao userDaoImpl = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
List<User> users = userDaoImpl.listUser();
System.out.println(users);
sqlSession.commit();
//把连接归还mybatis
sqlSession.close();查询不需要提交
添加 修改 删除 需要提交
7mybaits插件

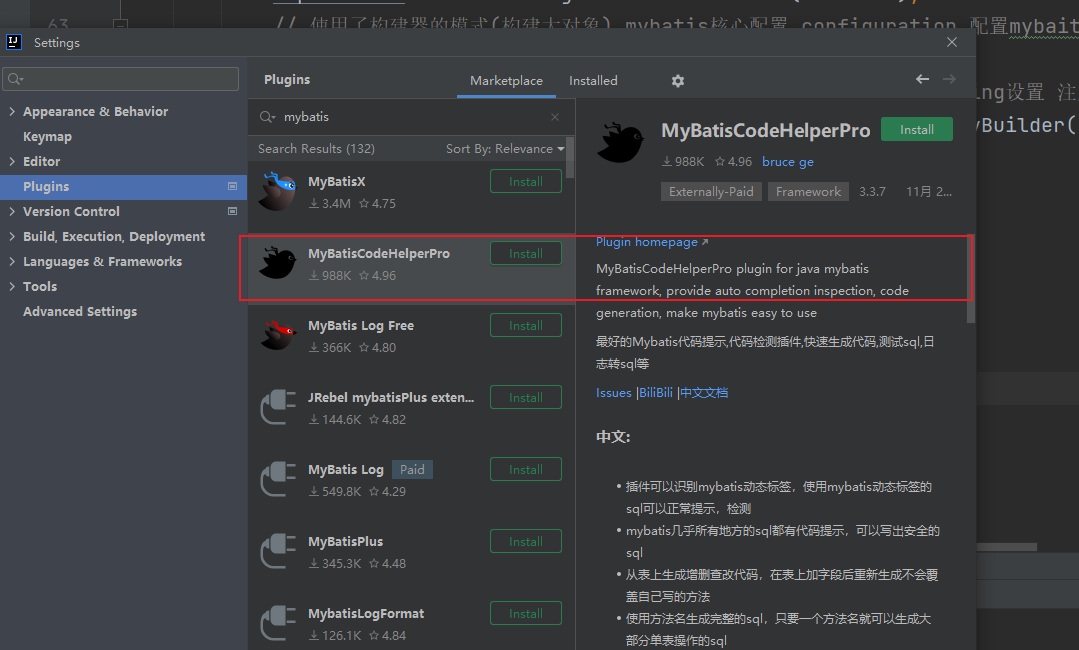




