ELK分布式日志管理平台部署
一、日志分析
在运维中,日志是非常重要的工具,用于记录系统、应用程序或设备的运行状态、事件和异常情况。
1.1 日志分析的作用
故障排除和问题诊断
日志是排查故障和诊断问题的关键信息源。
通过分析日志文件,可以查找和定位系统故障、错误和异常,帮助运维人员迅速找出问题的根本原因,并采取正确的修复措施。
性能分析和优化
通过监视和分析系统日志,可以了解系统的性能瓶颈、资源消耗情况和关键指标。
运维人员可以根据日志中的数据,优化系统配置、调整资源分配,以提高系统的性能和响应能力。
安全监控和威胁检测
日志可以帮助监控系统的安全性,并检测潜在的安全威胁。
通过分析日志,可以发现异常登录、未授权访问、恶意行为等安全问题,并及时采取措施进行应对和防范。
运营分析和规划
通过日志分析,可以更好地了解用户需求,进行容量规划,制定有效的运维策略和决策。
合规性和审计
通过记录和保留日志,可以应对合规性规定,并提供必要的审计跟踪,以满足法规和行业标准的要求。
因此,对于任何系统或应用程序,设置合适的日志记录和日志分析机制是非常重要的一环。
1.2 需要收集的日志
系统日志:为监控做准备,要收集tomcat系统日志,tomcat所在节点的日志。
服务日志:比如数据库mysql,收集慢查询日志、错误日志、普通日志,要收集tomcat服务日志。
业务日志(业务日志必须收集):业务口子日志在log4j,log4j是由java环境开发的,跑在tomcat上。
1.3 完整日志系统的基本特征
- 收集:能够采集多种来源的日志数据
- 传输:能够稳定的把日志数据解析过滤并传输到存储系统
- 存储:存储日志数据
- 分析:支持UI分析
警告:能够提供错误报告,监控机制
二、ELK概述
2.1 ELK简介
ELK平台是一套完整的日志集中处理解决方案。
将 ElasticSearch、Logstash 和 Kiabana 三个开源工具配合使用, 完成更强大的用户对日志的查询、排序、统计需求。
2.2 ELK的作用
集中化管理日志后,日志的统计和检索的效率降低。
ELK 提供了一个完整的日志管理和分析解决方案,能够帮助用户更好地理解数据、监控系统性能并进行故障排除。
三、ELK组件详解
3.1 Logstash
3.1.1 简介
Logstash 实现了数据的收集和处理。
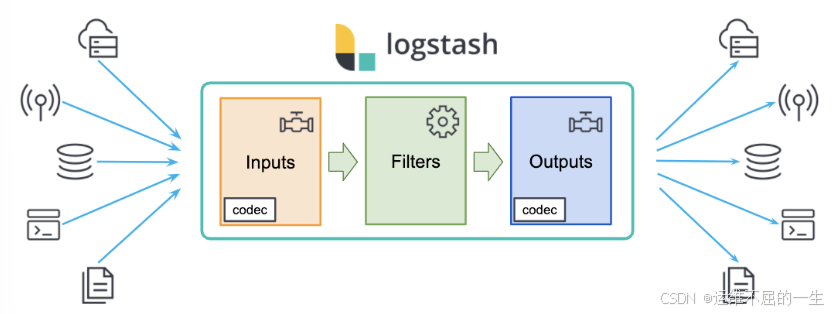
Logstash 是一个可扩展的数据收集、转换和传输工具。
它可以从各种来源(如日志文件、消息队列、数据库等)收集数据,并将其转换为统一的格式,然后发送到 Elasticsearch 进行存储和分析。
Logstash 提供了丰富的输入插件font>和输出插件,可以与各种数据源和目标进行集成。
它还具有强大的过滤功能,可以对数据进行处理、过滤和转换,以满足不同的业务需求。
3.1.2 Logstash命令常用选项
#Logstash 命令常用选项
-f:通过这个选项可以指定 Logstash 的配置文件,根据配置文件配置 Logstash 的输入和输出流
-e:从命令行中获取,输入、输出后面跟着字符串,该字符串可以被当作 Logstash 的配置(如果是空,则默认使用 stdin 作为输入,stdout 作为输出)
-t:测试配置文件是否正确,然后退出。
3.1.3 Logstash 的输入和输出流
定义输入和输出流
#输入采用标准输入
#输出采用标准输出(类似管道)
#新版本默认使用 rubydebug 格式输出
logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{} }'
使用 rubydebug 输出详细格式显示
#codec 为一种编解码器
logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{ codec=>rubydebug } }'
##举个例子##
#键入内容(标准输入)
www.baidu.com
#使用 `input` 插件来定义一个输入源#`stdin{}` 表示使用标准输入作为输入
#然后使用 `output` 插件来定义一个输出目标
#`stdout{ codec=>rubydebug }` 表示将数据打印到标准输出,并使用 `rubydebug` 编解码器来格式化输出。
 3.1.4 Logstash配置文件
3.1.4 Logstash配置文件
Logstash 配置文件基本由三部分组成:input、output 以及 filter。
filter部分选择性添加,可以没有。
input部分
表示从数据源采集数据。
常见的数据源如Kafka、日志文件等。
file beats kafka redis stdin
#基本格式
input {...}
filter部分
数据处理层,包括对数据进行格式化处理、数据类型转换、数据过滤等,支持正则表达式。
#基本格式
filter {...}
| 插件 | 作用 |
| grok | 对若干个大文本字段进行再分割成一些小字段 (?<字段名>正则表达式) |
| date | 对数据中的时间格式进行统一和格式化 |
| mutate | 对一些无用的字段进行剔除,或增加字段 |
| mutiline | 对多行数据进行统一编排,多行合并或拆分 |
字段名: 正则表达式匹配到的内容
output部分
表示将Logstash收集的数据经由过滤器处理之后输出到Elasticsearch。
#基本格式
output {...}
补充说明
在每个部分中,也可以指定多个访问方式font>。
#举个例子,若要指定两个日志来源文件,则格式如下:
input {
file { path =>"/var/log/messages" type =>"syslog"}
file { path =>"/var/log/httpd/access.log" type =>"apache"}
}
