HADOOP大数据处理技术6-JavaSe
人生 就要闯出条路来!

2024/4/1

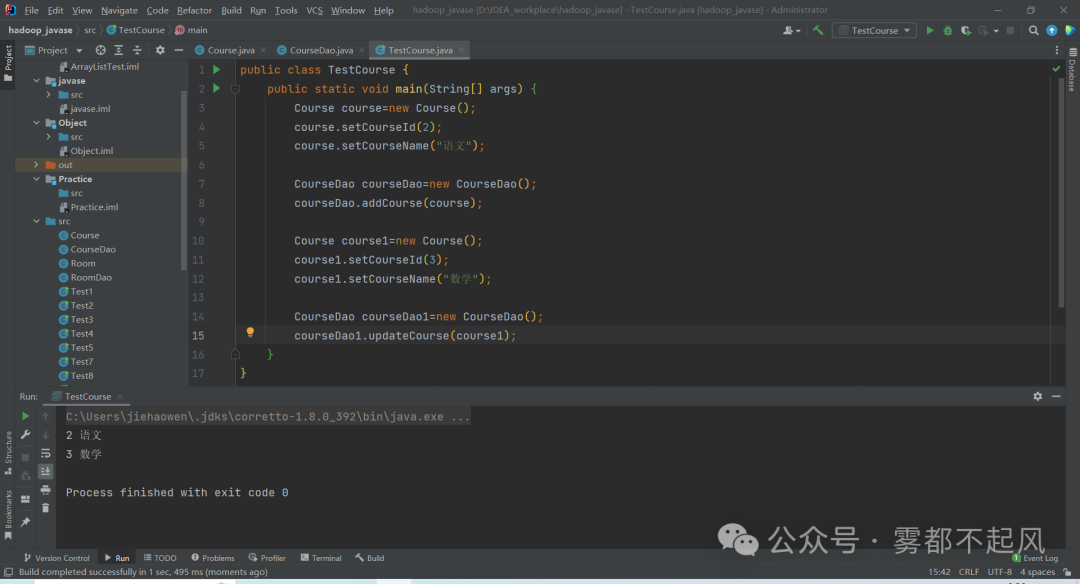
面向对象练习:大家完成一个学生管理类的设计 学生查询课程public class Course {private int courseId;private String courseName;public int getCourseId() {return courseId;}public void setCourseId(int courseId) {this.courseId = courseId;}public String getCourseName() {return courseName;}public void setCourseName(String courseName) {this.courseName = courseName;}}public class CourseDao {public void addCourse(Course course){System.out.println(course.getCourseId()+" "+course.getCourseName());}public String updateCourse(Course course){System.out.println(course.getCourseId()+" "+course.getCourseName());return "修改成功";}}public class TestCourse {public static void main(String[] args) {Course course=new Course();course.setCourseId(2);course.setCourseName("语文");CourseDao courseDao=new CourseDao();courseDao.addCourse(course);Course course1=new Course();course1.setCourseId(3);course1.setCourseName("数学");CourseDao courseDao1=new CourseDao();courseDao1.updateCourse(course1);}}
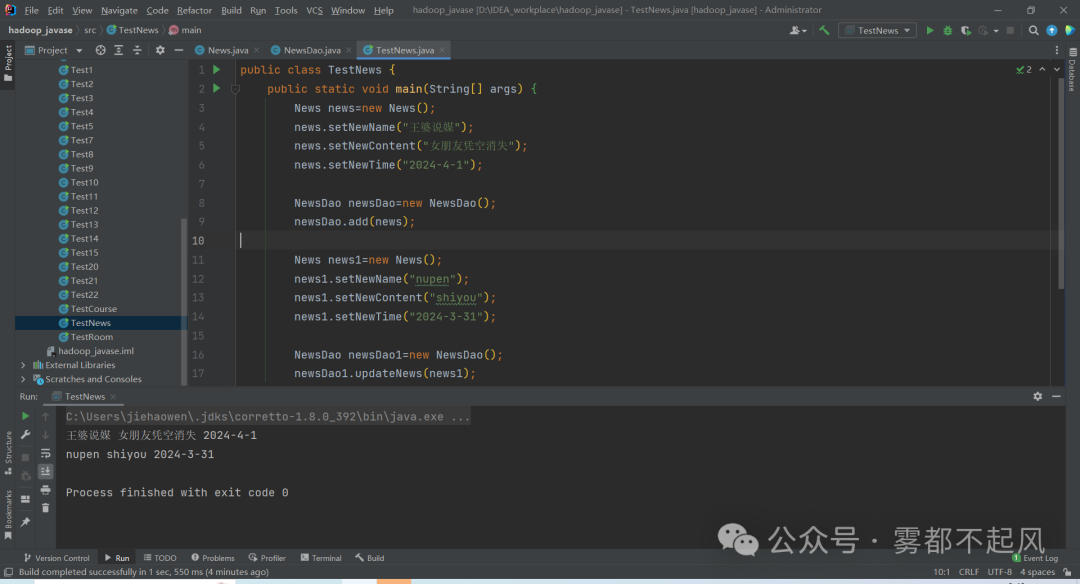
