每天40分玩转Django:Django DevOps实践指南
Django DevOps实践指南
1. 学习目标
- 掌握Django项目的CI/CD流程
- 学习使用GitHub Actions实现自动化部署
- 理解测试自动化和代码质量监控
- 掌握生产环境的部署和监控
2. 核心知识点
| 模块 | 重要程度 | 掌握要求 |
|---|---|---|
| CI/CD基础概念 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 深入理解 |
| GitHub Actions | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 熟练使用 |
| 自动化测试 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 掌握配置 |
| 代码质量检查 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 理解并应用 |
| 自动化部署 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 熟练掌握 |
3. CI/CD配置示例
3.1 GitHub Actions工作流配置
# .github/workflows/django.yml
name: Django CI/CD
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:13
env:
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres
POSTGRES_DB: github_actions
ports:
- 5432:5432
options: >-
--health-cmd pg_isready
--health-interval 10s
--health-timeout 5s
--health-retries 5
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v2
with:
python-version: '3.9'
- name: Install Dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
- name: Run Tests
env:
DATABASE_URL: postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5432/github_actions
run: |
python manage.py test
- name: Run Linting
run: |
pip install flake8
flake8 .
- name: Run Coverage
run: |
pip install coverage
coverage run manage.py test
coverage report
deploy:
needs: test
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main'
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Deploy to Production
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@master
with:
host: ${{ secrets.SERVER_HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.SERVER_USER }}
key: ${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}
script: |
cd /var/www/myproject
git pull origin main
source venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py collectstatic --noinput
sudo systemctl restart gunicorn
3.2 自动化测试配置
# myproject/settings_test.py
from .settings import *
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.postgresql',
'NAME': 'github_actions',
'USER': 'postgres',
'PASSWORD': 'postgres',
'HOST': 'localhost',
'PORT': '5432',
}
}
EMAIL_BACKEND = 'django.core.mail.backends.locmem.EmailBackend'
3.3 代码质量检查配置
# setup.cfg
[flake8]
max-line-length = 120
exclude = .git,*/migrations/*,venv
ignore = E501,W503
[coverage:run]
source = .
omit =
*/tests/*
*/migrations/*
venv/*
manage.py
[coverage:report]
fail_under = 80
show_missing = True
4. 部署脚本
4.1 生产环境部署脚本
#!/bin/bash
# deploy.sh
set -e
# 1. 更新代码
git pull origin main
# 2. 激活虚拟环境
source venv/bin/activate
# 3. 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
# 4. 收集静态文件
python manage.py collectstatic --noinput
# 5. 执行数据库迁移
python manage.py migrate --noinput
# 6. 重启Gunicorn
sudo systemctl restart gunicorn
# 7. 重启Nginx
sudo systemctl restart nginx
# 8. 清理缓存
rm -rf /tmp/django_cache/*
echo "部署完成!"
4.2 Gunicorn配置
# gunicorn.conf.py
import multiprocessing
bind = "unix:/run/gunicorn.sock"
workers = multiprocessing.cpu_count() * 2 + 1
threads = 2
worker_class = "gthread"
worker_connections = 1000
timeout = 30
keepalive = 2
errorlog = "/var/log/gunicorn/error.log"
accesslog = "/var/log/gunicorn/access.log"
loglevel = "info"
daemon = False
pidfile = "/run/gunicorn/pid"
user = "www-data"
group = "www-data"
reload = False
max_requests = 2000
max_requests_jitter = 400
capture_output = True
enable_stdio_inheritance = True
5. 监控配置