3.2 ElasticSearch
Elasticsearch 提供了强大的搜索和分析引擎。
Elasticsearch 是一个分布式、实时的搜索和分析引擎。
它基于 Lucene 搜索引擎库构建,具有分布式搜索、实时数据分析、高性能和高可伸缩性的特点。
Elasticsearch 可以存储和索引大规模的数据(比如日志),并提供快速的全文搜索、条件过滤、聚合和分析功能。
3.3 Kiabana
Kibana 提供了可视化和交互式分析的界面。
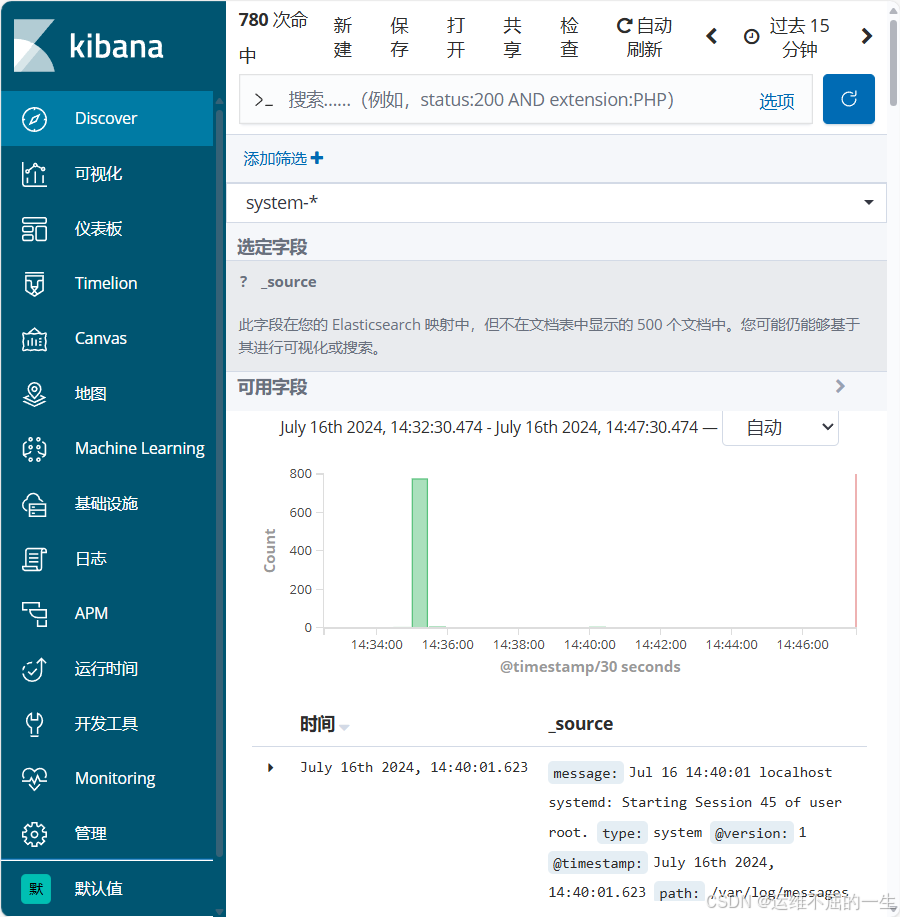
Kibana 是一个针对Elasticsearch的开源数据分析及可视化平台,用来搜索、查看交互存储在Elasticsearch索引中的数据。
使用Kibana,可以通过各种图表进行高级数据分析及展示,创建自定义仪表盘font>来展示关键指标和监控警报。
四、ELK的工作原理
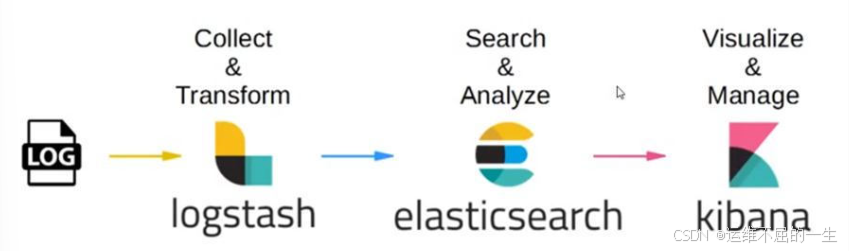
1)在所有需要收集日志的服务器上部署Logstash,或者先将日志进行集中化管理在日志服务器上,在日志服务器上部署 Logstash。
2)Logstash 收集日志,将日志格式化并输出到 Elasticsearch 群集中。
3)Elasticsearch 对格式化后的数据进行索引和存储。
4)Kibana 从 ES 群集中查询数据生成图表,并进行前端数据的展示。
综上所述:
logstash作为日志搜集器,从数据源采集数据,并对数据进行过滤,格式化处理,然后交由Elasticsearch存储,kibana对日志进行可视化处理。
五、部署ELK(Logstash作为日志收集器)
| 用户 | IP | 软件 | 系统 |
| node1 | 192.168.10.20 | Elasticsearch | CentOS7 |
| node2 | 192.168.10.30 | Elasticsearch | CentOS7 |
| client | 192.168.10.40 | Logstash、Kibana | CentOS7 |
5.1 环境准备
5.1.1 java环境
java -version#如果没有安装,yum -y install java
openjdk version "1.8.0_131"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_131-b12)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.131-b12, mixed mode)5.1.2 关闭防火墙
systemctl disable --now firewalld
setenforce 0
sed -i.bak 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config 5.2 安装部署 Elasticsearch 软件
5.2.1 安装 Elasticsearch 软件
[root@localhost opt]#ls
elasticsearch-6.7.2.rpm elasticsearch-head-master.zip node-v8.2.1.tar.gz phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2
[root@localhost opt]#rpm -ivh elasticsearch-6.7.2.rpm
[root@localhost opt]#cd /etc/elasticsearch/
[root@localhost elasticsearch]#mkdir bak
[root@localhost elasticsearch]#cp -a *.yml bak/
#备份5.2.2修改配置文件
[root@node1 elasticsearch]#vim elasticsearch.yml
17 cluster.name: my-elk-cluster
#修改集群名字
23 node.name: node1
24 node.master: true
25 node.data: true
#设置 节点名称 主从之间不能一致 24作为主节点 25作为数据节点
45 bootstrap.memory_lock: true
#内存锁开启 禁止使用 swap
59 network.host: 0.0.0.0
#监听地址
60 http.port: 9200
# 默认使用端口
61 transport.tcp.port: 9300
#内部传输端口
73 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.10.20:9300", "192.168.10.30:9300"]
#自动集群发现,加入主机名 使用单播 类似心跳线
[root@localhost elasticsearch]#grep -v "^#" elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: my-elk-cluster
node.name: node1
node.master: true
node.data: true
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
transport.tcp.port: 9300
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.10.20:9300", "192.168.10.30:9300"]5.2.3 修改系统配置
5.2.3.1 性能调优参数
[root@localhost elasticsearch]#vim /etc/security/limits.conf
......