教师管理新闻public class News {private String newName;private String newContent;private String newTime;public String getNewName() {return newName;}public void setNewName(String newName) {this.newName = newName;}public String getNewContent() {return newContent;}public void setNewContent(String newContent) {this.newContent = newContent;}public String getNewTime() {return newTime;}public void setNewTime(String newTime) {this.newTime = newTime;}}public class NewsDao {public void add(News n){System.out.println(n.getNewName()+" "+n.getNewContent()+" "+n.getNewTime());}public String updateNews(News n){System.out.println(n.getNewName()+" "+n.getNewContent()+" "+n.getNewTime());return "修改成功";}}public class TestNews {public static void main(String[] args) {News news=new News();news.setNewName("王婆说媒");news.setNewContent("女朋友凭空消失");news.setNewTime("2024-4-1");NewsDao newsDao=new NewsDao();newsDao.add(news);News news1=new News();news1.setNewName("nupen");news1.setNewContent("shiyou");news1.setNewTime("2024-3-31");NewsDao newsDao1=new NewsDao();newsDao1.updateNews(news1);}}
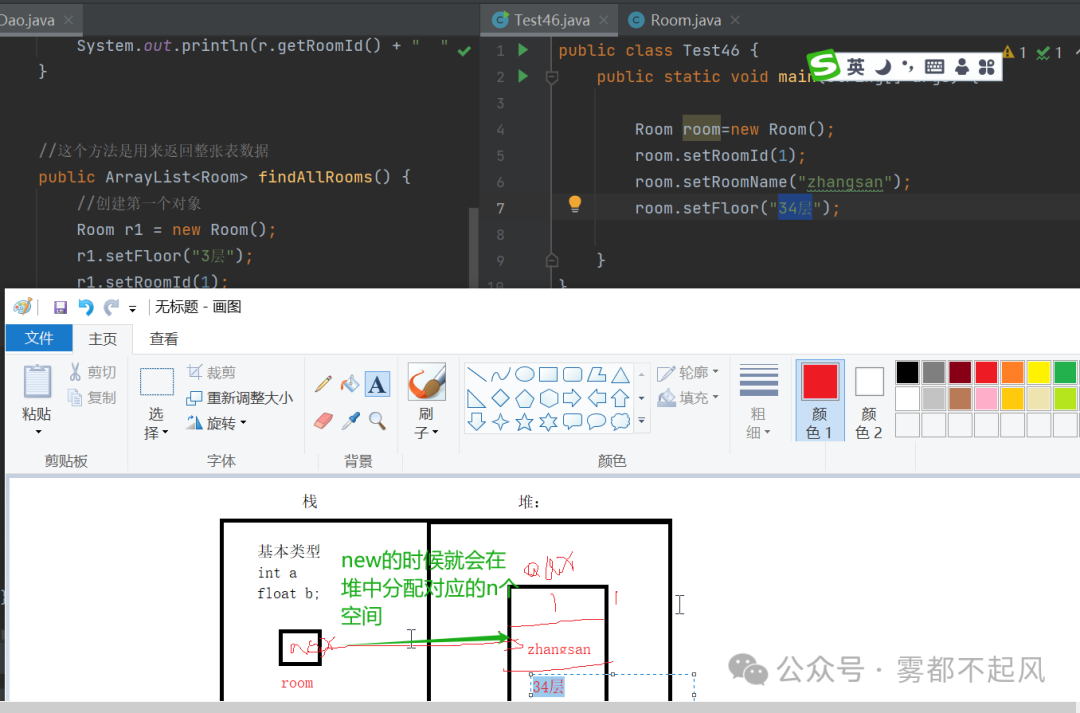
