力扣题目训练(13)
2024年2月6日力扣题目训练
2024年2月6日第十三天编程训练,今天主要是进行一些题训练,包括简单题3道、中等题2道和困难题1道。惰性太强现在才完成,不过之后我会认真完成的。
492. 构造矩形
链接: 构造矩形
难度: 简单
题目:

运行示例:

思路:
这道题本质就是暴力求解,但是注意要L和W之间差不多肯定是在平方根附近。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> constructRectangle(int area) {
int W = sqrt(area);
int L = area/W;
vector<int> ans;
while(L >= W){
if(L * W == area){
ans.push_back(L);
ans.push_back(W);
break;
}
W--;
L = area / W;
}
return ans;
}
};
495. 提莫攻击
链接: 提莫攻击
难度: 简单
题目:

运行示例:

思路:
这道题可以单次扫描,在扫描过程中注意两次中毒是否有交集,有的话需要单独处理。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int findPoisonedDuration(vector<int>& timeSeries, int duration) {
int ans = 0;
if(timeSeries.size() == 0) return 0;
int left = timeSeries[0],right = left+duration-1;
ans += duration;
for(int i = 1; i < timeSeries.size(); i++){
if(timeSeries[i] <= right){
ans += timeSeries[i]+ duration-1-right;
}else{
ans += duration;
}
left = timeSeries[i];
right = timeSeries[i]+ duration-1;
}
return ans;
}
};
500. 键盘行
链接: 键盘行
难度: 简单
题目:
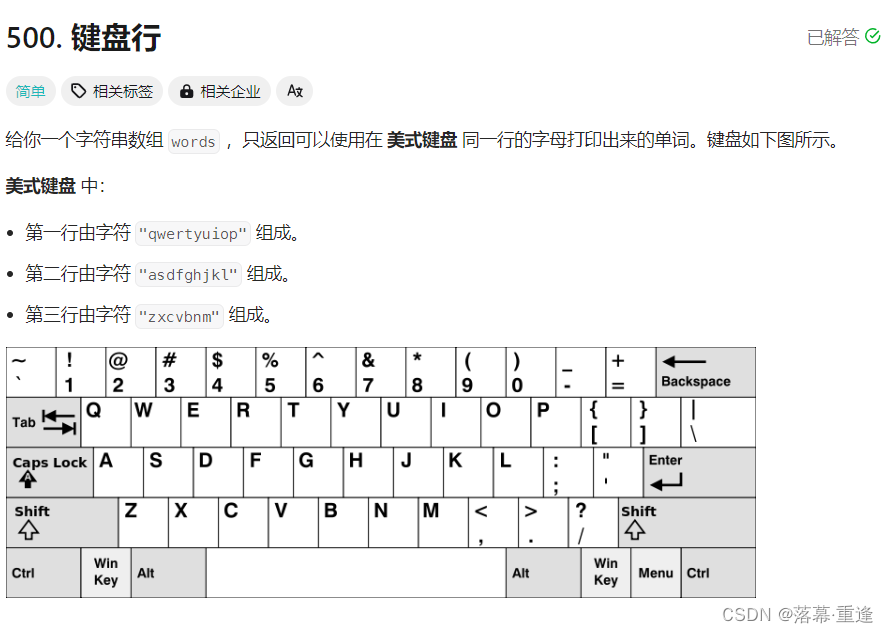
运行示例:

思路:
这道题其实就是单次扫描,为了方便,我们为每一个英文字母标记其对应键盘上的行号,然后检测字符串中所有字符对应的行号是否相同。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> findWords(vector<string>& words) {
vector<string> ans;
string rowIdx = "12210111011122000010020202";
for(auto &word : words){
bool isValid = true;
char idx = rowIdx[tolower(word[0]) - 'a'];
for(int i = 1; i < word.size(); i++){
if(rowIdx[tolower(word[i]) - 'a'] != idx){
isValid = false;
break;
}
}
if(isValid) ans.push_back(word);
}
return ans;
}
};
166. 分数到小数
链接: 分数到小数
难度: 中等
题目:
运行示例:

思路:
这道题利用长除法,存在整数和小数部分,在处理小数部分时,需要将余数*10进行计算,而且如果存在循环还需要利用哈希表记录循环部分。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
string fractionToDecimal(int numerators, int denominators) {
string ans;
long numerator = numerators;
long denominator = denominators;
if(numerator % denominator == 0) return to_string(numerator / denominator);
if(numerator < 0 ^ denominator < 0 ) ans += '-';
numerator = abs(numerator);
denominator = abs(denominator);
long intpart = numerator/denominator;
ans += to_string(intpart) + '.';
long rem = numerator % denominator;
unordered_map<long, int> remainderIndexMap;
int index = 0;
string frapart;
while(rem && !remainderIndexMap.count(rem)){
remainderIndexMap[rem] = index;
rem *= 10;
frapart += to_string(rem/denominator);
rem %= denominator;
index++;
}
if(rem != 0){
int indexs = remainderIndexMap[rem];
frapart = frapart.substr(0,indexs)+'('+frapart.substr(indexs)+')';
}
ans+=frapart;
return ans;
}
};
199. 二叉树的右视图
链接: 二叉树的右视图
难度: 中等
题目:

运行示例:
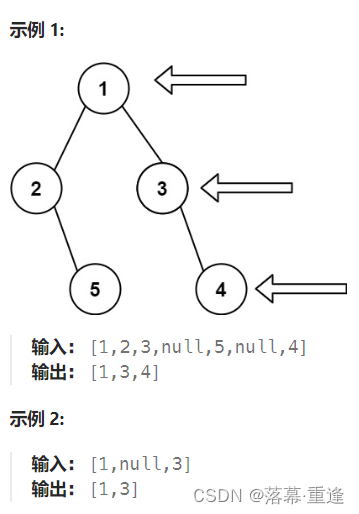
思路:
这道题本质就是记录每层的最右节点值,所以可以用层次遍历。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
if(root == NULL) return ans;
queue<TreeNode*> res;
res.push(root);
while(!res.empty()){
int size = res.size();
for(int i = 0 ; i < size; i++){
TreeNode* curr = res.front();
res.pop();
if(i == size - 1){
ans.push_back(curr->val);
}
if(curr->left != NULL) res.push(curr->left);
if(curr->right != NULL) res.push(curr->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
85. 最大矩形
链接: 最大矩形
难度: 困难
题目:
运行示例:
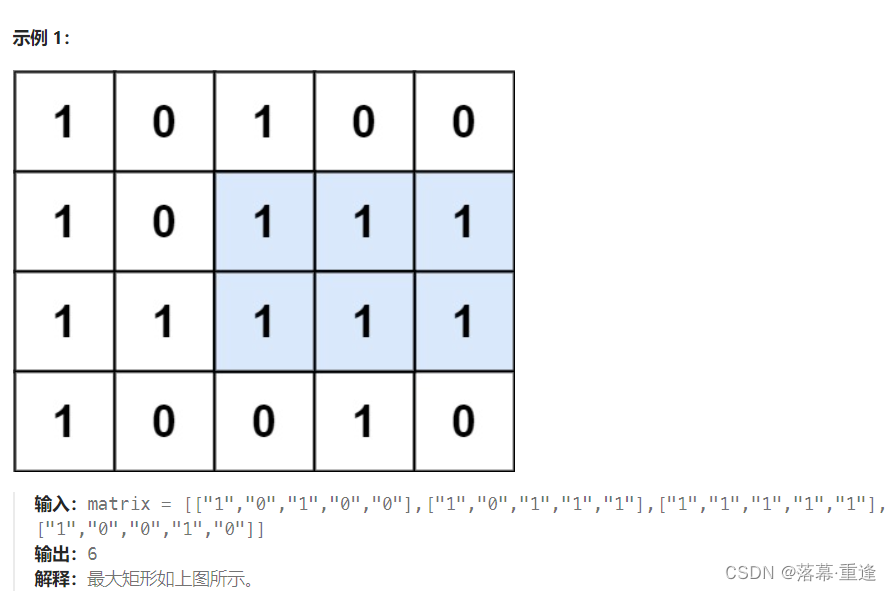
思路:
这道题与昨天的84. 柱状图中最大的矩形类似,只是在昨天的基础上多了几行,我们可以按行来判断。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {
int n = matrix.size();
int m = matrix[0].size();
if(n == 0) return 0;
vector<vector<int>> heights(n,vector<int>(m,0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {
heights[i][j] = (i == 0 ? 0: heights[i-1][j]) + 1;
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
vector<int> left(m,0),right(m,0);
stack<int> st;
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
while(!st.empty() && heights[i][st.top()] >= heights[i][j]){
st.pop();
}
left[j] = (st.empty()? -1:st.top());
st.push(j);
}
st = stack<int>();
for(int j = m-1; j >= 0; j--){
while(!st.empty() && heights[i][st.top()] >= heights[i][j]){
st.pop();
}
right[j] = (st.empty()? m:st.top());
st.push(j);
}
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
ans = max(ans, (right[j] - left[j] - 1) * heights[i][j]);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/LOVE_105/article/details/136119385
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
