设备驱动与设备树匹配机制详解
往期内容
I2C子系统专栏:
- I2C(IIC)协议讲解-CSDN博客
- SMBus 协议详解-CSDN博客
- I2C相关结构体讲解:i2c_adapter、i2c_algorithm、i2c_msg-CSDN博客
- 内核提供的通用I2C设备驱动I2c-dev.c分析:注册篇
- 内核提供的通用I2C设备驱动I2C-dev.c分析:file_ops篇
总线和设备树专栏:
前言
根据前面所讲的IIC的相关知识,讲解了内核提供的通用的IIC设备驱动i2c-dev.c驱动程序。那么就可以尝试自己实现一个IIC设备驱动程序,使用的还是我们所熟知的万能平台总线驱动模型。
在platform bus平台总线详解-CSDN博客中也提到过platform的相关信息,而对于平台总线驱动模型的匹配规则只是略微提了下,为了能更好的去理解和编写驱动程序,本章就讲一下对于设备树和驱动程序它们是如何匹配起来,进而调用probe函数的。下一章节再将如何去编写IIC设备的驱动程序。
看之前建议看一下这两章:
- platform bus平台总线详解-CSDN博客 ---- 下文用A来指代
- bus中设备驱动的probe触发逻辑和device、driver的添加逻辑-CSDN博客 — 下文用B来指代
1.什么时候开始匹配
在A文章中末文有提到:
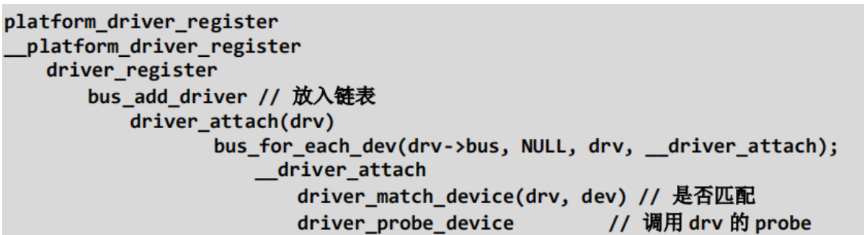
也就是在驱动程序调用platform_driver_register开始注册一个驱动程序的时候,就其内部就会掉去调用到driver_match_device函数去进行查看和platform_device是否匹配,而他一个有四种匹配方式,简单的如下:
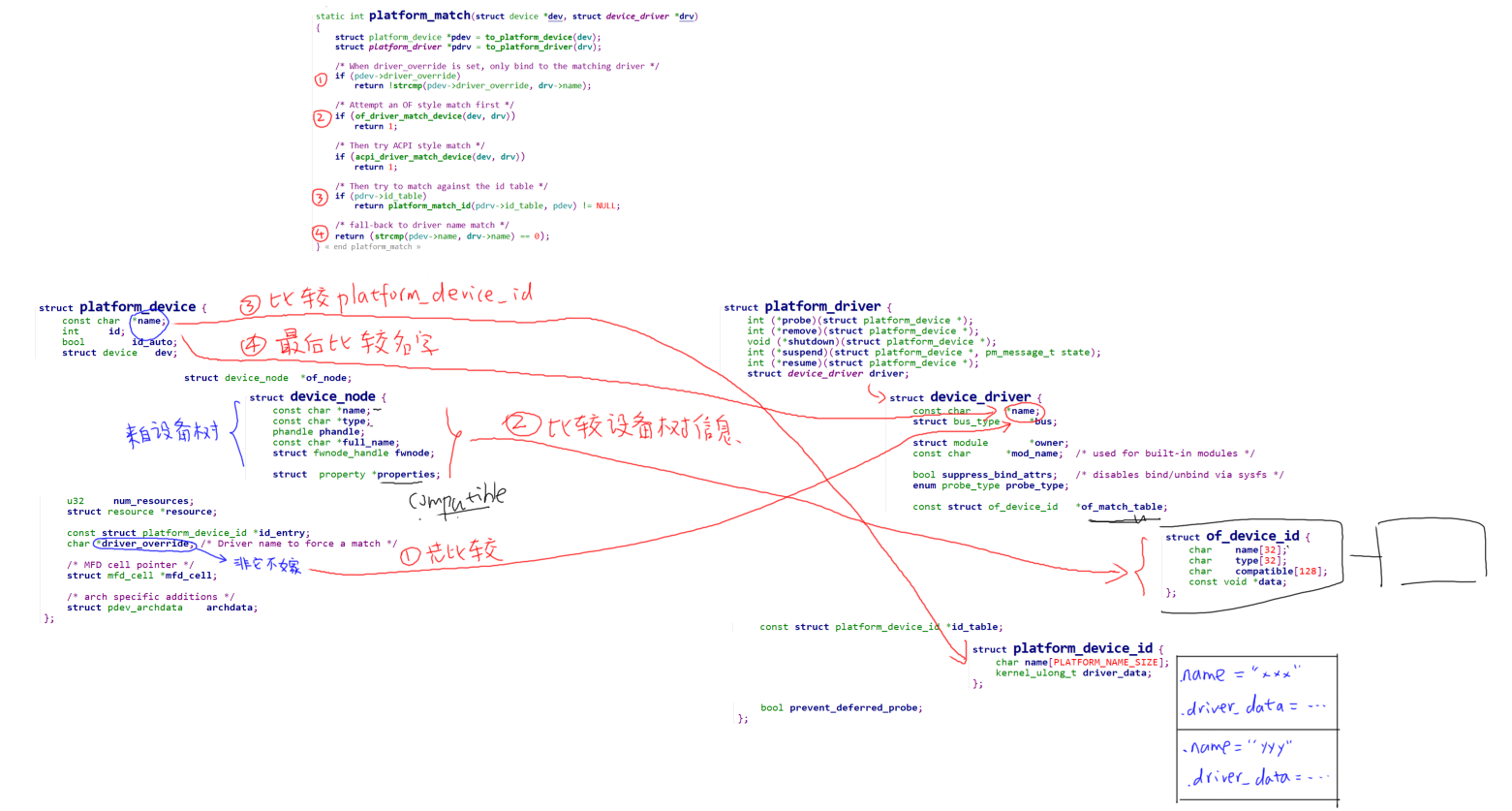
那么来看看driver_match_device函数:
static inline int driver_match_device(struct device_driver *drv,
struct device *dev)
{
return drv->bus->match ? drv->bus->match(dev, drv) : 1;
}
调用match函数,它是什么函数?可以在platform.c中去查看:
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {
.name= "platform",
.dev_groups= platform_dev_groups,
.match= platform_match, //这里
.uevent= platform_uevent,
.pm= &platform_dev_pm_ops,
};
static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);
/* When driver_override is set, only bind to the matching driver */
if (pdev->driver_override)
return !strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name);
/* Attempt an OF style match first */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try to match against the id table */
if (pdrv->id_table)
return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;
/* fall-back to driver name match */
return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);
}
四个if,就对应着四种匹配方式,这里来简单介绍一下
2.先来看下结构体
先来看一下需要用的结构体:
platform_device:
/*include/linux/platform_device.h*/
struct platform_device {
const char*name;
intid;
boolid_auto;
struct devicedev;
//dev中的成员struct device_node*of_node;
/*
struct device_node {
const char *name;
const char *type;
phandle phandle;
const char *full_name;
struct fwnode_handle fwnode;
structproperty *properties;
structproperty *deadprops;
structdevice_node *parent;
structdevice_node *child;
structdevice_node *sibling;
structkobject kobj;
unsigned long _flags;
void*data;
#if defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
const char *path_component_name;
unsigned int unique_id;