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 65536
* soft nproc 32000
* hard nproc 32000
* soft memlock unlimited
* hard memlock unlimited5.2.3.2 修改systemd 服务管理器
/etc/systemd/system.conf 文件是用于配置 systemd 的,这是一种用于 Linux 操作系统的系统和服务管理器。通过这个文件,你可以自定义与系统操作、性能和行为相关的各种设置
-
DefaultTimeoutStartSec=:设置启动服务的默认等待时间
-
DefaultTimeoutStopSec=:设置停止服务的默认等待时间
-
DefaultRestartSec=:设置在重新启动服务之前的默认休眠时间
-
DefaultLimitNOFILE=:设置打开文件数量的默认限制
-
DefaultLimitNPROC=:设置进程数量的默认限制
-
DefaultLimitCORE=:设置核心文件大小的默认限制
-
DefaultEnvironment=:指定服务的默认环境变量
实际修改
[root@localhost elasticsearch]#vim /etc/systemd/system.conf
DefaultLimitNOFILE=65536
DefaultLimitNPROC=32000
DefaultLimitMEMLOCK=infinity5.2.3.3 修改内核参数
[root@localhost elasticsearch]#vim /etc/sysctl.conf
#一个进程可以拥有的最大内存映射区域数,参考数据(分配 2g/262144,4g/4194304,8g/8388608)
vm.max_map_count=262144
sysctl -p
sysctl -a | grep vm.max_map_count![]()
5.2.4 重启服务器 启动 elasticsearch
reboot
systemctl start elasticsearch.service
systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
netstat -antp | grep 92005.2.5 查看节点信息
浏览器访问
http://192.168.10.20:9200
http://192.168.10.30:9200
查看节点 Node1、Node2 的信息。
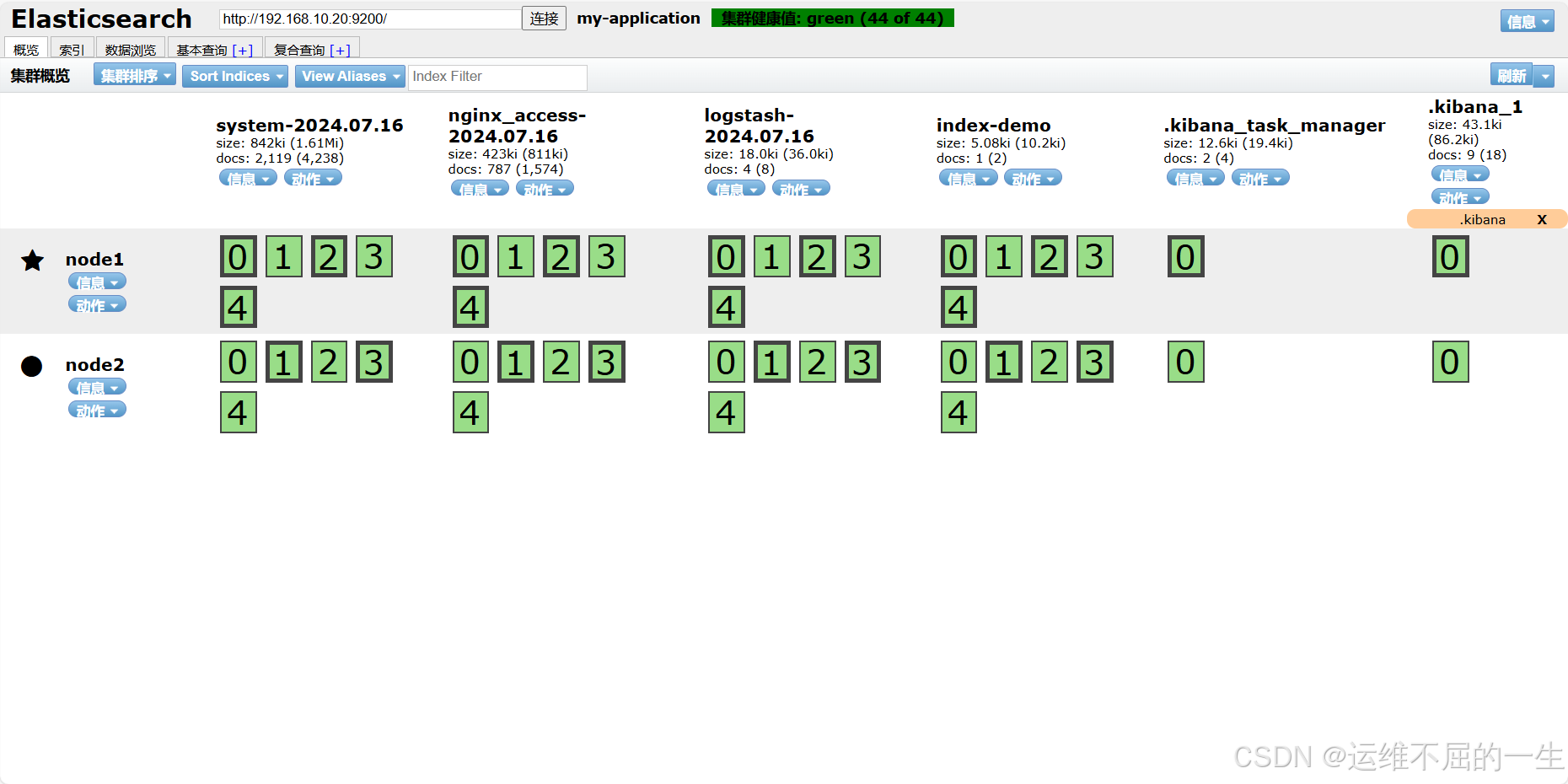
5.2.6编译安装 Elasticsearch-head 插件 主从都可以安装
Elasticsearch 在 5.0 版本后,Elasticsearch-head 插件需要作为独立服务进行安装,需要使用npm工具(NodeJS的包管理工具)安装。 安装 Elasticsearch-head 需要提前安装好依赖软件 node和 phantomjs。 node:是一个基于 Chrome V8 引擎的 JavaScript 运行环境。 phantomjs:是一个基于 webkit 的JavaScriptAPI,可以理解为一个隐形的浏览器,任何基于 webkit 浏览器做的事情,它都可以做到。
5.2.6.1编译安装node**组件
#上传软件包 node-v8.2.1.tar.gz 到/opt
yum install gcc gcc-c++ make -y
cd /opt
tar zxvf node-v8.2.1.tar.gz
cd node-v8.2.1/
./configure
make && make install5.2.6.2 安装 phantomjs
#上传软件包 phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2 到
cd /opt
tar jxvf phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2
cd /opt/phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64/bin
ln -s /opt/phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64/bin/phantomjs /usr/bin5.2.6.3安装 Elasticsearch-head 数据可视化工具
#上传软件包 elasticsearch-head-master.zip 到/opt
cd /opt
unzip elasticsearch-head-master.zip
cd /opt/elasticsearch-head-master/
npm install //安装依赖包5.2.6.4修改 Elasticsearch 主配置文件
vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
......
