企业常用Linux文件命令相关知识+小案例
远程连接工具无法连接VMWARE:
如果发现连接工具有时连不上,ip存在,这时候我们查看网络编辑器,更多配置,看vnet8是不是10段,nat设置是否是正确的?
- 软件重启一下
- 虚机还原一下网络编辑器
查看文件属性
ls –li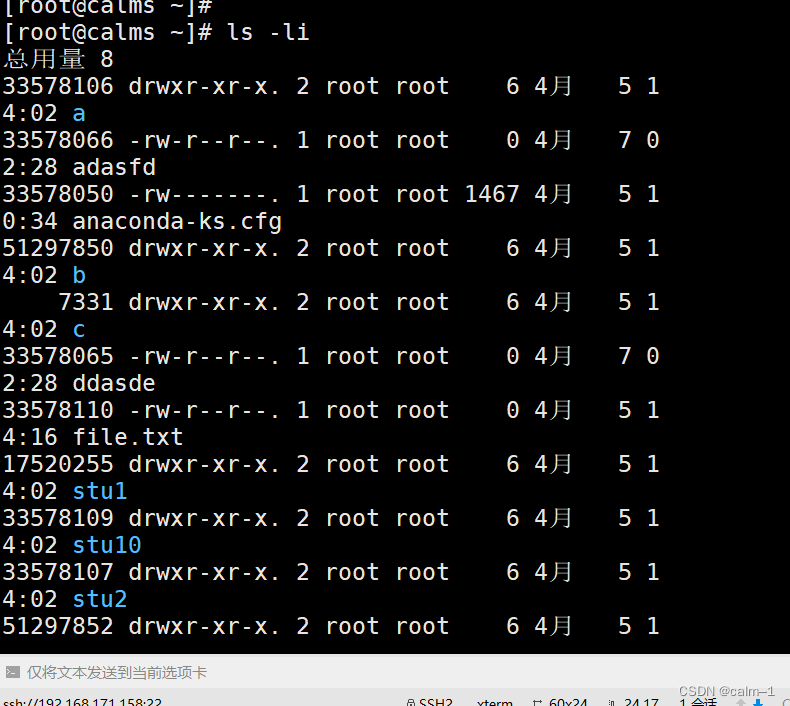
文件属性:大小,用户,组,权限,创建时间
查看etc目录下的hosts文件
stat /etc/hosts
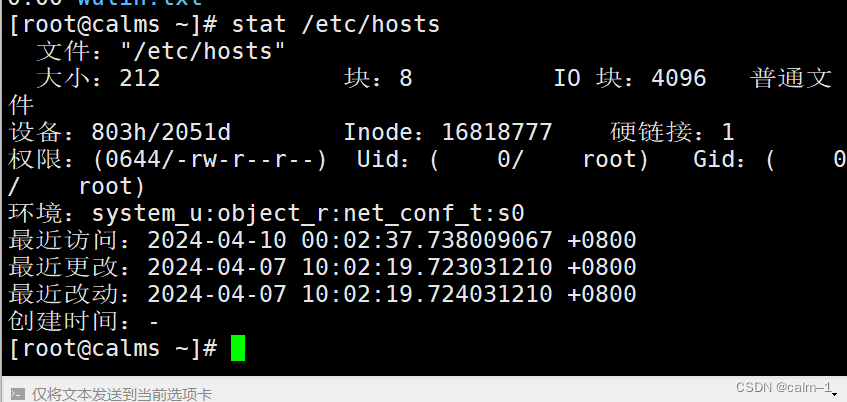
- 访问时间(access) 访问浏览,针对内容
- 最近更改 (modify) 最后更改时间,针对内容
- 最近改动(change) 状态改变,属性改变(touch时间戳)
[root@calms ~]# ls -li
总用量 8
33578106 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 4月 5 14:02 a
33578066 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 4月 7 02:28 adasfd
33578050 -rw-------. 1 root root 1467 4月 5 10:34 anaconda-ks.cfg
51297850 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 4月 5 14:02 b
7331 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 4月 5 14:02 c
- 第一列 索引节点,形态是数字 (33578106)
- 第二列 首字符代表文件类型 (-drwxr-xr-x.)
中间9个字符,文件权限
. 和selinux(高级安全组件)相关符号,开启有点,关闭没点
第三列 硬链接数 (2)
第四列,用户 (root)
第五列 用户组 (root)
第六列 文件大小(目录不是)(6)
第七到九列 日期加时间 (4月 5 14:02)
第十列 文件名 (anaconda-ks.cfg)
Linux文件类型
linux与window文件区别
windows文件类型:根据扩展名来的
Linux下面不根据扩展名确定类型,但是依然会有扩展名,为了给运维人员看清楚
系统不识别扩展名,那么系统怎么确定文件类型呢?
