【BFS】解决FloodFill 算法
图像渲染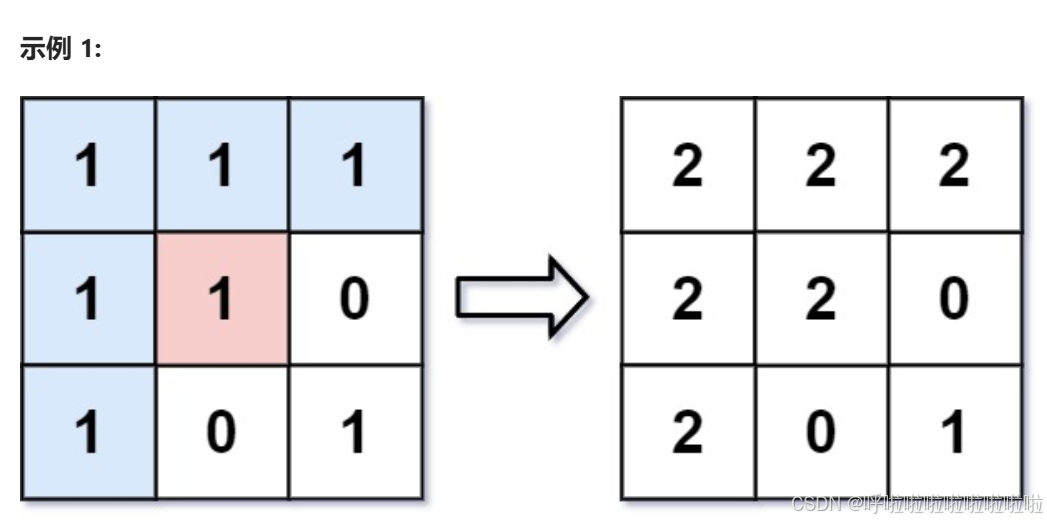
模版:
算法思路:
- 起始点:从给定的起始点开始,检查该点的颜色是否与目标颜色相同(如果相同,才会继续填充)。
- 队列:使用队列来存储待填充的像素。对于每个从队列中取出的像素,我们将其相邻的四个方向(上、下、左、右)的像素加入队列,继续填充。
- 边界检查:每次检查相邻像素时,要保证不会超出边界。
- 终止条件:当队列为空时,填充完成。
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
// 四个方向:上、下、左、右
int[] dx = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = {1, -1, 0, 0};
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
int oldColor = image[sr][sc]; // 获取起始点的颜色
if (oldColor == newColor) {
return image; // 如果起始点的颜色和目标颜色相同,直接返回
}
int m = image.length; // 图像的行数
int n = image[0].length; // 图像的列数
// BFS的队列
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{sr, sc}); // 将起始点加入队列
image[sr][sc] = newColor; // 将起始点的颜色更新为新颜色
// BFS 填充过程
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] curr = queue.poll();
int x = curr[0], y = curr[1];
// 遍历四个方向
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
// 检查新位置是否在图像范围内,并且与原始颜色相同
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && image[nx][ny] == oldColor) {
image[nx][ny] = newColor; // 将该位置的颜色更新为新颜色
queue.offer(new int[]{nx, ny}); // 将该位置加入队列
}
}
}
return image;
}
}
class Solution {
//设置偏移量 上下左右四个坐标
int[] dx = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int[] dy = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int color) {
// 记录初始颜色
int prev = image[sr][sc];
// 初始颜色和目标颜色相同,则直接返回原图
if (prev == color)
return image;
int m = image.length;
int n = image[0].length;
// 构造一个队列,先把起始点放进去
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[] { sr, sc });
// 当队列不为空
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] t = q.poll();
int a = t[0], b = t[1];
// 改变颜色
image[a][b] = color;
// 遍历四个方向
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = a + dx[i];
int y = b + dy[i];
// 防止越界 并且上下左右如果有跟原来的颜色相同 加入队列并修改颜色
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && image[x][y] == prev) {
q.offer(new int[] { x, y });
}
}
}
return image;
}
}岛屿数量

解题思路
- 遍历每个网格: 从左到右、从上到下依次遍历整个二维网格。如果当前位置是陆地('1'),并且没有访问过(
vis[i][j]是false),则说明发现了一个新的岛屿,岛屿计数加1。- 使用 BFS标记岛屿: 当发现一个新的岛屿后,利用广度优先搜索(BFS)从当前 '1' 开始,遍历整个岛屿并标记所有岛屿上的 '1' 为已访问(
vis[i][j]设置为true),这样可以避免重复计算。- BFS 过程:
- 将当前的陆地节点加入队列。
- 从队列中取出一个节点,检查它的四个方向(上下左右)。
- 如果相邻的位置是陆地并且未被访问过,就将这个位置加入队列,并标记为已访问。
- 重复此过程,直到队列为空,即完成了一个岛屿的所有陆地的遍历。
class Solution {
// 设置偏移量
int[] dx = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int[] dy = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
// 用来标记是否记录过当前岛屿
boolean[][] vis;
int m, n;
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
vis = new boolean[m][n];
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1' && vis[i][j] == false) {
ret++;
// 并且将此岛屿都标记成使用过
bfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
void bfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[] { i, j });
vis[i][j] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] t = q.poll();
int a = t[0], b = t[1];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = a + dx[k];
int y = b + dy[k];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == '1' && vis[x][y] == false) {
q.offer(new int[] { x, y });
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
}
}岛屿的最大面积

跟上题相似,找到一块区域,只需统计这块区域的个数即可
class Solution {
// 设置偏移量
int[] dx = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int[] dy = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
// 记录岛屿的面积
boolean[][] vis;
int m, n;
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
vis = new boolean[m][n];
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// 找到一块岛屿
if (grid[i][j] == 1 && vis[i][j] == false) {
// 计算面积
max = Math.max(max, bfs(grid, i, j));
}
}
}
return max;
}
int bfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j) {
int count = 1;
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[] { i, j });
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] t = q.poll();
int a = t[0], b = t[1];
vis[a][b] = true;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = a + dx[k], y = b + dy[k];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n
&& grid[x][y] == 1 && vis[x][y] == false) {
q.offer(new int[] { x, y });
vis[x][y] = true;
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}被围绕的区域

1.只需先把四周边界位置的'O'先找到 利用bfs 替换成其他符号 例如‘?’
2.遍历整个范围 不是 ‘?’的全部变成 ‘X’ 是‘?’的变成 ‘O’
class Solution {
int[] dx = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int[] dy = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
int m, n;
boolean[][] vis;
public void solve(char[][] board) {
m = board.length;
n = board[0].length;
vis = new boolean[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == 0 || j == n - 1) {
if (board[i][j] == 'O' && !vis[i][j]) {
// 都标记为其他字符 ?
bfs(board, i, j);
}
}
}
}
// 遍历
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(board[i][j] != '?') {
board[i][j] = 'X';
} else {
board[i][j] = 'O';
}
}
}
}
void bfs(char[][] board, int i, int j) {
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[] { i, j });
vis[i][j] = true;
board[i][j] = '?';
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] t = q.poll();
int a = t[0], b = t[1];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = a + dx[k];
int y = b + dy[k];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n
&& board[x][y] == 'O' && !vis[x][y]) {
q.offer(new int[] { x, y });
board[x][y] = '?';
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
}
}原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/chaodddddd/article/details/145140748
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