--末尾添加以下内容--
http.cors.enabled: true#开启跨域访问支持,默认为 false
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"#指定跨域访问允许的域名地址为所有
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
systemctl restart elasticsearch
#重启elasticsearch 服务5.2.6.5启动 elasticsearch-head 服务
必须在解压后的 elasticsearch-head 目录下启动服务,进程会读取该目录下的 gruntfile.js 文件,否则可能启动失败。
[root@localhost elasticsearch]#cd /data/elasticsearch-head/
[root@localhost elasticsearch-head]# npm run start &
> elasticsearch-head@0.0.0 start /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head
> grunt server
Running "connect:server" (connect) task
Waiting forever...
Started connect web server on http://localhost:9100
#elasticsearch-head 监听的端口是 9100
netstat -natp |grep 91005.2.6.6测试插件
192.168.10.20:9100
192.168.10.30:9100
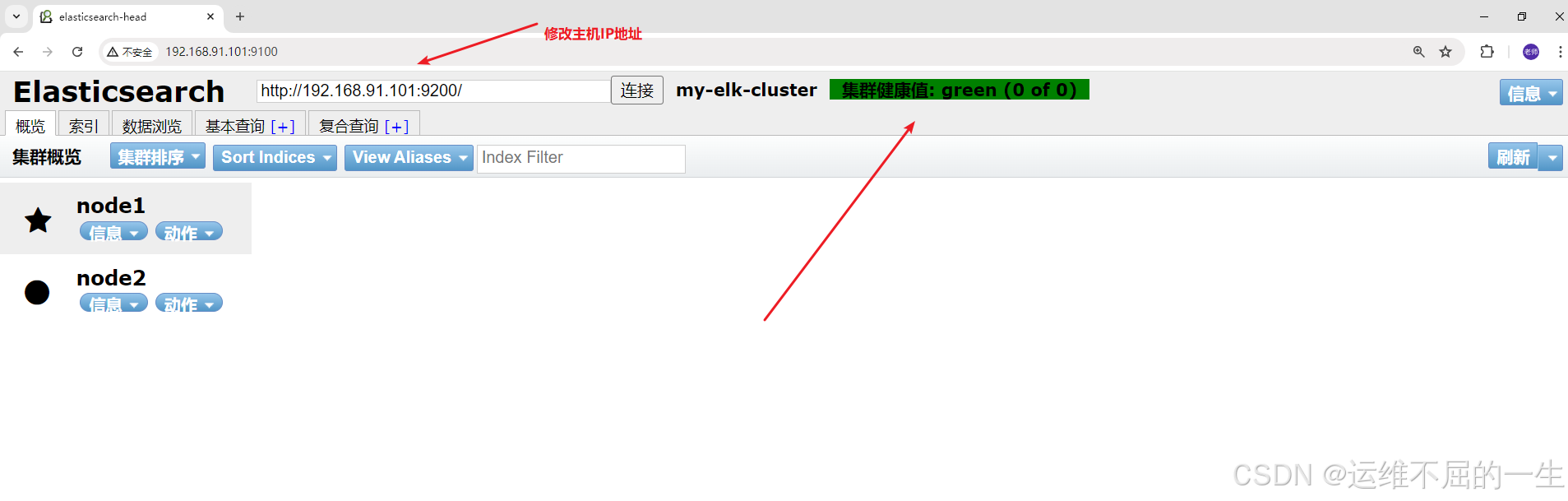
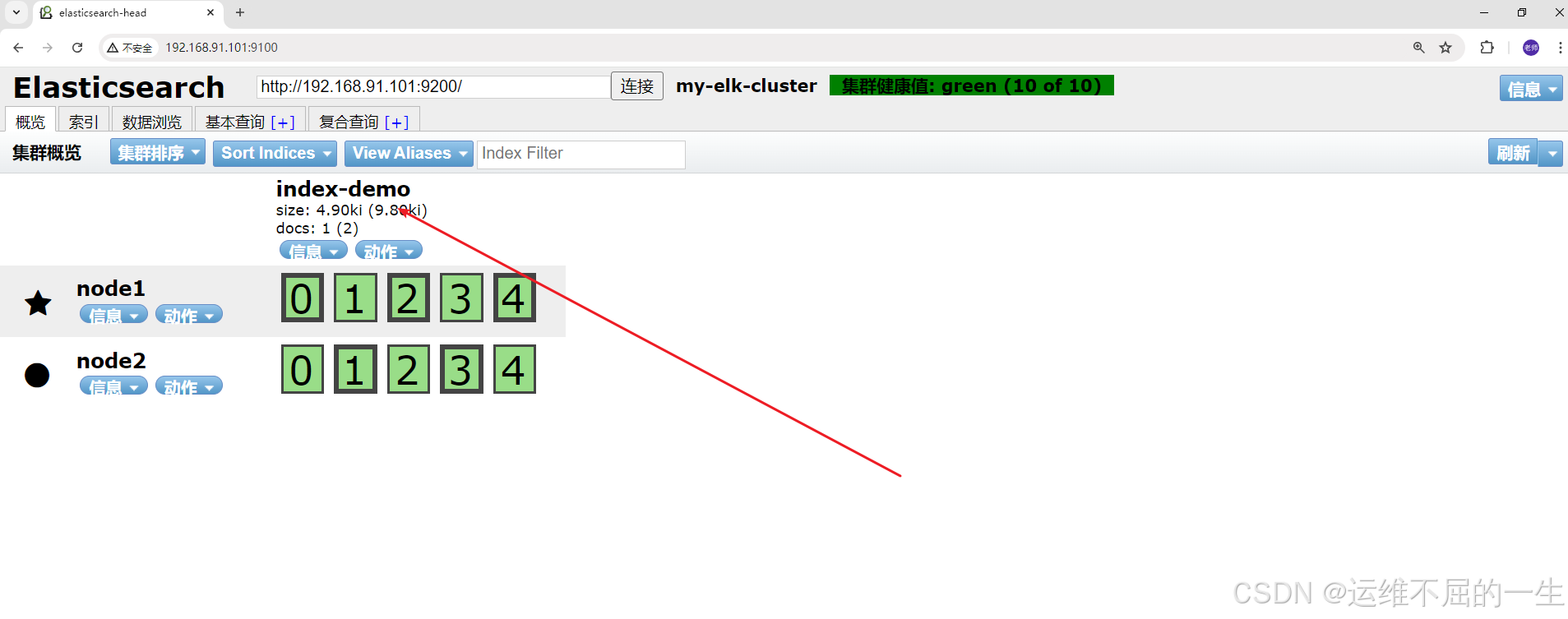
5.2.6.7插入索引测试
curl -X PUT 'localhost:9200/index-demo/test/1?pretty&pretty' -H 'content-Type: application/json' -d '{"user":"zhouzhou","mesg":"woaini"}'
-x 指定方法
-H 添加请求头
-d 请求体
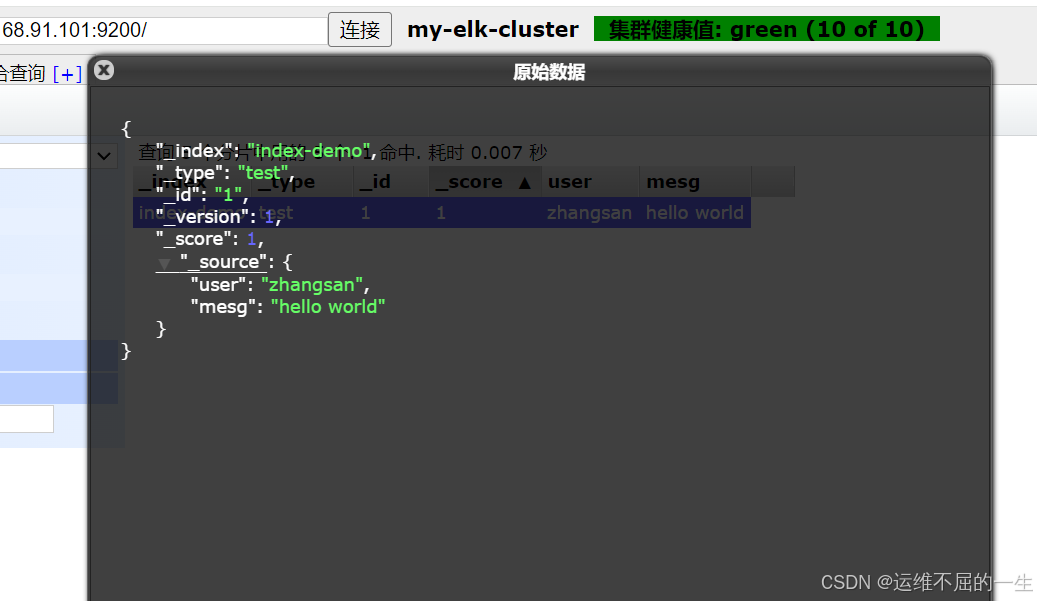
[root@node2 elasticsearch-head-master]#curl -X PUT 'localhost:9200/index-demo/test/1?pretty&pretty' -H 'content-Type: application/json' -d '{"user":"zhangsan","mesg":"hello world"}'
{
"_index" : "index-demo",
"_type" : "test",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1
}
刷新页面可以看到有新的数据
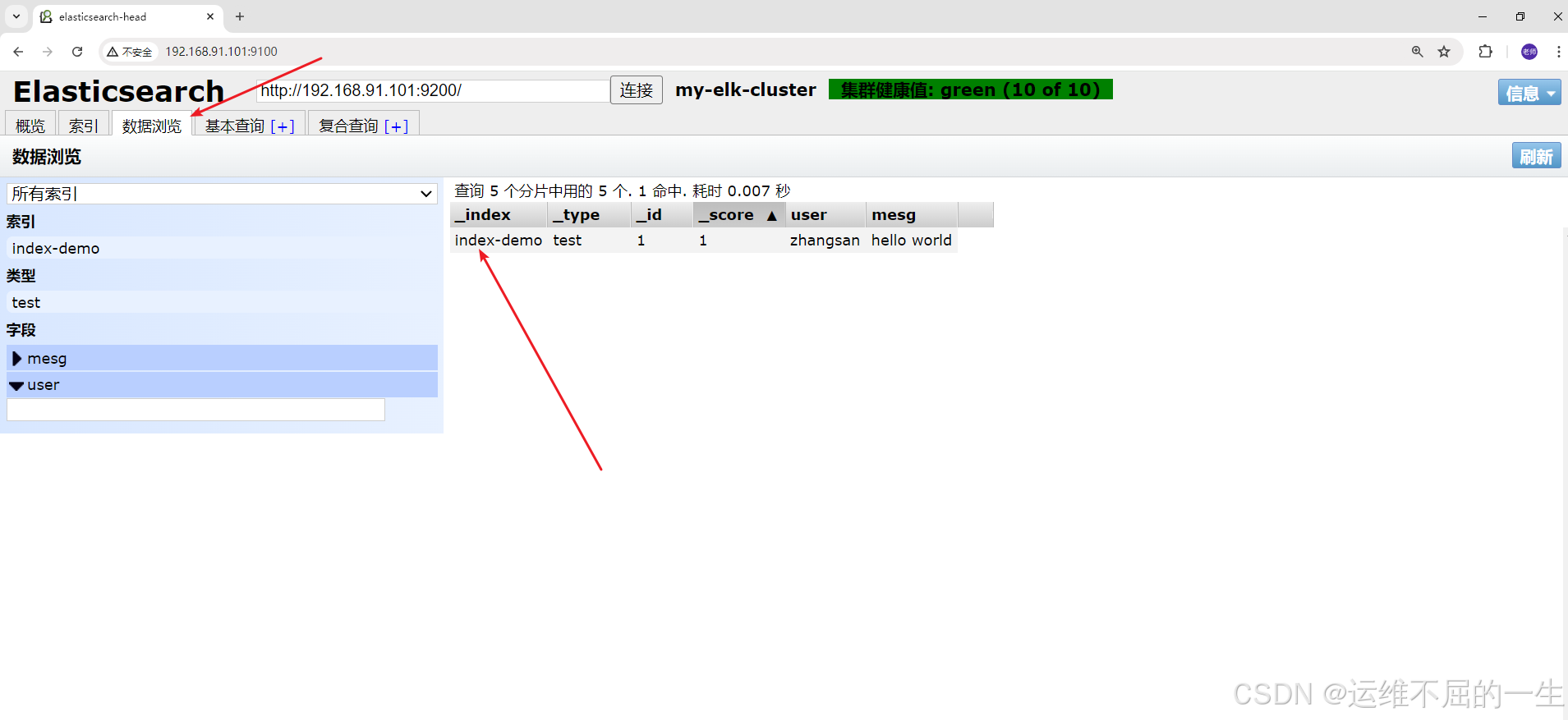
5.3在应用服务器部署 Logstash
在 client节点上操作
5.3.1更改主机名
[root@localhost elasticsearch]# hostnamectl set-hostname client5.3.2 安装服务
yum -y install java
java -version
