vue3.0(十五)状态管理vuex和pinia
文章目录
状态管理
状态管理是指对Vue.js应用中的数据进行统一管理的一种机制。在前端开发中,应用程序的数据通常会被分散存储在各个组件中,这样在跨组件之间共享数据时会变得困难。而Vue状态管理就是为了解决这一问题而设计的。
解决问题:
- 多个视图可能都依赖于同一份状态。
- 来自不同视图的交互也可能需要更改同一份状态。
Vue状态管理通过集中存储应用的状态,并提供一组API来更新和获取状态,从而实现了在多个组件中共享数据的能力。这个集中式的状态存储被称为「状态管理器」或「全局状态」。
一个组件是一个独立的单元<script setup> import { ref } from 'vue' // 状态 const count = ref(0) // 动作 function increment() { count.value++ } </script> <!-- 视图 --> <template>{{ count }}</template>
- 状态:驱动整个应用的数据源;
- 视图:对状态的一种声明式映射;
- 交互:状态根据用户在视图中的输入而作出相应变更的可能方式。

使用Vue状态管理,可以将应用的状态从组件中抽离出来,通过中央数据存储管理器来管理。这样,在不同的组件中就可以通过访问共享的状态来实现数据的一致性和同步更新。同时,由于状态的集中管理,我们可以更好地对状态进行统一的管理和控制,提高了应用的可维护性和可扩展性。
总结一下,Vue状态管理是一种集中式存储和管理Vue.js应用的数据的机制,可以通过使用Vuex库来实现。它提供了统一管理状态的能力,并且方便开发者在多个组件间共享和更新数据。通过Vue状态管理,我们可以更好地组织和维护应用的状态,提高开发效率和代码质量。
vuex
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式 + 库。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
1. 什么情况下应该使用 Vuex
Vuex 可以帮助我们管理共享状态,并附带了更多的概念和框架。这需要对短期和长期效益进行权衡。
如果不打算开发大型单页应用,使用 Vuex 可能是繁琐冗余的。
如果您的应用够简单,您最好不要使用 Vuex。一个简单的 store 模式就足够您所需了。
如果您需要构建一个中大型单页应用,您很可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择。
2. vuex的安装
// npm 安装指令
npm install vuex@next --save
// yarn 安装指令
yarn add vuex@next --save
3. vuex的五大属性
- state
定义了应用程序的状态,就是要管理的数据
存放应用程序的状态(数据),所有组件共享。它是vue实例的data属性的替代品,但是通过它存储和管理的状态,可以在整个应用程序中实现全局共享,即不同的组件可以通过定义的getter和setter访问同一状态数据// 初始化vuex对象 const store = new vuex.Store({ state: { // 管理数据 count: 0 } }) - getters
用于获取state中的状态,主要用于对state进行逻辑上的组合和应用,类似于vuex组件中的计算属性
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, getters: { doubleCount(state) { return state.count * 2 } } }) - mutations
用于修改state中的数据,是唯一可以修改state的地方。mutations接收state作为第一参数,接收payload作为第二个参数,用于修改state中的状态,只能同步执行。mutation必须是同步函数。因为它们不能出来异步行为,异步行为应该放在action中处理。
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { increment(state) { state.count++ }, add(state, payload) { state.count += payload } } }) - actions
用于异步操作和提高mutations,在actions中可以进行任何异步操作,最后在提交到mutations中同步修改state。actions接收context作为第二个参数,其中包含了state,getters和commit等属性
可以包含任意异步操作(例如从服务器获取数据),可以用mutations通过提交commit来修改stateconst store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { increment(state) { state.count++ } }, actions: { incrementAsync(context) { setTimeout(() => { context.commit('increment') }, 1000) } } }) - modules
用于将store分割成模块,每个模块都拥有自己的state,mutations,actions,getters和子模块,以便提高应用程序的可维护性。将state,getters,mutations, sctons模块化,便于组件化和模块化开发
const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules: { cart: { state: { items: [] }, mutations: { addItem(state, item) { state.items.push(item) } }, actions: { addAsyncItem(context, item) { setTimeout(() => { context.commit('addItem', item) }, 1000) } } } } })
4. vuex的五大属性在组件中的应用
- state
不再是vue2.0里什么mapGetter,mapState那些复杂的获取方式,
vue3.0里直接使用computed就可以调用vuex里的数据了。喜大普奔。
