《深入解析 Java 中的 ThreadLocal》
ThreadLocal
1.概述
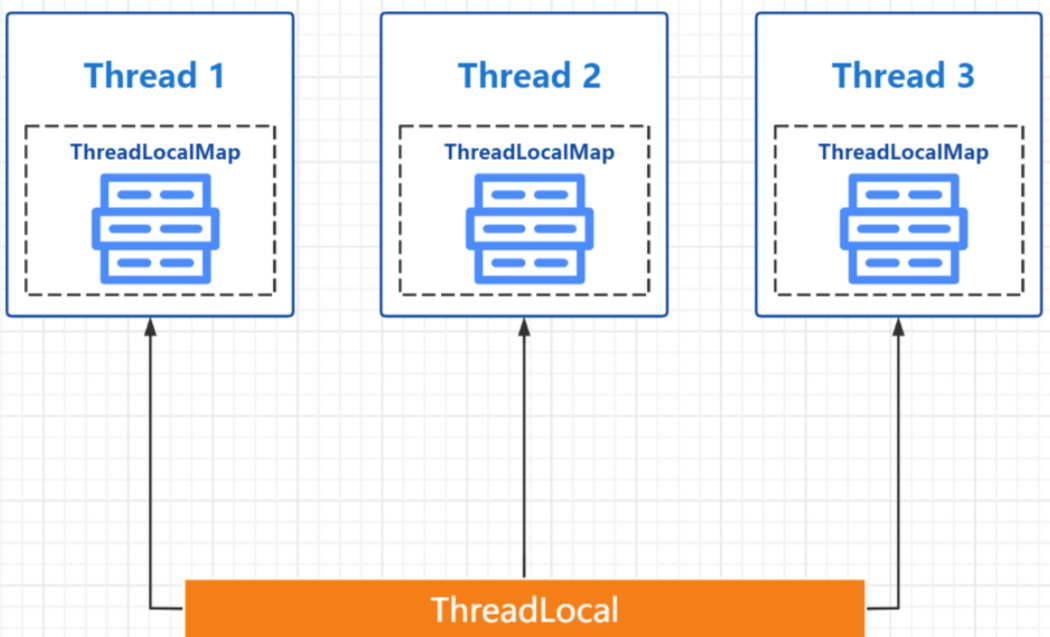
ThreadLocal被称为线程局部变量,用于在线程中保存数据。由于在ThreadLocal中保存的数据仅属于当前线程,所以该变量对其他线程而言是隔离的,也就是说该变量是当前线程独有的变量。
ThreadLocal用于在同一个线程间,在不同的类和方法之间共享数据的的场景,也可以用于在不同线程间隔离数据的场景。
ThreadLocal利用Thread中的ThreadLocalMap来进行数据存储。
示例:
public class Test {
// 线程局部变量
public static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
threadLocal.set("妲己");
show();
Sample.dosth();
}
},"线程1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
threadLocal.set("后羿");
show();
Sample.dosth();
}
},"线程2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
public static void show() {
String role = threadLocal.get();
System.out.println("show:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"分配角色:" + role);
}
}
class Sample {
public static void dosth() {
String role = Test.threadLocal.get();
System.out.println("dosth:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"分配角色:" + role);
}
}
2.常用方法
1.存储数据至当前线程的ThreadLocalMap:public void set(T value)
public void set(T value) {
// 获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// 获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
// 存储数据至当前线程的ThreadLocalMap中
// 使用ThreadLocal对象做key,保存数据value
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
2.从当前线程的ThreadLocalMap中获取数据:public T get()
public T get() {
// 获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
// 使用ThreadLocal对象做key,获取数据(Entry类型)
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
3.从当前线程的ThreadLocalMap中删除数据:public void remove()
在线程池的线程复用场景中,线程执行完毕时一定要调用remove(),避免在线程被重新放入线程池中时被本地变量的旧状态仍然被保存。
public void remove() {
// 获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
// 使用当前ThreadLocal对象做key,删除数据
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
ThreadLocal的get()方法、set()方法和remove()方法,其实最终操作的都是ThreadLocalMap类中的数据。
3. ThreadLocalMap内部结构
ThreadLocalMap内部数据结构是一个Entry类型的数组。每个Entry对象的key为ThreadLocal对象,value为存储的数据。
static class ThreadLocalMap {
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
...
private Entry[] table;
...
