嵌入式学习-C嘎嘎-Day03
嵌入式学习-C嘎嘎-Day03
1. 友元 friend
1.1 概念
定义:
类实现了数据的隐藏与封装,类的成员变量一般定义为私有成员,仅能通过类的成员函数才能读写。如果成员变量定义为公共的,则又破坏了封装性。但是某些情况下,需要频繁读写类的成员变量,特别是在对某些成员函数多次调用时,由于参数传递、类型检查和安全性检查等都需要时间开销,而影响程序的运行效率。
友元是一种定义在类外部的普通函数,但他需要在类体内进行说明,为了和该类的成员函数加以区别,在说明时前面加以关键字friend。友元不是成员函数,但是他能够访问类中的私有成员。
作用:
在于提高程序的运行效率,但是,他破坏了类的封装性和隐藏性,使得非成员函数能够访问类的私有成员。导致程序维护性变差,因此使用友元要慎用。
友元主要的应用场景是运算符重载。
用法:
- 友元函数
- 友元类
- 友元成员函数
1.2 友元函数
友元函数是一种在类内说明,但本身属于类外的函数,可以访问类内所有成员。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Girl
{
private:
int age;
public:
Girl(int age):age(age){}
int get_age() const
{
return 18;
}
// 友元关系说明
friend void get_real_age(Girl& g);
};
void get_real_age(Girl& g)
{
// 获取私有成员的数值并修改
cout << "真实年龄:" << g.age << endl;
g.age = 18;
cout << "修改后的真实年龄:" << g.age << endl;
}
int main()
{
Girl g(40);
cout << g.get_age() << endl; // 18
get_real_age(g);
}需要注意的是:
- 友元函数没有this指针
- 友元函数的类内说明可以在任何部分,不受权限的影响
- 一个函数可以是多个类的友元函数,只需要分别在个各类中说明
1.3 友元类
当一个类B成为了另一个类A的友元类时,类A的所有成员就可以被类B访问了。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
private:
int value = 1;
// 友元关系说明
friend class B;
};
class B
{
public:
void access(A& a)
{
cout << this << endl;
// cout << this->value << endl; 错误
// 读取和修改a的private成员
cout << a.value++ << endl;
cout << a.value << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
A a;
B b;
b.access(a);
}需要注意的是:
- 友元关系不能被继承
- 友元关系不具有交换性
- 友元关系不具有传递性
1.4 友元成员函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 3. 上一步用到了A类,补充A声明
class A;
// 2. 上一步中用到了B类,补充B类
class B
{
public:
void access(A& a);
};
class A
{
private:
int value = 1;
// 1. 说明友元关系
friend void B::access(A& a);
};
// 4. 补充友元成员函数的内容
void B::access(A &a)
{
cout << a.value++ << endl;
cout << a.value << endl;
}
int main()
{
A a;
B b;
b.access(a);
}
2. 运算符重载
2.1 概念
函数可以重载,在C++中运算符也可以重载,运算符默认的操作类型只能是基本数据类型,但是对于很多用户自定义类型,也需要类似的运算操作,此时可以重载运算符,赋予这些运算符新的功能,执行对于自定义类型的运算操作。
可以被重载的运算符:
算术运算符:+、-、*、/、%、++、--