同时注意,一点,不可以直接使用useStore()方法里的state对象,因为在输出useStore方法的数据中,state是浅灰色的。
浅灰色只可看到,但是不可以直接使用。

store文件中的设置
在组件中的应用import { createStore } from 'vuex' export default createStore({ state: { count: 1 }, })<template> <div>{{ constA }}</div> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { defineComponent, computed } from 'vue' import { useStore } from 'vuex' export default defineComponent({ setup () { const store = useStore() const constA = computed(() => { return store.state.count }) return { constA } } }) </script>
注意:
- state中的数据是自定义的,但是state属性名是固定的
- 获取数据可以通过 store.state
- 可以使用计算属性优化模板中获取数据的方式
- getters
getter用于对store中的数据进行加工处理形成的新的数据
不会修改store中的原数据 它只起到一个包装器的作用 将store中的数据变一种形式返回出来
-.getter可以对store中已有的数据加工处理之后形成新的数据,类似vue的计算属性
-.store中数据发生改变 getter中的数据也会跟着变化
store文件中的设置
在组件中的应用import { createStore } from 'vuex' export default createStore({ state: { count: 1 }, getters: { showCount: (state) => state.count }, mutations: { addCount (state, step) { console.log(step) state.count += step } }, actions: { updateCount (context, payload) { console.log(context, payload) // 模拟异步操作 setTimeout(() => { context.commit('addCount', payload) }, 1000) } }, modules: { } })<template> <div>{{ constA }}</div> <div>getters获取的state定义的count {{ getterCount }}</div> <div @click="handleAddCount">增加count</div> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { defineComponent, ref, reactive, computed } from 'vue' import { useStore } from 'vuex' export default defineComponent({ setup () { const store = useStore() console.log(store) const constA = computed(() => { return store.state.count }) // 用计算属性可以获取vuex中的getters中的数据 const getterCount = computed(() => { return store.getters.showCount }) function handleAddCount () { store.dispatch('updateCount', 3) // store.commit('addCount', 2) } return { constA, handleAddCount, getterCount } } }) </script> - mutations
mutations用于更变store中的数据(同步)
store文件中的设置
在组件中的应用import { createStore } from 'vuex' export default createStore({ state: { count: 1 }, getters: { }, mutations: { addCount (state, step) { console.log(step)// 调方法的时候,传的参数 state.count += step } }, })<template> <div>{{ constA }}</div> <div @click="handleAddCount">增加count</div> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { defineComponent, ref, reactive, computed } from 'vue' import { useStore } from 'vuex' export default defineComponent({ setup () { const store = useStore() console.log(store) const constA = computed(() => { return store.state.count }) function handleAddCount () { // 调用mutations中的方法 store.commit('addCount', 2) } return { constA, handleAddCount } } }) </script>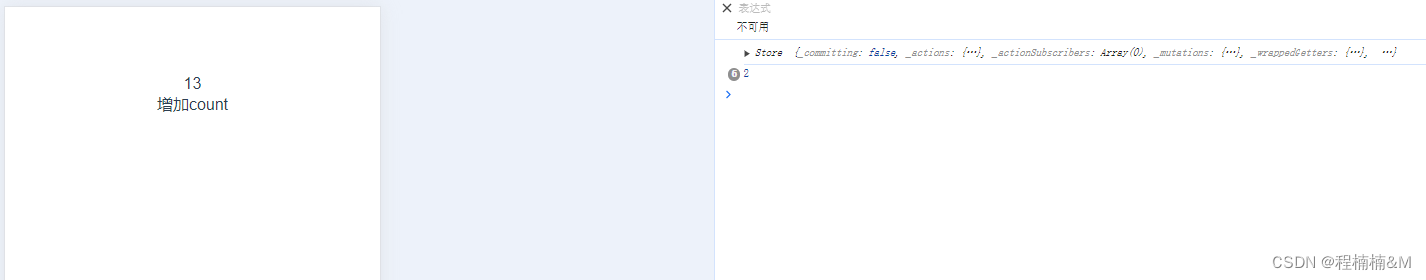
总结:
vue3中取vuex里的数据 需要用 computed获取
使用store.commit(“addCount”) 来触发vuex里的mutations方法
触发mutations时传递参数:store.commit(“addCount”,2) 通过第二个参数 - actions
主要用于处理异步的任务