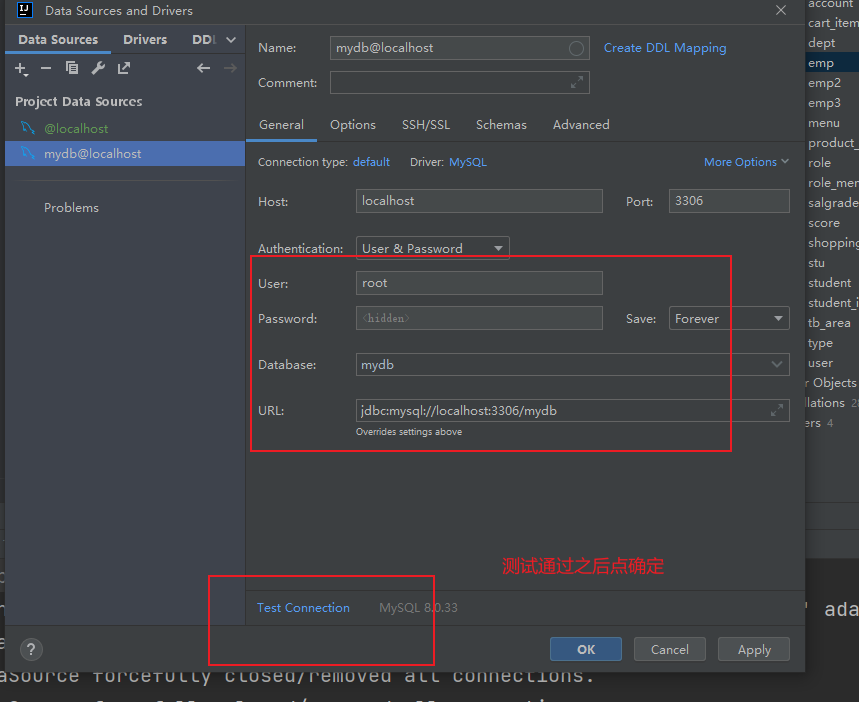
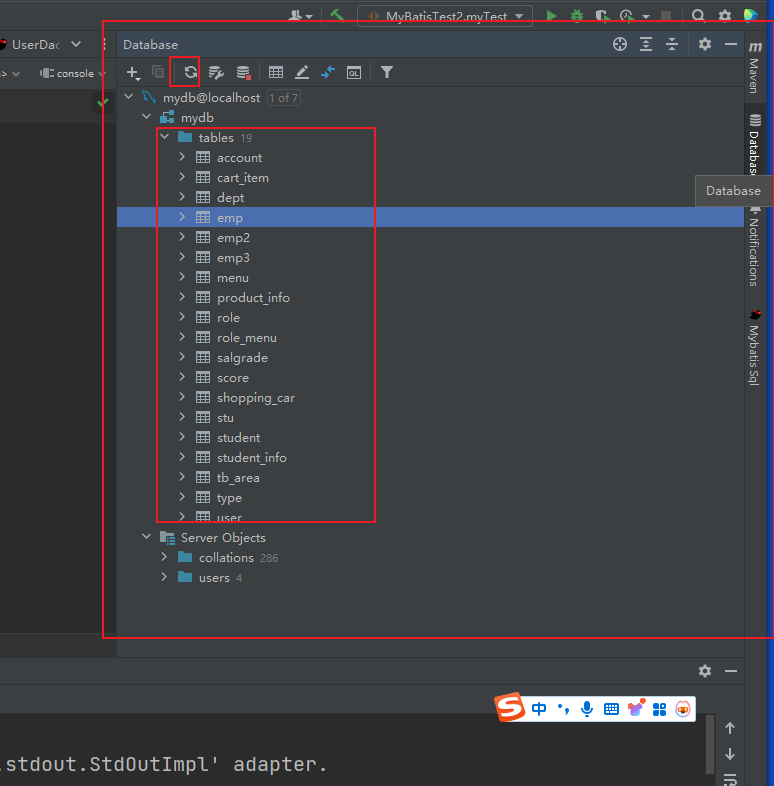

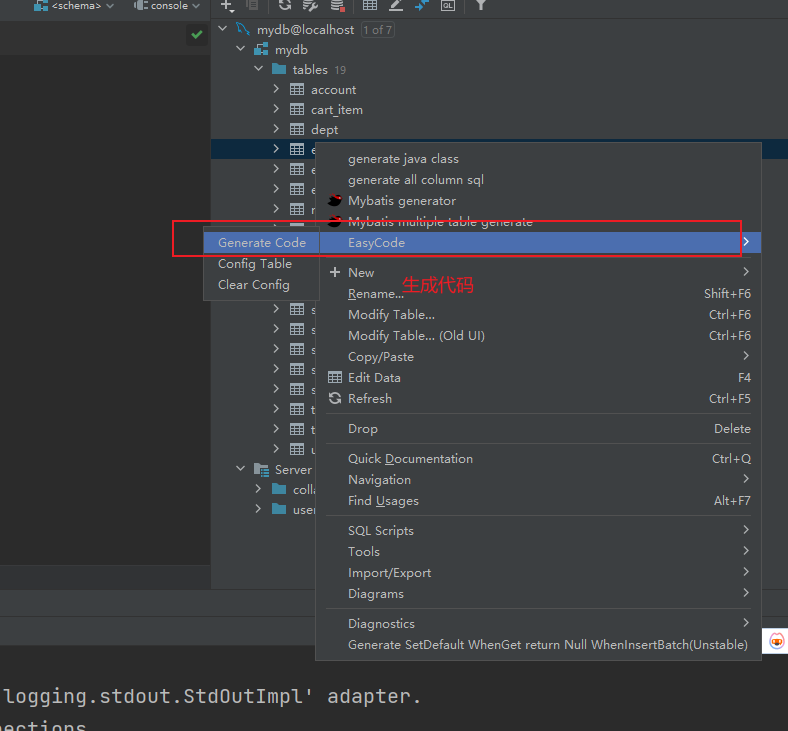
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2401_87910368/article/details/144043335
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