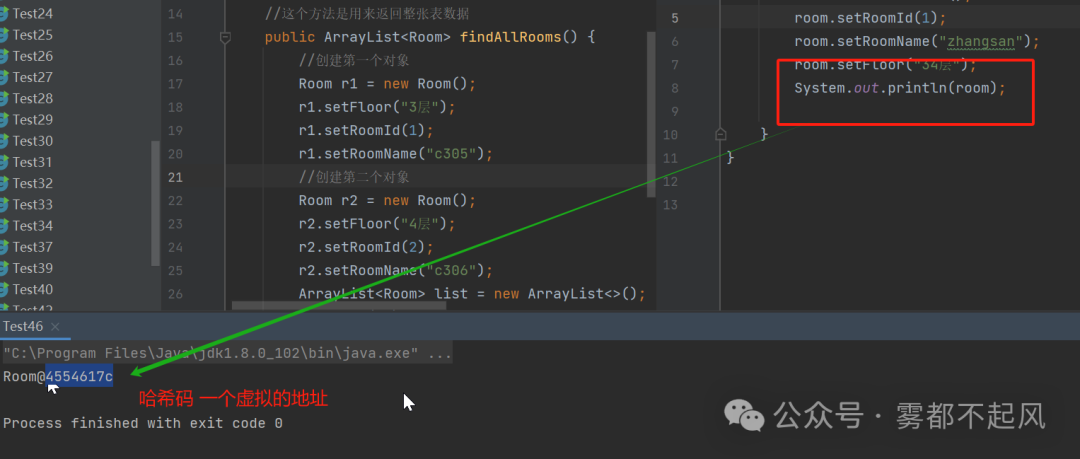
博主实现头像管理public class Head {private int headId;private String headName;public int getHeadId() {return headId;}public void setHeadId(int headId) {this.headId = headId;}public String getHeadName() {return headName;}public void setHeadName(String headName) {this.headName = headName;}}import java.util.ArrayList;public class HeadDao {public void addHead(Head h){System.out.println(h.getHeadId()+" "+h.getHeadName());}public String updateHead(Head h){System.out.println(h.getHeadId()+" "+h.getHeadName());return "修改成功";}public ArrayList<Head> findAllHeads(){ArrayList<Head> list=new ArrayList<>();Head h1=new Head();h1.setHeadId(4);h1.setHeadName("张飞");list.add(h1);Head h2=new Head();h2.setHeadId(6);h2.setHeadName("lisi");list.add(h2);return list;}}import java.util.ArrayList;public class TestHead {public static void main(String[] args) {Head h=new Head();h.setHeadId(1);h.setHeadName("元神");HeadDao headDao=new HeadDao();headDao.addHead(h);Head h1=new Head();h1.setHeadId(2);h1.setHeadName("二次元");String res=headDao.updateHead(h1);System.out.println(res);HeadDao