yum install -y epel-release
#安装epel源 额外 rpeo
yum install nginx -y5.3.3 安装logstash
cd /opt
[root@localhost opt]# rpm -ivh logstash-6.7.2.rpm
#开启服务
systemctl enable --now logstash.service
[root@localhost opt]# ln -s /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash /usr/bin/
# 做软连接5.3.4 使用logstash
Logstash 命令常用选项: -f:通过这个选项可以指定 Logstash 的配置文件,根据配置文件配置 Logstash 的输入和输出流。 -e:从命令行中获取,输入、输出后面跟着字符串,该字符串可以被当作 Logstash 的配置(如果是空,则默认使用 stdin 作为输入,stdout 作为输出)。 -t:测试配置文件是否正确,然后退出。
例子:在命令行中收集日志数据
#输入采用标准输入,输出采用标准输出(类似管道),新版本默认使用 rubydebug 格式输出
[root@localhost opt]# logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{} }'
# 等待时间较长
WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults
Could not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console
[INFO ] 2024-07-16 00:42:00.411 [main] writabledirectory - Creating directory {:setting=>"path.queue", :path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/queue"}
[INFO ] 2024-07-16 00:42:00.468 [main] writabledirectory - Creating directory {:setting=>"path.dead_letter_queue", :path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/dead_letter_queue"}
[WARN ] 2024-07-16 00:42:01.196 [LogStash::Runner] multilocal - Ignoring the 'pipelines.yml' file because modules or command line options are specified
[INFO ] 2024-07-16 00:42:01.211 [LogStash::Runner] runner - Starting Logstash {"logstash.version"=>"6.7.2"}
[INFO ] 2024-07-16 00:42:01.269 [LogStash::Runner] agent - No persistent UUID file found. Generating new UUID {:uuid=>"31865788-3782-4fb6-9472-c755f27c98ed", :path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/uuid"}
