Netty ByteBuf 分配 | 池化复用 、直接内存
Netty ByteBuf 分配
本文主要内容关于 ByteBuf 分配介绍,为了更好的理解本文,我们可以带着几个问题思考
- 在IO密集型业务场景下,可能涉及大量ByteBuf分配,这时我们需
- 要考虑会不会产生OOM
- 会不会出现频繁GC
- 会不会内存泄露
根据上面的问题,没准你也设计出netty的分配方案,主要关键点
- 避免重复分配,你也许会想到 线程池类似的复用技术
- 解放GC,你会如何绕过GC , 于是想到直接内存,因为直接内存需要手动释放资源,因此你需要考虑潜在的内存泄露问题
ByteBufAllocator
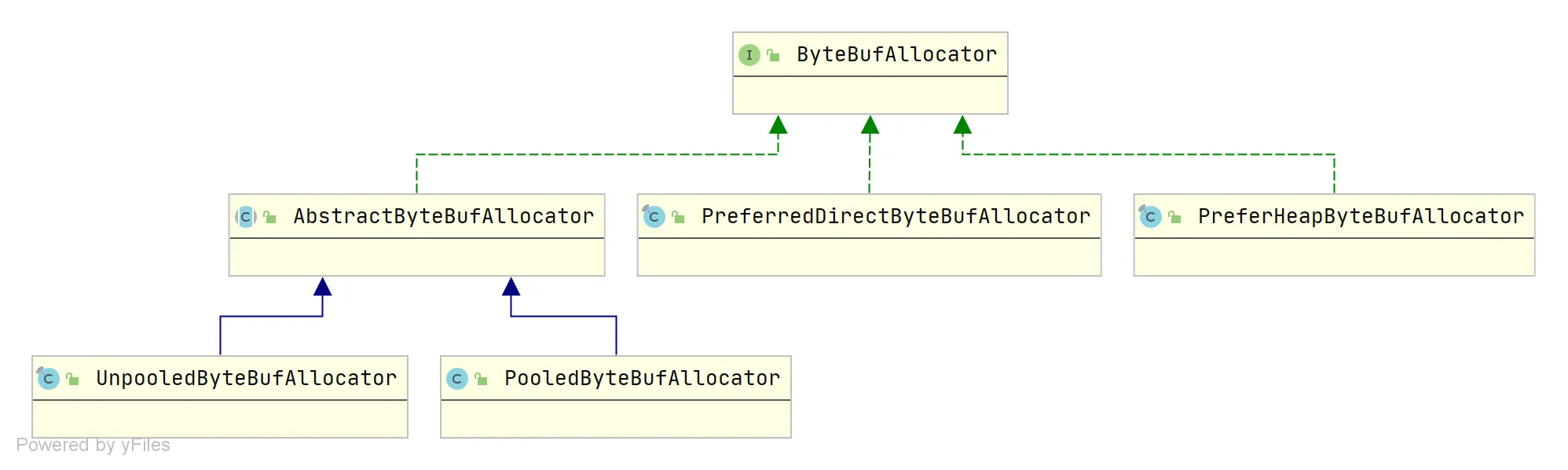
ByteBufAllocator 是 Netty用于分配 ByteBuf 对象 的接口,ByteBuf 分配方式主要有下面两个维度
-
在堆上分配还是使用直接内存
堆上分配,受JVM 垃圾回收管理,不需要手动释放资源。
直接内存不受JVM垃圾收集机制的管理,需要手动释放资源,在处理I/O操作时,直接内存可以提高性能,因为它减轻垃圾收集的压力
-
使用缓存池复用 和 不使用缓存池
池化技术我们平常接触的有数据库连接池、线程池等,它避免资源重复创建和销毁带来的代价,Netty 对象分配也支持用缓冲池复用。
ByteBufAllocator 分配方法介绍
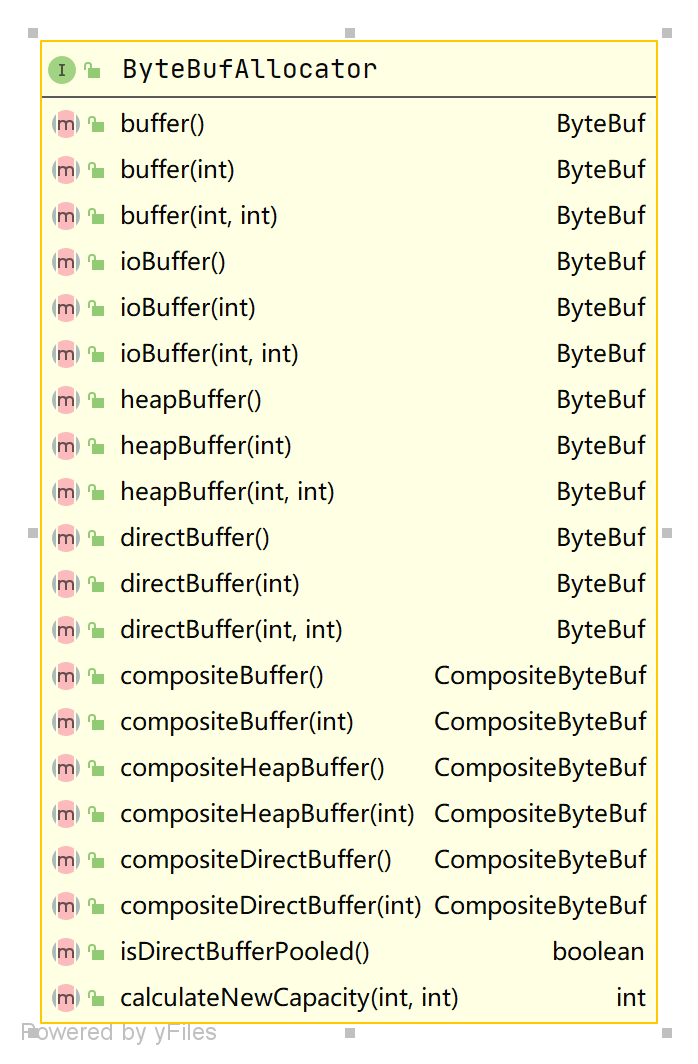
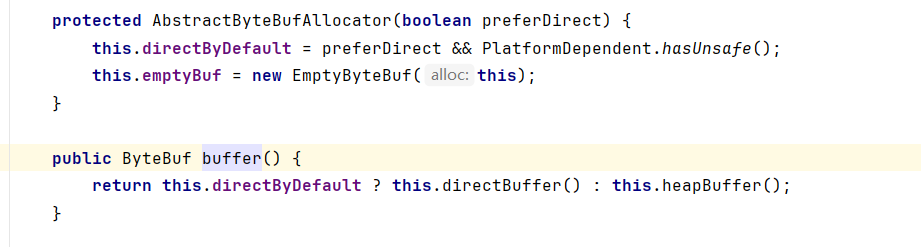
- buffer()
自动判断在堆上分配 or 直接内存上分配(判断依据是否支持Unsafe)
-
ioBuffer()
尽可能在对直接内存上分配,因为直接内存更适合用于IO,如果不支持则在堆上分配。
-
heapBuffer()
在堆上分配,受垃圾回收机制管理
- directBuffer()
使用直接内存分配
- CompositeByteBuf 分配
compositeBuffer()/compositeHeapBuffer()/compositeDirectBuffer()/ 用于CompositeByteBuf 分配
ByteBufAllocator 主要实现类
- PooledByteBufAllocator
使用缓冲池技术,通过重复利用已经分配的ByteBuf,能够有效地减少内存分配和释放的开销。
- UnpooledByteBufAllocator
它在每次分配ByteBuf时都会创建一个新的实例。
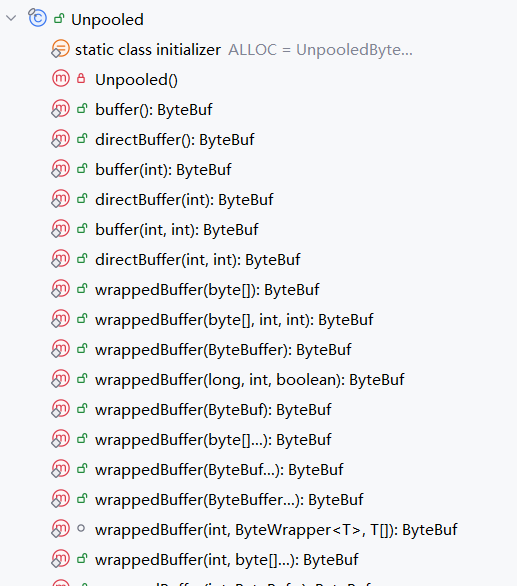
Unpooled
非池化分配也可以使用Unpooled 工具类,Unpooled 工具类其实调用UnpooledByteBufAllocator进行分配的,它提供了许多便捷的静态方法。
使用举例
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.buffer.PooledByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.buffer.UnpooledByteBufAllocator;
public class ByteBufAllocatorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用池化分配器
ByteBufAllocator pooledAllocator = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