struct of_irq_controller *irq_trans;
#endif
};
*/
u32num_resources;
struct resource*resource;
const struct platform_device_id*id_entry;
char *driver_override; /* Driver name to force a match */
/* MFD cell pointer */
struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;
/* arch specific additions */
struct pdev_archdataarchdata;
};
platform_driver:
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
struct device_driver driver;
/*
struct device_driver {
const char*name;
struct bus_type*bus;
const struct of_device_id*of_match_table;
/*
struct of_device_id {
charname[32];
chartype[32];
charcompatible[128];
const void *data;
};
/*
int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
//........
};
*/
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
/*
struct platform_device_id {
char name[PLATFORM_NAME_SIZE];
kernel_ulong_t driver_data;
};
*/
bool prevent_deferred_probe;
};
具体的就不讲的,要是想弄清这些结构体各个成员的意思,可以点击以下文章查看:
驱动中的device和device_driver结构体-CSDN博客
device_node:解压设备树与生成内核设备节点树的流程概述-CSDN博客
这三篇都位于总线和设备树专栏
3.第一种匹配方式
那么接下来就可以看第一种匹配的方式:
static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);
/* When driver_override is set, only bind to the matching driver */
if (pdev->driver_override)
return !strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name);
看完上文的结构体后是不是可以一下子了然,platform_device-->char *driver_override和platform_driver-->struct device_driver driver-->name进行比较,driver_override在注册platform_device的时候是可以自己去指定的,它并不是来自设备树。而name???怎么来的呢
来看看一个驱动示例中的定义的内容:
static const struct of_device_id gpio_keys_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "gpio-keys", },
{ },
};
static struct platform_driver gpio_keys_device_driver = {
.probe= gpio_keys_probe,
.remove= gpio_keys_remove,
.driver= {
.name= "gpio-keys",
.pm= &gpio_keys_pm_ops,
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(gpio_keys_of_match),
}
};
static int __init gpio_keys_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&gpio_keys_device_driver);
}
是不是可以看到.driver={}中定义了name=“gpio-keys”,platform_device的driver_override就是和它进行比较的。
注意:.driver就是platform_driver的成员truct device_driver driver:
struct device_driver {
const char*name;
struct bus_type*bus;
int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
const struct of_device_id*of_match_table;
/*
struct of_device_id {
charname[32];
chartype[32];
charcompatible[128];
const void *data;
};
/*
//........