在组件中应用import { createStore } from 'vuex' export default createStore({ state: { count: 1 }, getters: { }, mutations: { addCount (state, step) { console.log(step) state.count += step } }, actions: { updateCount (context, payload) { console.log(context, payload) // 模拟异步操作 payload是接收的参数 setTimeout(() => { // 通过commit调用mutctions中的方法修改state中的数据 context.commit('addCount', payload) }, 1000) } }, modules: { } })<template> <div>{{ constA }}</div> <div @click="handleAddCount">增加count</div> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { defineComponent, ref, reactive, computed } from 'vue' import { useStore } from 'vuex' export default defineComponent({ setup () { const store = useStore() console.log(store) const constA = computed(() => { return store.state.count }) function handleAddCount () { //使用diapatch调中store文件中的action属性中定义的异步函数 store.dispatch('updateCount', 3) } return { constA, handleAddCount } } }) </script> - modules
- 默认的模块( 不带命名空间 ) : 在组件或者js文件中取值或者调用对应方法时,state 区分模块,其他 getters mutations actions 都在全局(通俗讲就是不带命名空间子模块定义的state数据,即时变量名和全局state中定义的变量名相同,也可以通过模块名取到对应的值,例如:store.state.模块名.变量名),但是 getters ,mutations, actions中定义的方法或属性如果跟全局中定义的相同,那么取到的是全局的。
- 带命名空间 namespaced: true 的模块:所有功能区分模块,更高封装度和复用(同名变量或者方法,可以在多个模块中使用)。
modules中的user文件
store中index文件import { createStore } from 'vuex' export default createStore({ state: { name: '迪西' }, })
在组件中的应用import { createStore } from 'vuex' // 引入模块文件 import user from './modules/user' export default createStore({ state: { count: 1 }, getters: { showCount: (state) => state.count }, mutations: { addCount (state, step) { console.log(step) state.count += step } }, actions: { updateCount (context, payload) { console.log(context, payload) // 模拟异步操作 setTimeout(() => { context.commit('addCount', payload) }, 1000) } }, modules: { user } })<template> <div>{{ constA }}</div> <div>getters获取的state定义的count {{ getterCount }}</div> <div>姓名{{ name }}</div> <div @click="handleAddCount">增加count</div> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { defineComponent, ref, reactive, computed } from 'vue' import { useStore } from 'vuex' export default defineComponent({ setup () { const store = useStore() console.log(store) const constA = computed(() => { return store.state.count }) // 引入user模块的数据 const name = computed(() => { return store.state.user.name }) const getterCount = computed(() => { return store.getters.showCount }) function handleAddCount () { store.dispatch('updateCount', 3) // store.commit('addCount', 2) } return { constA, handleAddCount, getterCount, name } } }) </script>
5. 数据持久化
问题:存储在vuex中的状态,刷新页面,会丢失。为了解决刷新页面数据丢失,才有了数据持久化。最简单的做法就是利用插件 vuex-persistedState。
- 安装
cnpm install vuex-persistedState -S - 使用
import createPersistedState from 'vuex-persistedstate' const store = new Vuex.Store({ state, mutations, actions, getters, plugins: [createPersistedState({ storage: sessionStorage, key: "token" })]//会自动保存创建的状态。刷新还在 })