headDao1=new HeadDao();ArrayList<Head> list=headDao1.findAllHeads();for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){Head hh=list.get(i);System.out.println(hh.getHeadId()+" "+hh.getHeadName());}}}
微博信息管理public class Microblog {private String Mcontent;private String Mtime;public String getMcontent() {return Mcontent;}public void setMcontent(String mcontent) {Mcontent = mcontent;}public String getMtime() {return Mtime;}public void setMtime(String mtime) {Mtime = mtime;}}import java.util.ArrayList;public class MicroblogDao {public void addMicroblog(Microblog m){System.out.println(m.getMcontent()+" "+m.getMtime());}public String updateMicroblog(Microblog m){System.out.println(m.getMcontent()+" "+m.getMtime());return "修改成功";}public ArrayList<Microblog> findAllMicroblog(){ArrayList<Microblog> list=new ArrayList<>();Microblog m1=new Microblog();m1.setMcontent("开玩笑");m1.setMtime("2024-4-1");list.add(m1);Microblog m2=new Microblog();m2.setMcontent("和你一起");m2.setMtime("2024-4-1");list.add(m2);return list;}}import java.util.ArrayList;public class TestMicroblog {public static void main(String[] args) {Microblog m=new Microblog();m.setMcontent("水果大胡子");m.setMtime("2021-10-12");MicroblogDao microblogDao=new MicroblogDao();microblogDao.addMicroblog(m);Microblog m1=new Microblog();m1.setMcontent("水性杨花");m1.setMtime("2022-10-12");String res=microblogDao.updateMicroblog(m1);System.out.println(res);MicroblogDao microblogDao1=new MicroblogDao();ArrayList<Microblog> list=microblogDao1.findAllMicroblog();for (int i=0;i<list.size();i++){Microblog mm=list.get(i);System.out.println(mm.getMcontent()+" "+mm.getMtime());}}}
当清晨的第一缕阳光穿过窗帘,洒在静谧的房间里,你慢慢睁开双眼,感受到一天的开始。在这个充满可能性的日子里,你是生活的主角,每一个微笑、每一次努力都是为了让自己更加美好。让心灵和梦想一同飞翔,在每一个细微的瞬间感受到生命的温暖和美好。无论遇到什么困难和挑战,都要坚信自己的力量,勇敢前行,因为你值得拥有最美好的人生。让我们一起相信,美好的事情即将发生。
12.面向对象的特征
1.封装:+private

对象的本身也是一种封装
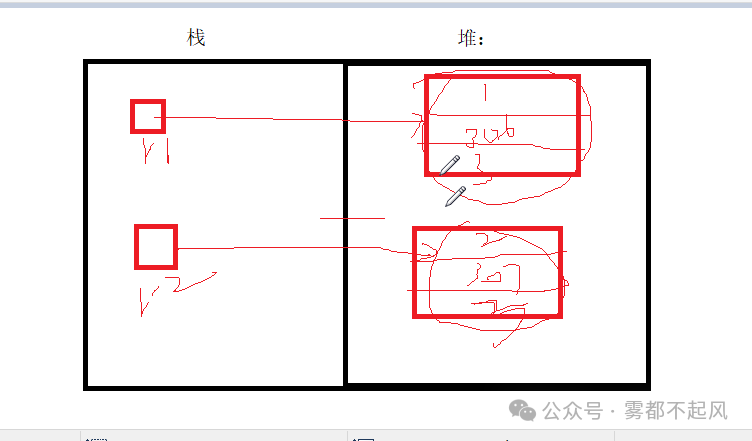
2.继承:
学生package ext;public class Student {public void play(){System.out.println("玩游戏");}}package ext;public class BigStudent extends Student{}package ext;public class LittleStudent extends Student {}package ext;public class TestStu {public static void main(String[] args) {LittleStudent l=new LittleStudent();l.play();}}