执行ls –li后第二列,首字符代表文件类型,一切皆为文件
– 普通文件(白色) d 目录(浅蓝色)l软链接文件 (在Windows上是快捷方式,指向程序真正的路径)
查看Linux文件快捷方式
ls –l /bin
Linux创建快捷方式(以etc目录下的hosts为例)
ln –s /etc/hosts /tmp/a.hosts
前面为源文件,后面是快捷方式
c 字符设备
ls /dev/ –l
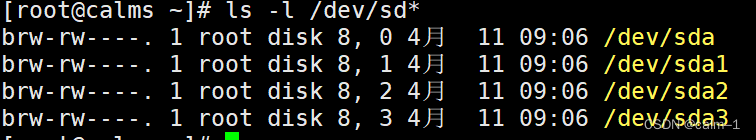
b 块设备
ls –l /dev/sd*(第一块分区第二块分区)
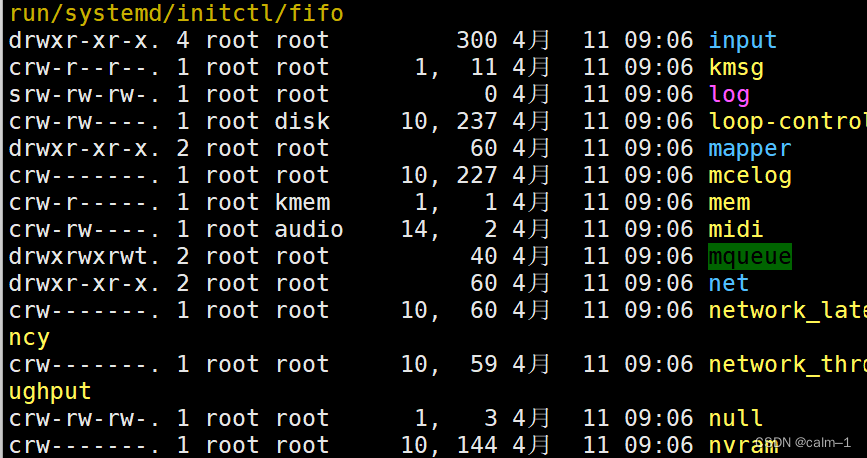
s socket文件(进程通信才会用到)
ls –l /dev/log
查看文件类型用file命令
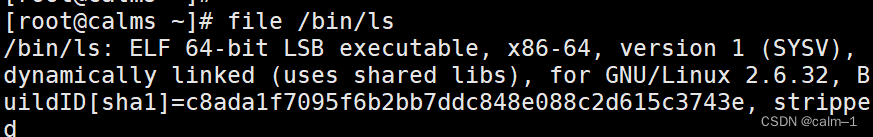
file /etc/hosts
file /bin/ls
WC命令查看行数,字符数
–l查看行数,–L查看字符数
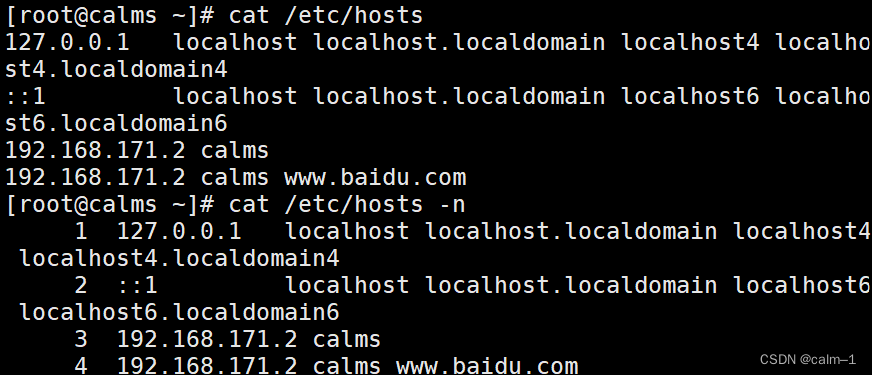
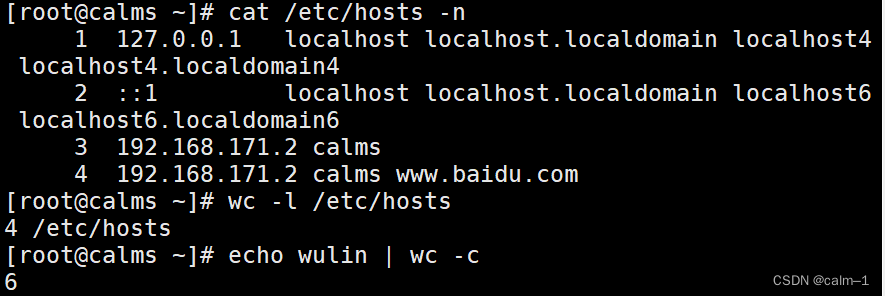
cat /etc/hosts主机名文件,看不到加–n
wc –l /etc/hosts就可以看到这个文件

echo wulin |wc –c查看行数(这个文件)
查找命令:
**which查看二进制所在路径(从path环境变量查找,打印echo $PATH
1.分隔符号为冒号:
2.路径都是命令)**
which ls

which cp

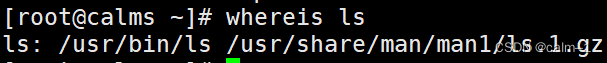
where 查看文件及文件帮助等路径
–b 查看二进制命令所在路径
whereis ls
locate命令查找文件及相关内容(内置数据库,通过updatedb)
先进行updatedb进行更新
需要安装**
yum install mlocate –y
**
find(面试笔试必考)命令
find 路径 选项 [参数] 选项2 [参数2]
按名字查找–name
find / –name “hosts”
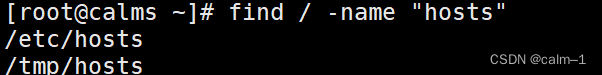
中间所有(按名字模糊查找,*表示所有)
find / –name “ho*ts”
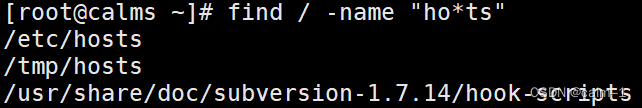
按类型查找
–type c
f d l c b s
在man find
通过/type,n继续搜/–type
-type c