[INFO ] 2024-07-16 00:42:09.884 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] pipeline - Starting pipeline {:pipeline_id=>"main", "pipeline.workers"=>2, "pipeline.batch.size"=>125, "pipeline.batch.delay"=>50}
[INFO ] 2024-07-16 00:42:10.147 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] pipeline - Pipeline started successfully {:pipeline_id=>"main", :thread=>"#<Thread:0x6a4c4acf sleep>"}
The stdin plugin is now waiting for input:
[INFO ] 2024-07-16 00:42:10.244 [Ruby-0-Thread-1: /usr/share/logstash/lib/bootstrap/environment.rb:6] agent - Pipelines running {:count=>1, :running_pipelines=>[:main], :non_running_pipelines=>[]}
[INFO ] 2024-07-16 00:42:10.635 [Api Webserver] agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
# 此处输入需要的信息
hello world
#############
/usr/share/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/2.5.0/gems/awesome_print-1.7.0/lib/awesome_print/formatters/base_formatter.rb:31: warning: constant ::Fixnum is deprecated
{
"message" => "hello world",
"host" => "localhost.localdomain",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => 2024-07-15T16:42:54.195Z
}
5.3.5 使用 Logstash 将信息写入 Elasticsearch 中
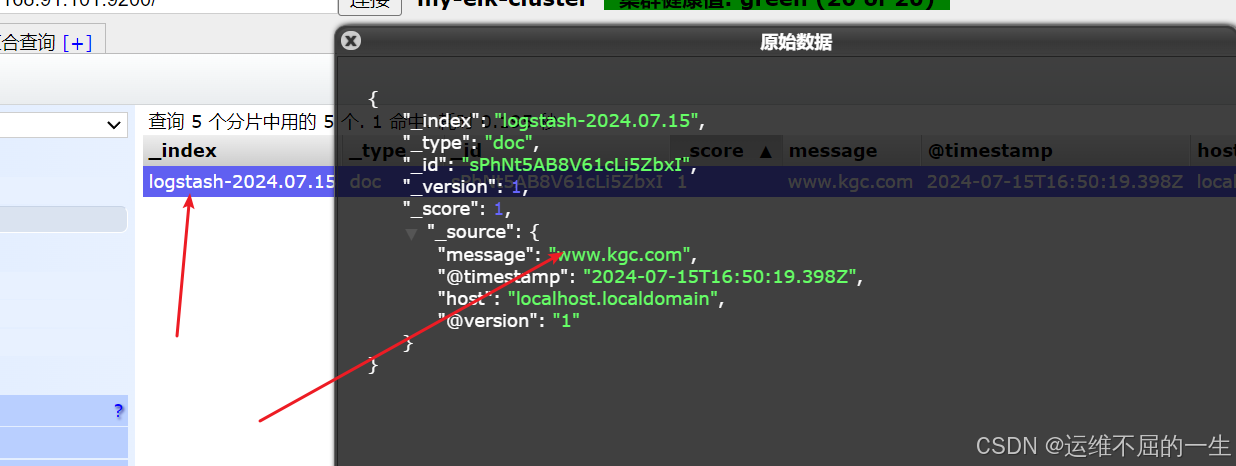
[root@localhost opt]#logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { hosts=>["192.168.10.20:9200"] } }'
对接
//结果不在标准输出显示,而是发送至 Elasticsearch 中,可浏览器访问 http://192.168.10.20:9100/ 查看索引信息和数据浏览。
logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { hosts=>["192.168.10.20:9200","192.168.10.30:9200"]} }'
............................