5.1 Prometheus配置
# prometheus.yml
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
evaluation_interval: 15s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'django'
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:8000']
metrics_path: '/metrics'
5.2 Django应用监控
# monitoring.py
from prometheus_client import Counter, Histogram
from django.conf import settings
# 请求计数器
REQUEST_COUNT = Counter(
'django_http_requests_total',
'Total HTTP requests count',
['method', 'endpoint', 'status']
)
# 请求延迟直方图
REQUEST_LATENCY = Histogram(
'django_http_request_duration_seconds',
'HTTP request latency',
['method', 'endpoint']
)
class PrometheusMiddleware:
def __init__(self, get_response):
self.get_response = get_response
def __call__(self, request):
if request.path == '/metrics':
return self.get_response(request)
method = request.method
path = request.path
with REQUEST_LATENCY.labels(method=method, endpoint=path).time():
response = self.get_response(request)
REQUEST_COUNT.labels(
method=method,
endpoint=path,
status=response.status_code
).inc()
return response
6. 流程图
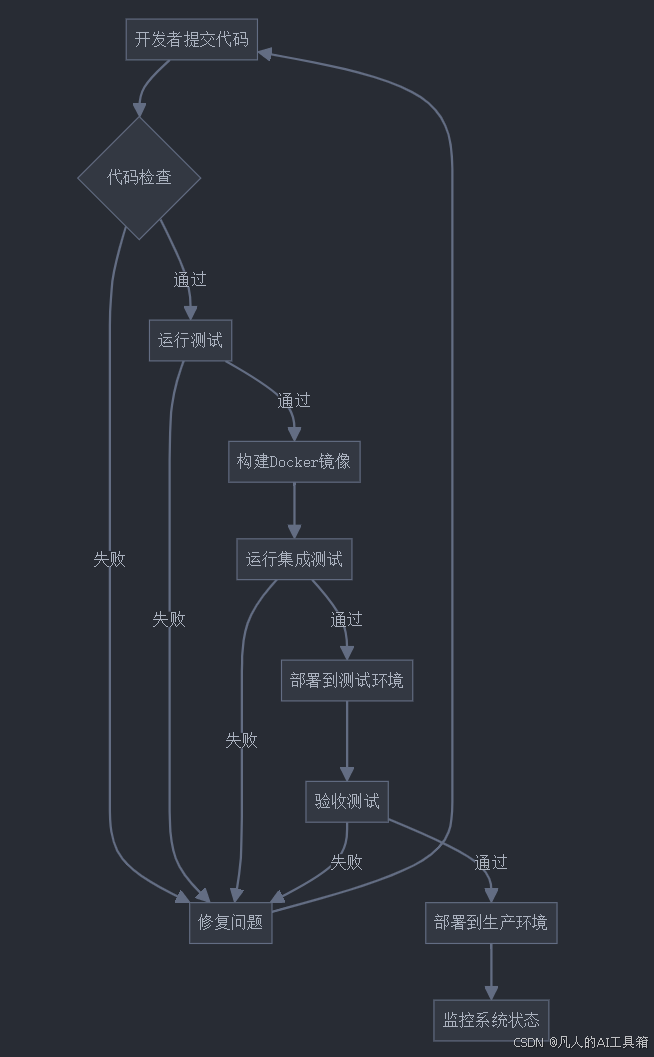
7. 最佳实践建议
7.1 安全措施
# security.py
from django.conf import settings
from django.http import HttpResponseForbidden
class SecurityMiddleware:
def __init__(self, get_response):
self.get_response = get_response
def __call__(self, request):
# 检查IP白名单
if settings.IP_WHITELIST and request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR') not in settings.IP_WHITELIST:
return HttpResponseForbidden()
# 添加安全头
response = self.get_response(request)
response['X-Content-Type-Options'] = 'nosniff'
response['X-Frame-Options'] = 'DENY'
response['X-XSS-Protection'] = '1; mode=block'
return response
7.2 备份策略
# backup.py
import os
import datetime
import subprocess
def backup_database():
date = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S')
filename = f'backup_{date}.sql'
# 数据库备份
subprocess.run([
'pg_dump',
'-U', os.getenv('DB_USER'),
'-h', os.getenv('DB_HOST'),
os.getenv('DB_NAME'),
'-f', f'/backups/{filename}'
])
# 压缩备份文件
subprocess.run(['gzip', f'/backups/{filename}'])
# 上传到S3
subprocess.run([
'aws', 's3', 'cp',
f'/backups/{filename}.gz',
f's3://{os.getenv("BACKUP_BUCKET")}/databases/'
])
8. 性能优化
8.1 缓存配置
# settings.py
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.redis.RedisCache',
'LOCATION': 'redis://127.0.0.1:6379/1',
'OPTIONS': {
'CLIENT_CLASS': 'django_redis.client.DefaultClient',
'PARSER_CLASS': 'redis.connection.HiredisParser',
'CONNECTION_POOL_CLASS': 'redis.connection.BlockingConnectionPool',
'CONNECTION_POOL_CLASS_KWARGS': {
'max_connections': 50,
'timeout': 20,
}
}
}
}
# 缓存会话
SESSION_ENGINE = "django.contrib.sessions.backends.cache"
SESSION_CACHE_ALIAS = "default"
8.2 数据库优化
# settings.py
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.postgresql',
'NAME': os.getenv('DB_NAME'),
'USER': os.getenv('DB_USER'),
'PASSWORD': os.getenv('DB_PASSWORD'),
'HOST': os.getenv('DB_HOST'),
'PORT': os.getenv('DB_PORT', '5432'),
'CONN_MAX_AGE': 60,
'OPTIONS': {
'connect_timeout': 10,
'statement_timeout': 30000,
}
}
}
配置完成后,你的Django项目就具备了完整的DevOps支持,包括自动化测试、部署和监控。记住要根据实际项目需求调整这些配置。定期检查和更新这些配置也是保持系统健康的重要部分。
怎么样今天的内容还满意吗?再次感谢朋友们的观看,关注GZH:凡人的AI工具箱,回复666,送您价值199的AI大礼包。最后,祝您早日实现财务自由,还请给个赞,谢谢!
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40780178/article/details/144998730
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