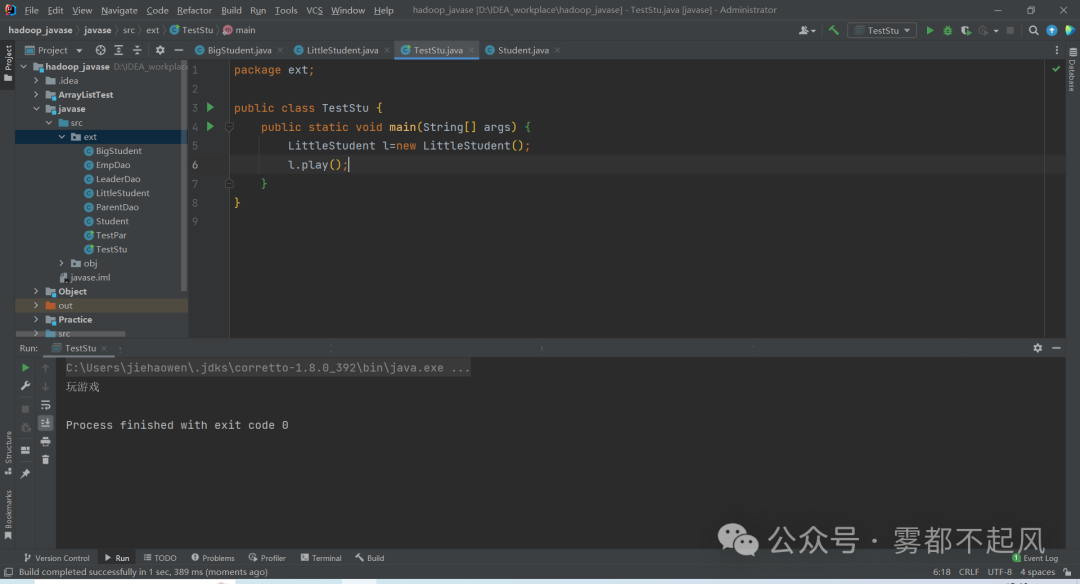
父子关系:
1)父类可以接受子类的对象 同时可以调用父类方法 但是 不能调用子类的方法
package ext;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {int a=12;long b=64;float f=2255f;double d=22d;//当范围大时 范围大的变量 能接受范围小的值d=f;b=a;//父类可以接受子类的对象 同时可以调用父类方法 但是 不能调用子类的方法ParentDao parentDao1=new EmpDao();parentDao1.signature();ParentDao parentDao2=new LeaderDao();parentDao2.signature();}}
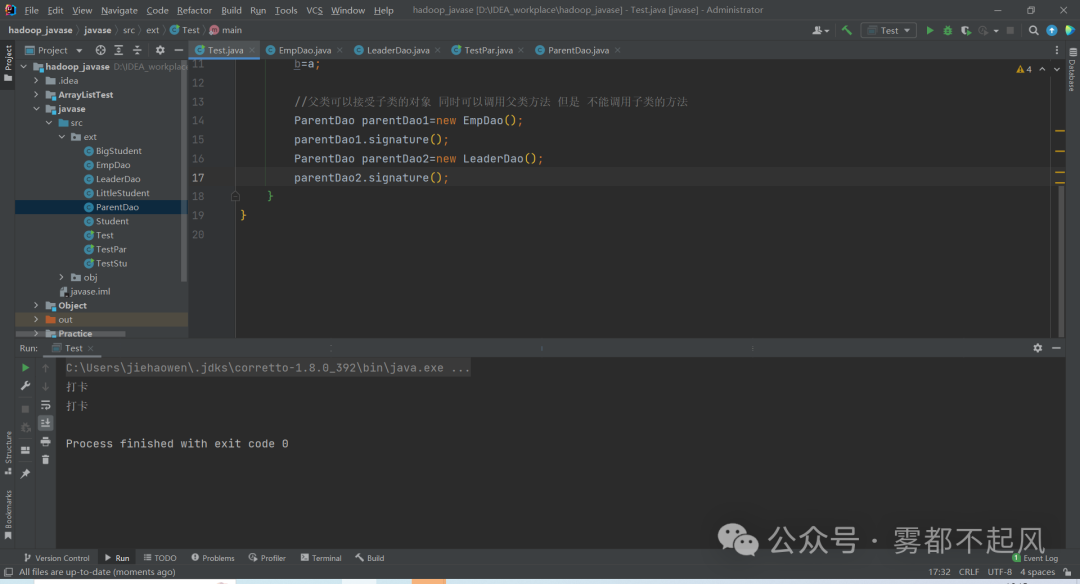
2)当用父类当作参数时 好处是什么 :只要是子类 都可以传递
package ext;public class Test1 {//当用父类当作参数时 好处是什么//只要是子类 都可以传递public void invoke(ParentDao parentDao){//本来要写两个方法 现在只需要写一个方法parentDao.signature();}public static void main(String[] args) {//父类的范围比较大Test1 t=new Test1();EmpDao empDao=new EmpDao();t.invoke(empDao);//有参数就需要传值 那么我们就可以传子类的对象LeaderDao leaderDao=new LeaderDao();t.invoke(leaderDao);}}
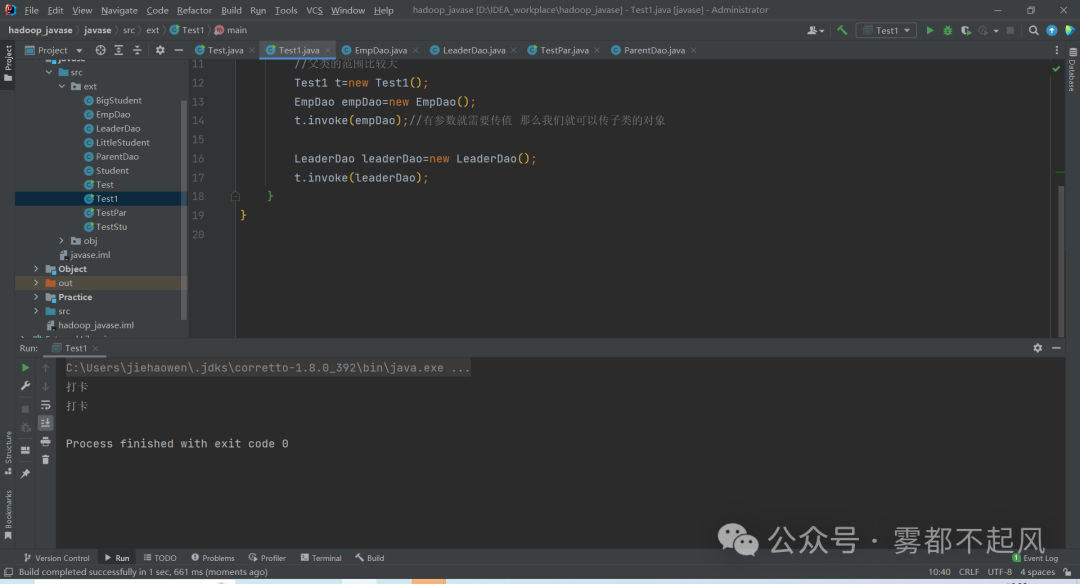
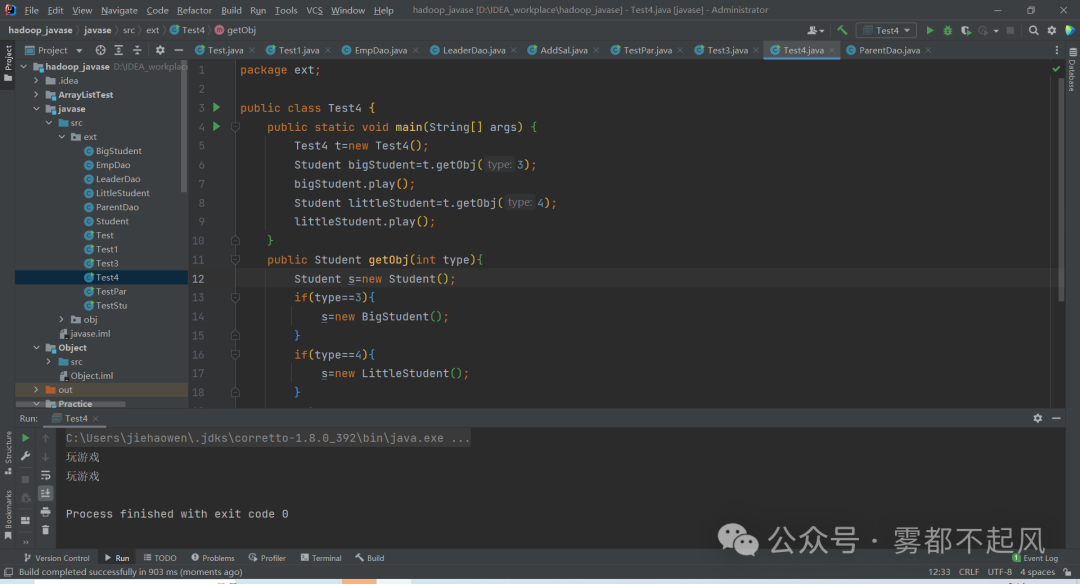
3)当用父类当作返回值类型时 可以返回任何子类对象 (需要强转)