[INFO ] 2024-07-16 00:50:12.096 [Api Webserver] agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
# 输入信息
www.kgc.com
hello world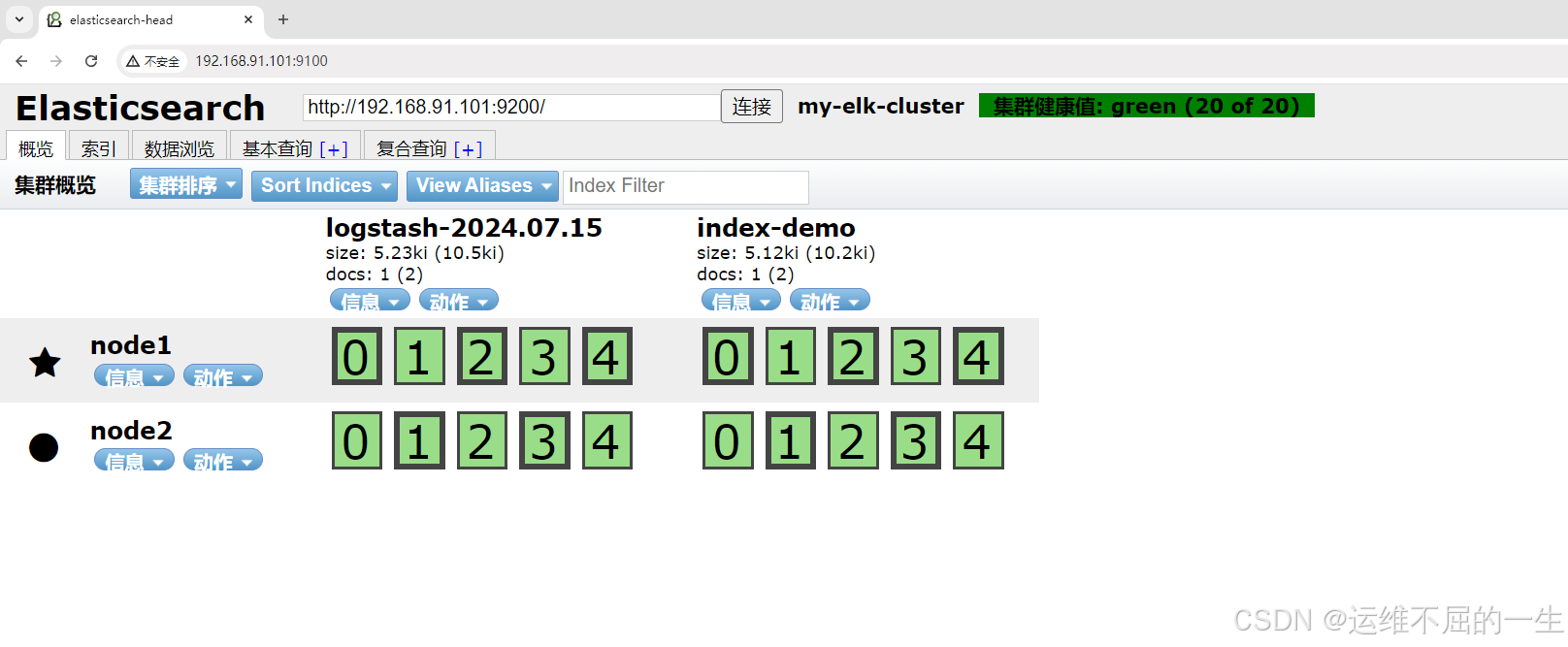
5.3.6 使用配置文件
Logstash 配置文件基本由三部分组成:input、output 以及 filter(可选,根据需要选择使用)
-
input:表示从数据源采集数据,常见的数据源如Kafka、日志文件等 file beats kafka redis stdin
-
filter:表示数据处理层,包括对数据进行格式化处理、数据类型转换、数据过滤等,支持正则表达式 grok 对若干个大文本字段进行再分割成一些小字段 (?<字段名>正则表达式) 字段名: 正则表达式匹配到的内容 date 对数据中的时间格式进行统一和格式化 mutate 对一些无用的字段进行剔除,或增加字段 mutiline 对多行数据进行统一编排,多行合并或拆分
-
output:表示将Logstash收集的数据经由过滤器处理之后输出到Elasticsearch。 elasticsearch stdout
#格式如下:
input {...}
filter {...}
output {...}
#在每个部分中,也可以指定多个访问方式。例如,若要指定两个日志来源文件,则格式如下:
input {
file { path =>"/var/log/messages" type =>"syslog"}
file { path =>"/var/log/httpd/access.log" type =>"apache"}
vim system.conf
input {
file{
path =>"/var/log/messages"
type =>"system"
start_position =>"beginning"
# ignore_older => 604800
sincedb_path => "/etc/logstash/sincedb_path/log_progress"
add_field => {"log_hostname"=>"${HOSTNAME}"}
}
}
#path表示要收集的日志的文件位置
#type是输入ES时给结果增加一个叫type的属性字段
#start_position可以设置为beginning或者end,beginning表示从头开始读取文件,end表示读取最新的,这个要和ignore_older一起使用
#ignore_older表示了针对多久的文件进行监控,默认一天,单位为秒,可以自己定制,比如默认只读取一天内被修改的文件
#sincedb_path表示文件读取进度的记录,每行表示一个文件,每行有两个数字,第一个表示文件的inode,第二个表示文件读取到的位置(byteoffset)。默认为$HOME/.sincedb*
#add_field增加属性。这里使用了${HOSTNAME},即本机的环境变量,如果要使用本机的环境变量,那么需要在启动命令上加--alow-env
output {
elasticsearch {#输出到 elasticsearch
hosts => ["192.168.91.100:9200","192.168.91.101:9200"]#指定 elasticsearch 服务器的地址和端口
index =>"system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"#指定输出到 elasticsearch 的索引格式
}
}
实际例子:
[root@localhost log]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/system-log.conf
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/messages"
type => "system"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => [ "192.168.10.20:9200","192.168.10.30:9200" ]
index => "system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
[root@localhost conf.d]# chmod +r /var/log/messages
#添加权限
[root@localhost conf.d]# logstash -f system-log.conf
#启动logstash
........................................................................