File is of type c:
b block (buffered) special
c character (unbuffered) special
d directory
p named pipe (FIFO)
f regular file
l symbolic link; this is never true if
the -L option or the -follow option is
in effect, unless the symbolic link is
broken. If you want to search for sym‐
bolic links when -L is in effect, use
-xtype.
s socket
find /root –type d(查找目录)
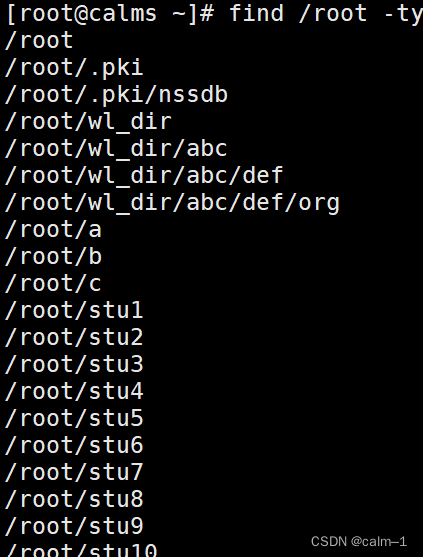
find /root –type f(查找文件)
组合查找:(find默认取交集(–a),并集(–o))
1. 查文件类型为文件,并且名字为hosts
find / –name “hosts” –a –type f
2. 并集:查找名为hosts,或者类型为d
find /–name “hosts”–o –type d –name “wulin”
3. 取反:!查找名字不是file1
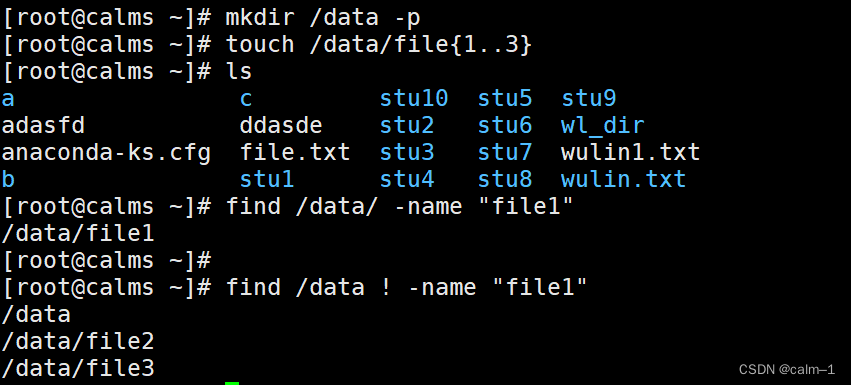
mkdir /data –p
touch /data/file{1..3}
find /data –name “file1”
find /data ! –name “file1”
按大小查找
–size +1M 大于1M
–size 1M 1m
–size –1M 小于1m
k,g
find /etc/ –size –1M
–mtime按修改时间查找
–atime按访问时间查找
–ctime按改变时间查找–mtime +7 七天以前的
–mtime 7 第7天的
–mtime –7最近七天
测试:
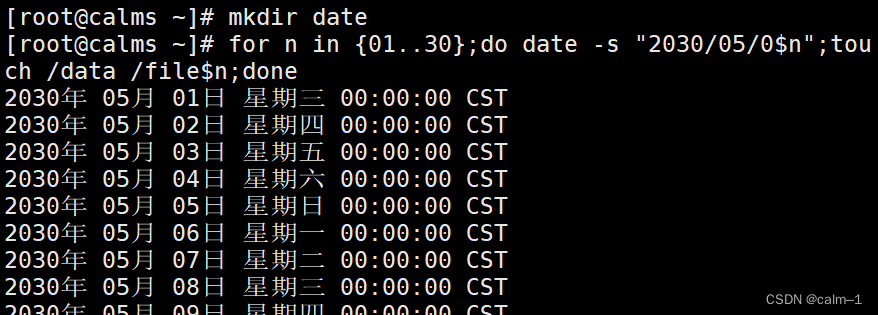
mkdir date
for n in {01…30} ;do date -s "2030/05/0 n " ; t o u c h / d a t a / f i l e n";touch /data /file n";touch/data/filen;done
每天创建一个文件,连续30天
ls
把时间改成了5月1号
pwd
date
find ./ -mtime -7
find . -mtime 7
find. -mmtime +7
.和./表示当前目录