}
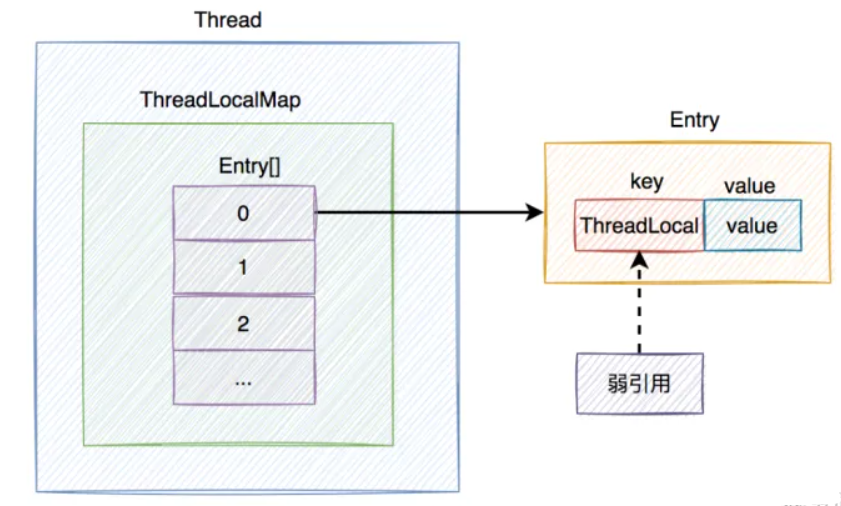
4.为什么用ThreadLocal做key?
如果在应用中,一个线程中只使用了一个ThreadLocal对象,那么使用Thread做key也是可以的,代表每个Thread线程对应一个value。
public class ThreadLocalService {
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
但是,在实际应用程序开发过程中,一个线程中很有可能不只使用了一个ThreadLocal对象。这时使用Thread做key就会产生混淆。
public class ThreadLocalService {
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal1 = new ThreadLocal<>();
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal2 = new ThreadLocal<>();
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal3 = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
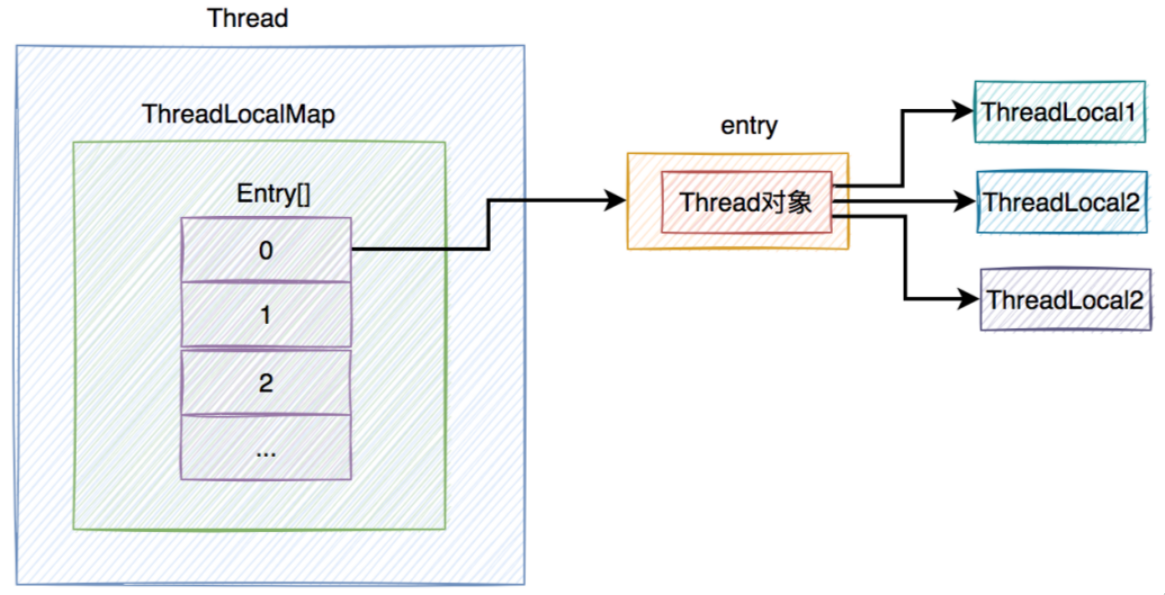
所以,不能使用Thread做key,而应该改成用ThreadLocal对象做key,这样才能通过具体ThreadLocal对象的get()方法,获取到当前线程的ThreadLocalMap,然后进一步获取到对应的Entry。
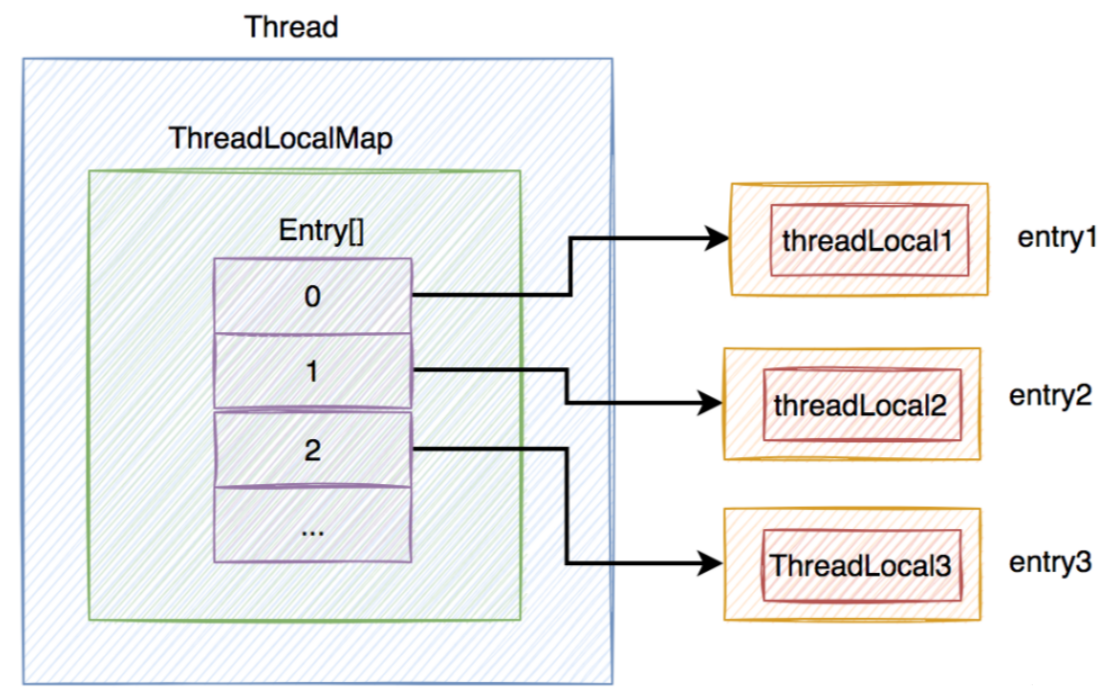
5.ThreadLocalMap如何查找数据?
