Matlab 深度学习工具箱 案例学习与测试————求二阶微分方程
clc
clear
% 定义输入变量
x = linspace(0,2,10000)';
% 定义网络的层参数
inputSize = 1;
layers = [
featureInputLayer(inputSize,Normalization="none")
fullyConnectedLayer(10)
sigmoidLayer
fullyConnectedLayer(1)
sigmoidLayer];
% 创建网络
net = dlnetwork(layers);
% 训练轮数
numEpochs = 15;
% 每个Batch的数据个数
miniBatchSize = 100;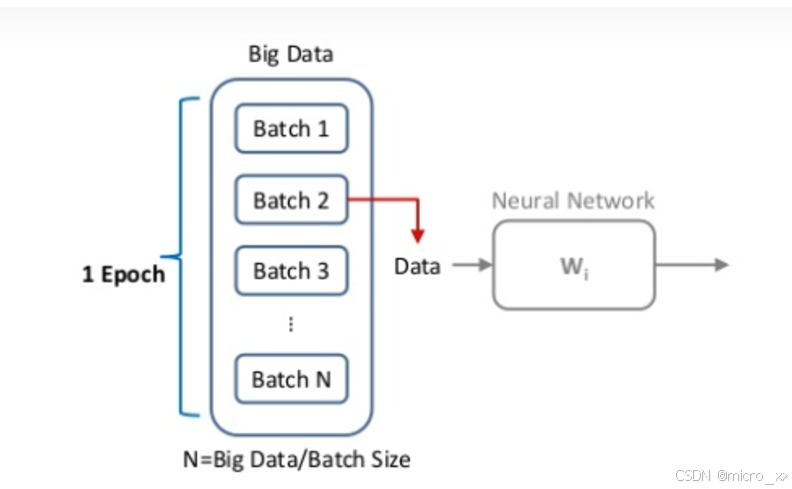
% SGDM优化方法设置的参数
initialLearnRate = 0.5;
learnRateDropFactor = 0.5;
learnRateDropPeriod = 5;
momentum = 0.9;
velocity = [];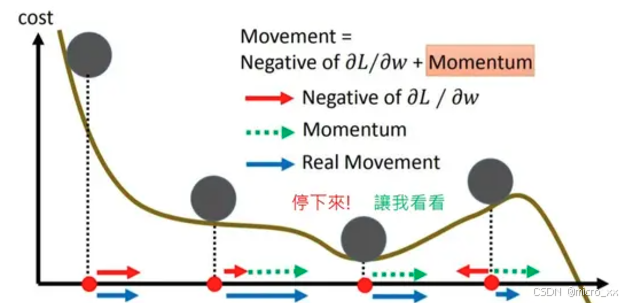
% 损失函数里面考虑初始条件的系数
icCoeff = 7;
% ArrayDatastore
ads = arrayDatastore(x,IterationDimension=1);
% 创建一个用于处理管理深度学习数据的对象
mbq = minibatchqueue(ads, ...
MiniBatchSize=miniBatchSize, ...
PartialMiniBatch="discard", ...
MiniBatchFormat="BC");
% 用于迭代过程监控
numObservationsTrain = numel(x);
numIterationsPerEpoch = floor(numObservationsTrain / miniBatchSize);
numIterations = numEpochs * numIterationsPerEpoch;
% 创建监控对象
% 由于计时器在您创建监控器对象时启动,因此请确保在靠近训练循环的位置创建对象。
monitor = trainingProgressMonitor( ...
Metrics="LogLoss", ...
Info=["Epoch" "LearnRate"], ...
XLabel="Iteration");
% Train the network using a custom training loop
epoch = 0;
iteration = 0;
learnRate = initialLearnRate;
start = tic;
% Loop over epochs.
while epoch < numEpochs && ~monitor.Stop
epoch = epoch + 1;
% Shuffle data,打乱数据.
mbq.shuffle
% Loop over mini-batches.
while hasdata(mbq) && ~monitor.Stop
iteration = iteration + 1;
% Read mini-batch of data.
X = next(mbq);
% Evaluate the model gradients and loss using dlfeval and the modelLoss function.
[loss,gradients] = dlfeval(@modelLoss, net, X, icCoeff);
% Update network parameters using the SGDM optimizer.
[net,velocity] = sgdmupdate(net,gradients,velocity,learnRate,momentum);
% Update the training progress monitor.
recordMetrics(monitor,iteration,LogLoss=log(loss));
updateInfo(monitor,Epoch=epoch,LearnRate=learnRate);
monitor.Progress = 100 * iteration/numIterations;
end
% Reduce the learning rate.
if mod(epoch,learnRateDropPeriod)==0
learnRate = learnRate*learnRateDropFactor;
end
end
xTest = linspace(0,4,1000)';
yModel = minibatchpredict(net,xTest);
yAnalytic = exp(-xTest.^2);
figure;
plot(xTest,yAnalytic,"-")
hold on
plot(xTest,yModel,"--")
legend("Analytic","Model")在深度学习中,被求导的对象(样本/输入)一般是多元的(向量x),绝大多数情况是标量y对向量x进行求导,很少向量y对向量x进行求导,否则就会得到复杂的微分矩阵。所以经常把一个样本看做一个整体,它包含多个变量(属性),对其所有属性求导后再加和,就得到了这个样本的偏导数之和。
% 损失函数
function [loss,gradients] = modelLoss(net, X, icCoeff)
% 前向传播计算
y = forward(net,X);
% Evaluate the gradient of y with respect to x.
% Since another derivative will be taken, set EnableHigherDerivatives to true.
dy = dlgradient(sum(y,"all"),X,EnableHigherDerivatives=true);
% Define ODE loss.
eq = dy + 2*y.*X;
% Define initial condition loss.
ic = forward(net,dlarray(0,"CB")) - 1;
% Specify the loss as a weighted sum of the ODE loss and the initial condition loss.
loss = mean(eq.^2,"all") + icCoeff * ic.^2;
% Evaluate model gradients.
gradients = dlgradient(loss, net.Learnables);
end原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33268208/article/details/143951380
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