package ext;public class Test3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Test3 t=new Test3();ParentDao leaderDao=t.getObj(1);leaderDao.signature();ParentDao empDao=t.getObj(2);empDao.signature();}//如果返回值是父类 那么你可以返回任何子类对象public ParentDao getObj(int type){ParentDao p=new ParentDao();if(type==1){p=new EmpDao();}if(type==2){p=new LeaderDao();}return p;}}
父类的应用:ArrayList list=new ArrayList(); 不写泛型 可以添加任何形式的值
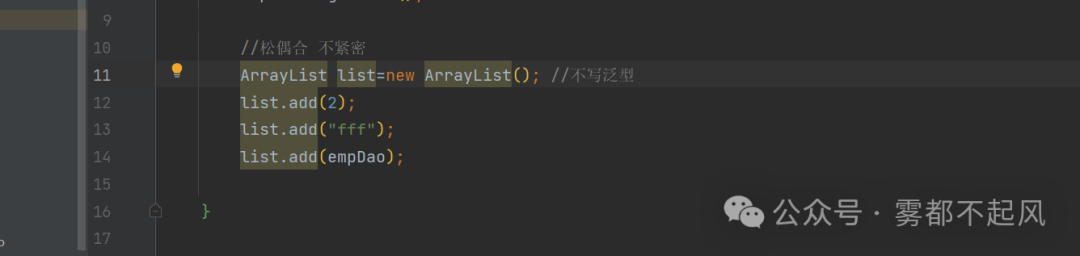
练习:大学生 小学生 使用他们的父类当返回值类型 返回子类对象package ext;public class Test4 {public static void main(String[] args) {Test4 t=new Test4();Student bigStudent=t.getObj(3);bigStudent.play();Student littleStudent=t.getObj(4);littleStudent.play();}public Student getObj(int type){Student s=new Student();if(type==3){s=new BigStudent();}if(type==4){s=new LittleStudent();}return s;}}
当夜幕降临,星星点点在无边的夜空中闪烁,仿佛是为了为你点亮前行的路途。闭上双眼,聆听心灵深处的声音,感受内心的宁静与力量。在这个瞬间,你是自己的主宰,你的梦想是无尽的星辰,你的希望是永不熄灭的火焰。让每一个瞬间都充满感恩和喜悦,因为生活的美好就在身边。愿你在这个宁静的夜晚,感受到内心的平静和满足,带着对未来的希望和期待,迎接每一个黎明的曙光。生活因你而美好,你也因生活而精彩。
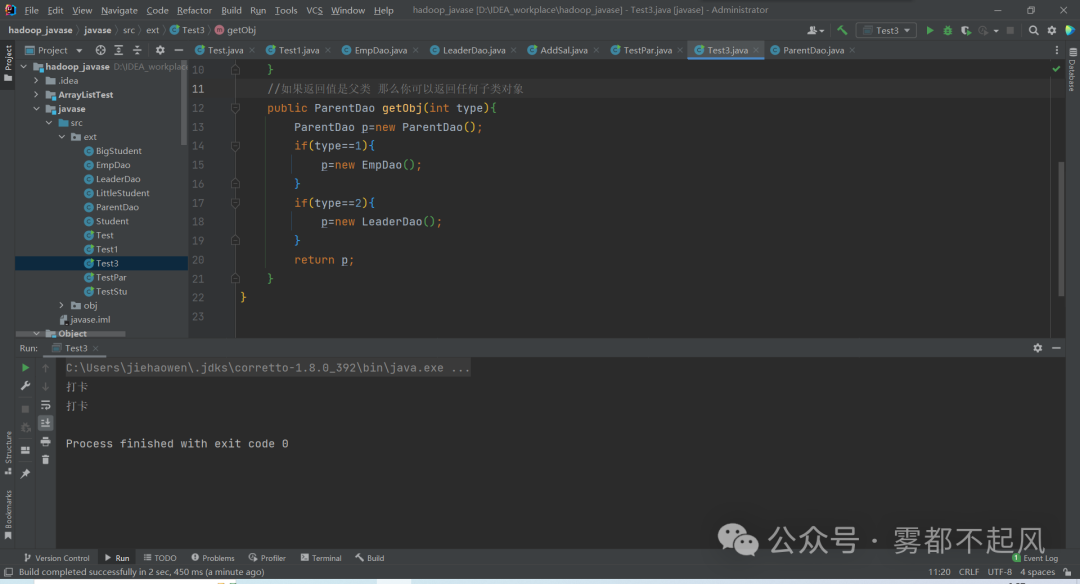
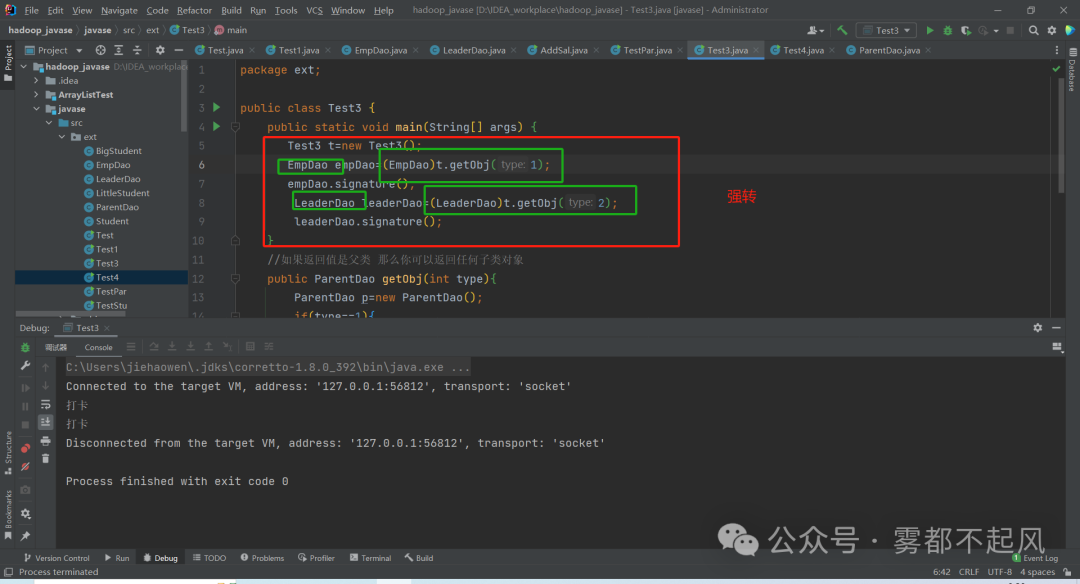
强转:当用父类当返回值类型的时候 学会强转 返回值类型是父类 接收的时候 实际是子类的 理论上可以用子类接受 但是范围较小 所以我们要学会强转
