Python--类中作用域
1、在面向对象编程中,主要的变量就是成员变量(属性)和局部变量
class Cat:
# 属性
name = None
age = None
# n1, n2, result为局部变量
def cal(self, n1, n2):
result = n1 + n2
print(f"result={result}")2、作用域的分类:属性作用域为整个类。即在整个类中,所有的成员方法都可以使用到属性。
class Cat:
# 属性
name = None
age = None
# n1, n2, result为局部变量
def cal(self, n1, n2):
result = n1 + n2
print(f"result={result}")
print(f"cal()使用属性name{self.name}")
def cry(self):
print(f"cry()使用属性name{self.name}")
def eat(self):
print(f"eat()使用属性name{self.name}")
cat = Cat()
cat.cal(10, 20)
cat.cry()
cat.eat()输出结果:
result=30
cal()使用属性nameNone
cry()使用属性nameNone
eat()使用属性nameNone3、局部变量:成员方法中定义的变量,作用域在它的方法中
若将局部变量用于其他的成员方法中,程序会报错,如下图所示。其中,result是cal方法中的局部变量,若将该变量用于cry成员方法中,则会报错。
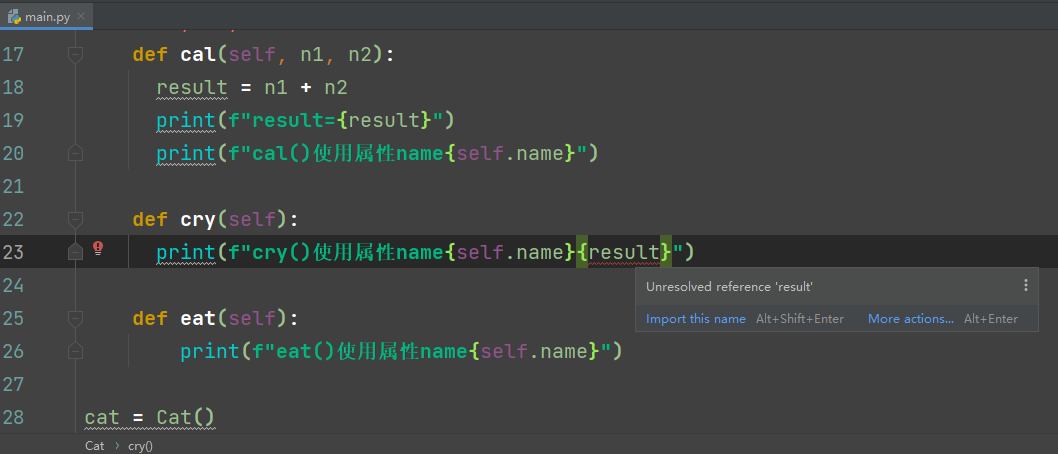
4、属性和局部变量可以重名,访问时带上self,表示访问的属性,没有带self,则是访问局部变量
class Cat:
# 属性
name = None
age = None
def hi(self):
name = "皮皮"
print(f"name={name}")
print(f"name={self.name}")
cat = Cat()
cat.hi()运行结果:
name=皮皮
name=None原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_48241022/article/details/136822787
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