// 分配一个堆内存 ByteBuf
ByteBuf heapBuf = pooledAllocator.heapBuffer(1024);
heapBuf.writeBytes("Hello, Heap Buffer!".getBytes());
System.out.println("Heap Buffer: " + heapBuf.toString(io.netty.util.CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
heapBuf.release();
// 分配一个直接内存 ByteBuf
ByteBuf directBuf = pooledAllocator.directBuffer(1024);
directBuf.writeBytes("Hello, Direct Buffer!".getBytes());
System.out.println("Direct Buffer: " + directBuf.toString(io.netty.util.CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
directBuf.release();
// 使用非池化分配器
ByteBufAllocator unpooledAllocator = UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
// 分配一个堆内存 ByteBuf
ByteBuf heapBufUnpooled = unpooledAllocator.heapBuffer(1024);
heapBufUnpooled.writeBytes("Hello, Unpooled Heap Buffer!".getBytes());
System.out.println("Unpooled Heap Buffer: " + heapBufUnpooled.toString(io.netty.util.CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
heapBufUnpooled.release();
// 分配一个直接内存 ByteBuf
ByteBuf directBufUnpooled = unpooledAllocator.directBuffer(1024);
directBufUnpooled.writeBytes("Hello, Unpooled Direct Buffer!".getBytes());
System.out.println("Unpooled Direct Buffer: " + directBufUnpooled.toString(io.netty.util.CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
directBufUnpooled.release();
ByteBuf unpooledBuffer = Unpooled.buffer(1024);
}
}
总结
要不要使用缓冲池,使用直接内存还是Java堆都要看具体业务,在IO场景Netty 内部优先使用直接内存;频繁的IO操作推荐使用缓冲池分配,避免内存频繁创建和销毁带来的开销。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/happycao123/article/details/143578967
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