…和…/都表示上级目录
不重要的
**–perm 按权限
–user按用户**
find /data –perm 755
chown wulin wulindir
find /data –user wulin
对找到的东西,进行处理
方法一 –exec执行动作
find / –name “wulin” –exec rm –f {} \;
find /data –name “file*”回车–mtime +7|sort –r
find /data –name “file1”–mtime +7 –exec rm –f{} \;
find 再查没了
ls 查看
原理:
rm –f file01
rm –f file02
rm -f file03
方法2
!for找到最近for命令
rm –f $(find /data –name “file”–type f –mtime +7)*
先查后面的,放到rm后删除
rm –f
find /data –name “file*”–type f –mtime +7反样引号也可以 特殊情况:
命令行:$(命令)或命令,拼路径与命令
方法3:xargs
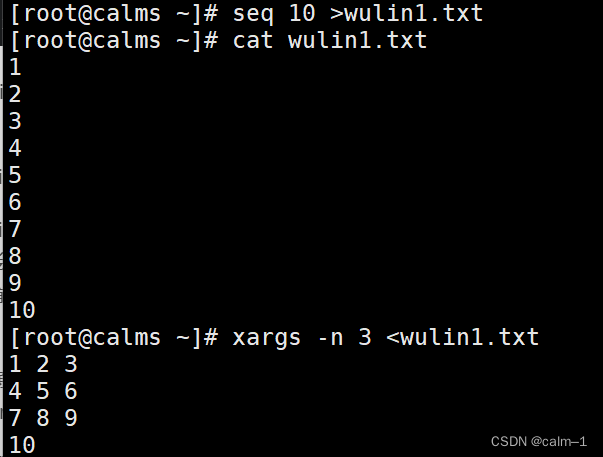
–n分组
seq 10 >wulin.txt
cat wulin.txt查看
xargs -n 3 <wulin.txt
-i
!for
find /data –name “file*”–mtime –7
find /data –name “file*”–mtime –7|xargs –i rm –f {}
会把前面内容放到大括号进行,不加–i不能执行这个过程,大括号接受前面结果
(不用加i加大括号,xargs默认放到后面,简写)
原理:(删除效率比上面更高)
题:查找/data大于20k,7天以内的文件,复制到/opt
cp /etc/services
ls
find /data –size +20k –mtime –7回车
find /data –size +20k –mtime –7|xargs cp {} /opt
ls /opt/
cp,源 目标 cp –t 目标 源
上面也可以这样操作
find /data –size +20k –mtime –7|xargs cp –t /tmp
ls /tmp/
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2302_78067597/article/details/137573045
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!