package ext;public class Test3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Test3 t=new Test3();EmpDao empDao=(EmpDao)t.getObj(1);empDao.signature();LeaderDao leaderDao=(LeaderDao)t.getObj(2);leaderDao.signature();}//如果返回值是父类 那么你可以返回任何子类对象public ParentDao getObj(int type){ParentDao p=new ParentDao();if(type==1){p=new EmpDao();}if(type==2){p=new LeaderDao();}return p;}}

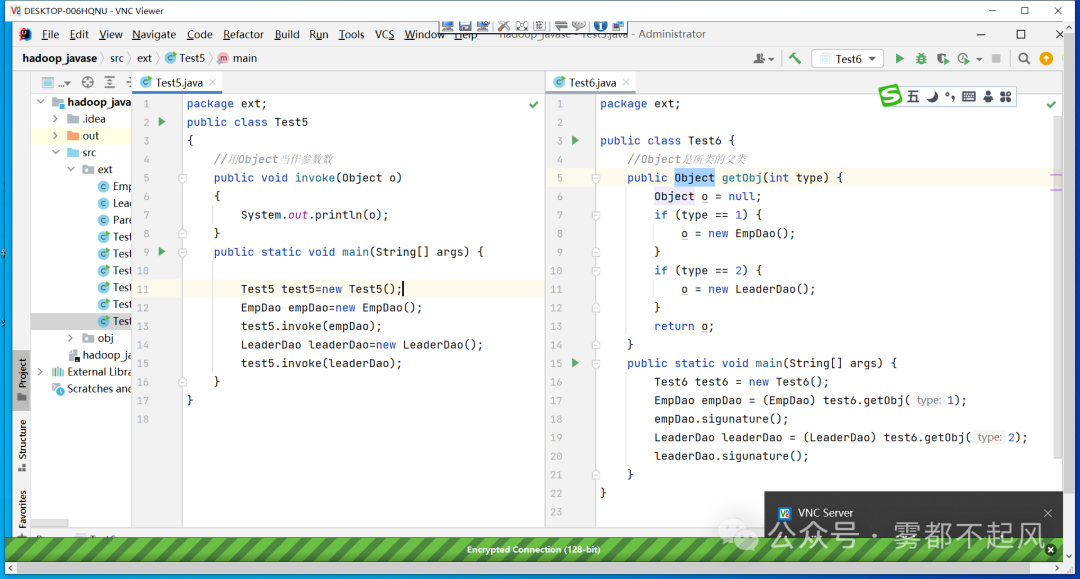
4)Object是所有类的父类 可以用Object作参数 用Object当返回值类型
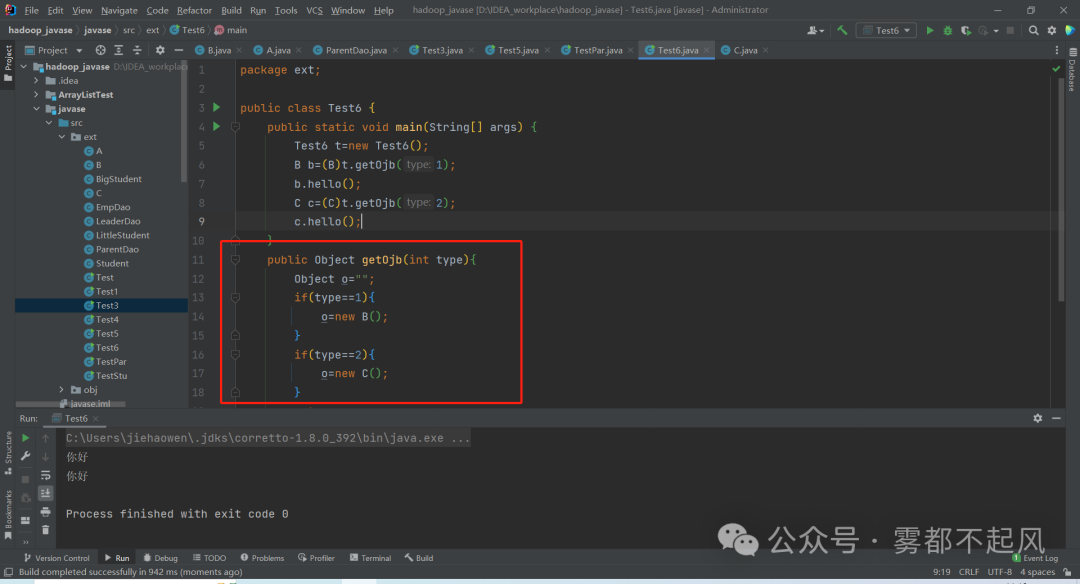
package ext;public class A {public void hello(){System.out.println("你好");}}package ext;public class B extends A{}package ext;public class C extends A{}package ext;public class Test6 {public static void main(String[] args) {Test6 t=new Test6();B b=(B)t.getOjb(1);b.hello();C c=(C)t.getOjb(2);c.hello();}public Object getOjb(int type){Object o="";if(type==1){o=new B();}if(type==2){o=new C();}return o;}}

人生快不快乐看心情 幸不幸福看心态 漫长人生中 什么都不是一眼看到头的 一时的春风得意算不了什么 一时的失败也不能算数
任何业绩的质变都来自于量变的积累


雾都不起风
太阳升起时你未曾离开 太阳落下时希望你依然还在.
公众号
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_77836489/article/details/137774525
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