};
4.第二种匹配方式
4.1 小前言
先看下:device_node
struct device_node {
const char *name;
const char *type;
structdevice_node *parent;
structdevice_node *child;
structproperty *properties;
//其它略
};
来看一个设备树节点:
i2c1: i2c@400a0000 {
/* ... master properties skipped ... */
clock-frequency = <100000>;
flash@50 {
compatible = "atmel,24c256";
reg = <0x50>;
};
pca9532: gpio@60 {
compatible = "nxp,pca9532";
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <2>;
reg = <0x60>;
};
};
flash@50:flash是node name,50是unit address。那么flash就被赋值给device_node-->name。一下子明白了吧???至于怎么解析设备树填充device_node的,在之前对设备树进行解析章节中也有讲过了:device_node:解压设备树与生成内核设备节点树的流程概述-CSDN博客
那么接下来device_node-->parent就是父节点,也就是i2c1,没有子节点child。
device_node-->properties就是compatible = “atmel,24c256”;的atmel,24c256
差不多了,只要知道device_node–>properties对应compatible
platform_driver中的device_driver的struct of_device_id *matches:
sstruct device_driver {
const char*name;
struct bus_type*bus;
int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
const struct of_device_id*of_match_table;
/*
struct of_device_id {
charname[32];
chartype[32];
charcompatible[128];
const void *data;
};
/*
//........
};
name、type、compatible怎么定义的??
static const struct of_device_id gpio_keys_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "gpio-keys", },
{ },
};
static struct platform_driver gpio_keys_device_driver = {
.probe= gpio_keys_probe,
.remove= gpio_keys_remove,
.driver= {
.name= "gpio-keys",
.pm= &gpio_keys_pm_ops,
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(gpio_keys_of_match),
}
};
static int __init gpio_keys_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&gpio_keys_device_driver);
}
就是gpio_keys_device_driver中的.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(gpio_keys_of_match)
其中gpio_keys_of_match就定义了of_device_id,不用说了把。compatible就是gpio-keys
platform_driver和platform都讲到了其内部的compatible,是不是可以猜到了,没错,就是比较各自的compatible,这也是最常用的方法
4.2 正式讲解
当第一种匹配方式行不通的就是,就会调用第二种
static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);
//第一种行不通
//第二种
/* Attempt an OF style match first */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
进入看看:
static inline int of_driver_match_device(struct device *dev,
const struct device_driver *drv)
{
return of_match_device(drv->of_match_table, dev) != NULL;
}
继续进入:
const struct of_device_id *of_match_device(const struct of_device_id *matches,
const struct device *dev)
{
if ((!matches) || (!dev->of_node))
return NULL;
return of_match_node(matches, dev->of_node); //进入
}
就是platform_driver中的of_device_id *matches和platform_deivce中的device的struct device_node of_node进行比较。继续进入看:
\Linux-4.9.88\drivers\of\base.c
const struct of_device_id *of_match_node(const struct of_device_id *matches,
const struct device_node *node)
{
const struct of_device_id *match;
unsigned long flags;
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&devtree_lock, flags);
match = __of_match_node(matches, node); //继续进入看
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&devtree_lock, flags);
return match;
}
__of_match_node继续进入看:
static
const struct of_device_id *__of_match_node(const struct of_device_id *matches,
const struct device_node *node)
{
const struct of_device_id *best_match = NULL;
int score, best_score = 0;
if (!matches)
return NULL;
for (; matches->name[0] || matches->type[0] || matches->compatible[0]; matches++) {
score = __of_device_is_compatible(node, matches->compatible,
matches->type, matches->name);
if (score > best_score) {
best_match = matches;
best_score = score;
}
}
return best_match;
}
其中__of_device_is_compatible,注意一下传进来的参数:
\Linux-4.9.88\drivers\of\base.c:
static int __of_device_is_compatible(const struct device_node *device,
const char *compat, const char *type, const char *name)
{
struct property *prop;
const char *cp;
int index = 0, score = 0;
/* Compatible match has highest priority */
if (compat && compat[0]) {
prop = __of_find_property(device, "compatible", NULL); //这里--(1)
for (cp = of_prop_next_string(prop, NULL); cp;
cp = of_prop_next_string(prop, cp), index++) {
if (of_compat_cmp(cp, compat, strlen(compat)) == 0) {
score = INT_MAX/2 - (index << 2);
break;
}
}
if (!score)
return 0;
}
/* Matching type is better than matching name */
if (type && type[0]) {
if (!device->type || of_node_cmp(type, device->type))
return 0;
score += 2;
}
/* Matching name is a bit better than not */
if (name && name[0]) {
if (!device->name || of_node_cmp(name, device->name))
return 0;
score++;
}
return score;
}
(1)其中prop = __of_find_property(device, "compatible", NULL);就是去获取到const struct device_node *device中关于compatible的属性,也就是其成员property
至于platform_driver的compatible,已经通过参数传进来的,也就是 const char *compat,对应of_device_id *matches的compatible
5.结
至于第三、四种方法就不讲啦,看下图中的3、4点就行了,感兴趣的也可以自己去深究一下:

只要四种方式中有一种成功匹配了,那么就会去调用probe函数。
了解之后,有助于我们更好的去编写驱动程序,下节讲解IIC设备驱动框架编写更容易看懂。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/caiji0169/article/details/142994180
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