[INFO ] 2024-07-16 01:02:41.716 [Api Webserver] agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9601}
刷新页面

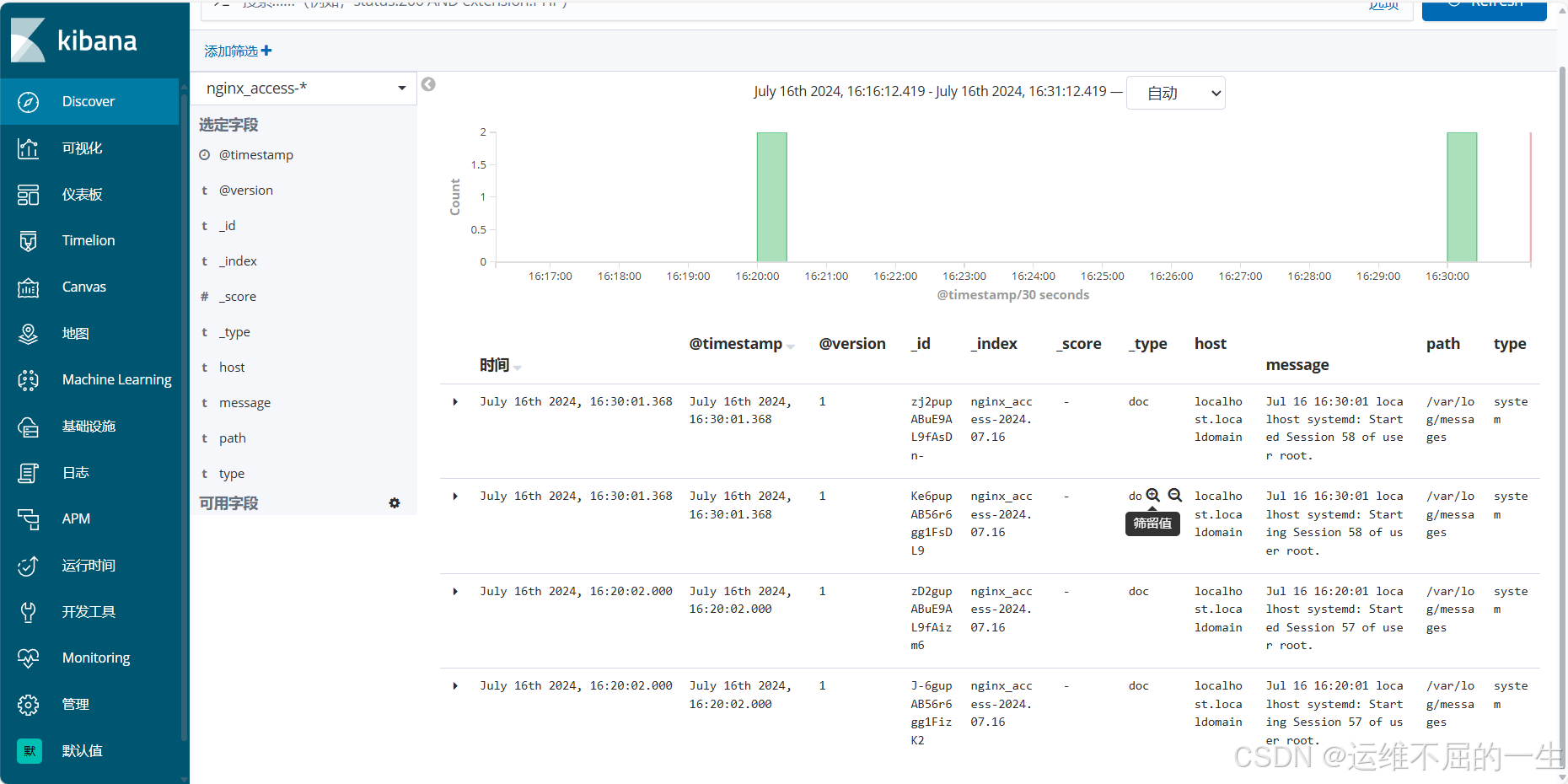
5.3.7 配置nginx日志
在/etc/logstash/conf.d下配置一个nginx_log.conf
[root@localhost conf.d]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/nginx_log.conf
input {
file{
path => "/var/log/nginx/access_log"
type => "access"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.10.20:9200","192.168.10.30:9200"]
index => "nginx_access-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
在nginx配置文件中将日志文件格式修改为json格式
[root@localhost nginx]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
...
http {
log_format log_json '{ "@timestamp": "$time_local",
"remote_addr": "$remote_addr",
"remote_user": "$remote_user",
"server_addr": "$server_addr",
"request": "$request",
"status": "$status",
"body_bytes_sent": "$body_bytes_sent",
"http_referer": "$http_referer",
"http_user_agent": "$http_user_agent",
"request_time": "$request_time" }';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log log_json;
5.4 安装 kibana 在client服务器
5.4.1 安装
root@localhost opt]# rpm -ivh kibana-6.7.2-x86_64.rpm 5.4.2 修改配置
[root@localhost opt]# cd /etc/kibana/
[root@localhost kibana]# cp kibana.yml kibana.yml.bak -a
[root@localhost kibana]# vim kibana.yml
2 server.port: 5601 #打开端口
7 server.host: "0.0.0.0" #监听端口
28 elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://192.168.10.20:9200", "http://192.168.10.30:9200"] #el服务器地址
37 kibana.index: ".kibana" #打开索引
96 logging.dest: /var/log/k.log #指定日志文件, 需要手动建立文件
114 i18n.locale: "zh-CN" #中文设置
[root@localhost kibana]# chown kibana:kibana /var/log/k.log5.4.3 启动 kibana
[root@localhost kibana]# systemctl enable --now kibana.service
[root@localhost kibana]# ss -nap |grep 5601
tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:5601 *:* users:(("node",pid=42235,fd=19))5.4.4 访问测试
192.168.10.40:5601
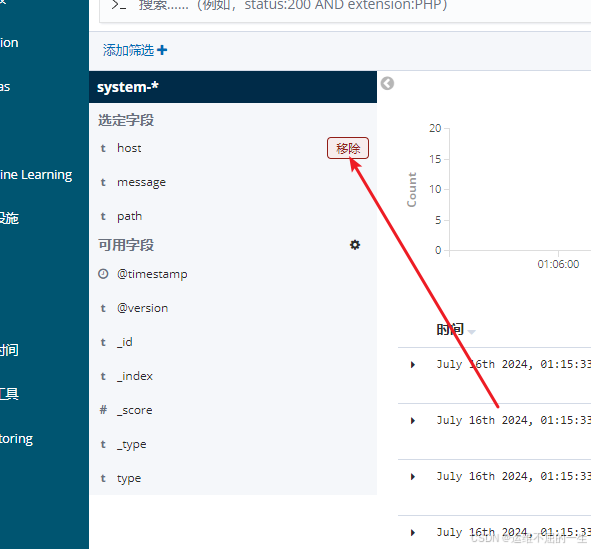
5.4.5 建立索引










原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_67497257/article/details/140465068
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!