当我们使用ThreadLocal获取当前线程中保存的Value数据时,是以ThreadLocal对象作为Key,通过访问Thread当前线程对象的内部
ThreadLocalMap集合来获取到Value。
ThreadLocalMap集合的底层数据结构使用Entry[]数组保存Key-Value键值对数据。所以,当通过ThreadLocal的get、set()、remove()等
方法,访问ThreadLocalMap时,最终都会通过一个下标,来完成对数组中的元素访问。
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
通过key的“hashCode值”跟"数组的长度减1" 做“&按位与”运算。其中key就是ThreadLocal对象。这种计算方式,相当于用“hashCode值”跟“数组的长度”进行“%取余”运算。
假设:len=16,key.threadLocalHashCode=31
hash & len-1的计算结果与hash % len的计算结果一直,均为15,但是“&按位与”运算的效率更高。
6.父子线程如何共享数据?
在实际工作中,有可能需要在父子线程中共享数据的。即:在父线程中往ThreadLocal设置了值,在子线程中能够获取到。
ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>();
threadLocal.set("天王盖地虎");
System.out.println("main主线程:" + threadLocal.get());
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("子线程:" + threadLocal.get());
}
});
thread.start();
}
在这种情况下使用ThreadLocal是行不通的。main方法是在主线程中执行的,相当于父线程。在main方法中开启了另外一个线程,相当于子线程。两个线程对象,各自拥有不同的ThreadLocalMap。应该使用InheritableThreadLocal,它是JDK自带的类,继承了ThreadLocal类。
InheritableThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<String>();
threadLocal.set("天王盖地虎");
System.out.println("main主线程:" + threadLocal.get());
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("子线程:" + threadLocal.get());
});
thread.start();
}
7.ThreadLocal如何避免内存泄露?
在finally调用ThreadLocal对象的remove()方法。
需要特别注意的地方是:一定要在finally代码块中,调用remove()方法清理没用的数据。如果业务代码出现异常,也能及时清理没用的数据。
remove()方法中会把Entry中的key和value都设置成null,这样就能被GC及时回收,无需触发额外的清理机制,所以它能解决内存泄露问题。
8.ThreadLocal应用场景
1线程数据隔离
ThreadLocal的主要价值在于线程隔离,ThreadLocal中的数据只属于当前线程,该数据对别的线程是不可见的,起到隔离作用。这样操作,可以在多线程环境下,可以防止当前线程的数据被其他线程修改。另外,由于各个线程之间的数据相互隔离,避免了同步加锁带来的性能损失,大大提升了并发性的性能。
例如:SqlSession会话对象绑定,避免多个线程使用同一个SqlSession对象,由于关闭导致异常。
private static final ThreadLocal threadSession = new ThreadLocal();
public static SqlSession getSession() {
SqlSession s = (SqlSession) threadSession.get();
if (s == null) {
s = getSqlSessionFactory().openSqlSession();
threadSession.set(s);
}
}
2跨函数传递
数据通常用于同一个线程内,跨类、跨方法传递数据时,如果不用ThreadLocal,那么相互之间的数据传递势必要靠返回值和参数,这样无形之中增加了这些类或者方法之间的耦合度.
// SpringMVC或SpringBoot框架使用中获取HttpServletRequest
HttpServletRequest request =
((ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
@Nullable
public static RequestAttributes getRequestAttributes() {
// 获取当前线程中的存储的Request Attribute
RequestAttributes attributes = requestAttributesHolder.get();
if (attributes == null) {
attributes = inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.get();
}
return attributes;
}
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> requestAttributesHolder = new NamedThreadLocal<>("Request attributes");
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> inheritableRequestAttributesHolder = new NamedInheritableThreadLocal<>("Request context");
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_67028830/article/details/142488388
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