pinia
1.Pinia 对比 Vuex
- Pinia 同时支持 Vue2 以及 Vue3 ,这让同时使用两个版本的小伙伴更容易上手;
- Pinia 中只存在 State,getter,action,剔除掉了 Vuex 中的 Mutation 及 Module;
- Pinia 中的 action 可同时支持同步任务、异步任务;
- 更友好的支持了 TypeScript ,无需创建自定义复杂包装器来支持 TypeScript,所有内容都是类型化的,并且 API 的设计方式尽可能利用 TS 类型推断;
- Pinia 在修改状态的时候不需要通过其他 api,如:vuex 需通过 commit,dispatch 来修改,所以在语法上比 vuex 更容易理解和使用灵活;
- 由于去除掉了 Module ,无需再创建各个模块嵌套了。Vuex 中,如果数据过多,通常会通过划分模块来进行管理,而 Pinia 中,每个 Store 都是独立的,互不影响;
- 支持服务端渲染;
2.安装及引入
yarn add pinia
// 或者使用 npm
npm install pinia
安装完 Pinia 包之后,需要在 main.js 文件中导入 createPinia 函数并将 Pinia 插件与 Vue 应用程序绑定:
代码如下(示例):
import { createApp } from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
// 引入 createPinia 函数
import { createPinia } from 'pinia';
const app = createApp(App)
// 使用 createPinia() 来创建 Pinia(根存储),并应用到整个应用中
app.use(createPinia());
app.mount('#app');
使用 createPinia() 函数创建并初始化 Pinia 插件实例,将其与 Vue 应用程序绑定使用 app.use(pinia)。
3.三大属性
Pinia 的核心概念包括状态(State)、动作(Actions)和获取器(Getters)。这些概念为你提供了一种组织和管理应用状态的方式。
-
State
状态是你在 store 中存储的数据。每个 Pinia store 都有自己的状态,这个状态是一个 JavaScript 对象。你可以在定义 store 时初始化状态:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'; const useStore = defineStore({ id: 'myStore', state: () => ({ count: 0, user: null, }), }); -
Actions
动作是一种修改 store 状态的方法。在 Pinia 中,你可以在 actions 属性中定义动作:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'; const useStore = defineStore({ id: 'myStore', state: () => ({ count: 0, }), actions: { increment() { this.count++; }, }, }); -
Getters
获取器是一种依赖于 store 状态并产生计算值的函数。这些值将被缓存,直到依赖的状态改变。在 Pinia 中,你可以在 getters 属性中定义获取器:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'; const useStore = defineStore({ id: 'myStore', state: () => ({ count: 0, }), getters: { doubleCount() { return this.count * 2; }, }, });
4.三大属性在组件中的运用
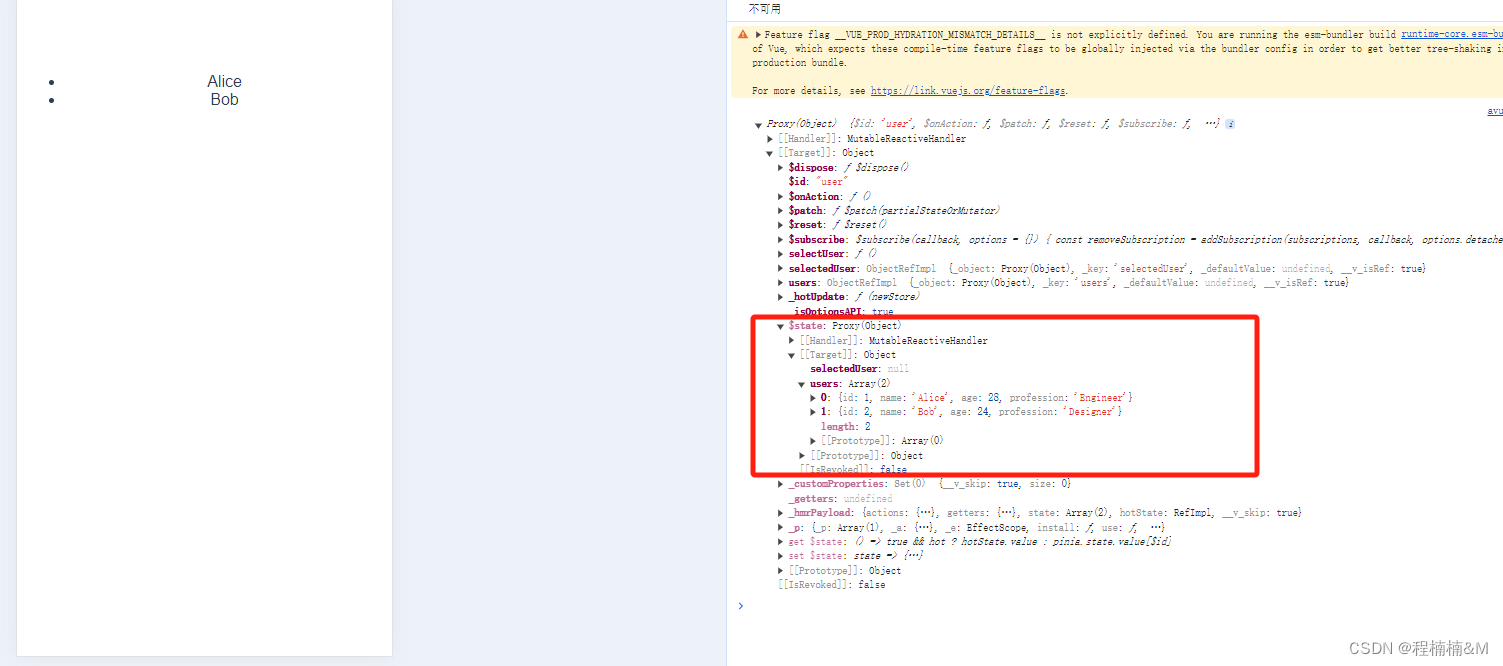
store文件中的使用
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {
state: () => ({
users: [
{
id: 1,
name: 'Alice',
age: 28,
profession: 'Engineer'
},
{
id: 2,
name: 'Bob',
age: 24,
profession: 'Designer'
}
],
selectedUser: null
}),
actions: {
selectUser (user: any) {
this.selectedUser = user
}
}
})
组件中的使用
<template>
<ul>
<li v-for="user in users" :key="user.id" @click="selectUser(user)">
{{ user.name }}
</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, ref, reactive, computed } from 'vue'
import { useUserStore } from '../store/userStore'
export default defineComponent({
setup () {
const store = useUserStore()
console.log(store)
function selectUser (item: any) {
store.selectUser(item);
}
return {
selectUser,
users: store.users,
}
}
})
</script>
总结
Pinia 是一个轻量级且强大的状态管理库,它使得在 Vue.js 应用中管理状态变得更简单、更直观。如果你正在使用 Vue.js 构建应用,并需要一个简单易用的状态管理解决方案,那么 Pinia 是一个很好的选择。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/chengcheng9876/article/details/139932225
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