位操作运算符:&、|、~、^(位异或)、<<(左移)、>>(右移)
逻辑运算符:!、&&、||
比较运算符:<、>、>=、<=、==、!=
赋值运算符:=、+=、-=、*=、/=、%=、&=、|=、^=、<<=、>>=
其他运算符:[]、()、->、,、new、delete、new[]、delete[]
不被重载的运算符:
成员运算符“.”、指针运算符“*”、三目运算符“? :”、sizeof、作用域“::”
通常有两种运算符重载的方式(部分运算符只支持一种):
- 友元函数运算符重载
- 成员函数运算符重载
可以把运算符重载看做是一种特殊的函数重载,运算符是一种特殊的函数。
2.2 友元函数运算符重载
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
* @brief The Integer class 整数类
*/
class Integer
{
private:
int value;
public:
Integer(int v):value(v){}
int get_value() const
{
return value;
}
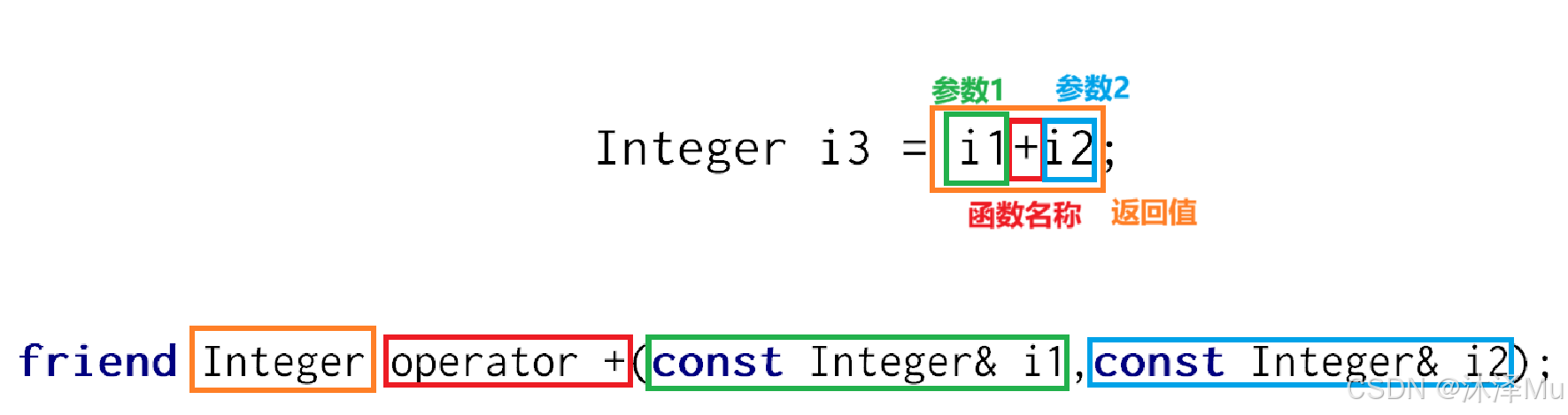
friend Integer operator +(const Integer& i1,const Integer& i2);
friend Integer operator ++(Integer& i); // 前置
friend Integer operator ++(Integer& i,int); // 后置
};
Integer operator +(const Integer& i1,const Integer& i2)
{
return i1.value + i2.value;
}
Integer operator ++(Integer& i)
{
return ++i.value;
}
Integer operator ++(Integer& i,int)
{
return i.value++;
}
int main() {
Integer i1(1);
Integer i2(2);
Integer i3 = i1+i2;
cout << i3.get_value() << endl; // 3
cout << (++i3).get_value() << endl; // 4
cout << (i3++).get_value() << endl; // 4
cout << i3.get_value() << endl; // 5
return 0;
}
2.3 成员函数运算符重载
成员函数运算符重载与友元函数运算符重载的最大区别是,成员函数运算符重载的输入参数比友元函数运算符重载少一个,因为友元函数的第一个参数在成员函数中使用this指针表示。

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
* @brief The Integer class 整数类
*/
class Integer
{
private:
int value;
public:
Integer(int v):value(v){}
int get_value() const
{
return value;
}
Integer operator +(const Integer& i);
Integer operator ++(); // 前置
Integer operator ++(int); // 后置
};
Integer Integer::operator +(const Integer& i)
{
// this指针可以不写,因为只要不重名编译器自动添加
return this->value + i.value;
}
Integer Integer::operator ++()
{
return ++this->value;
}
Integer Integer::operator ++(int)
{
return this->value++;
}
int main() {
Integer i1(1);
Integer i2(2);
Integer i3 = i1+i2;
cout << i3.get_value() << endl; // 3
cout << (++i3).get_value() << endl; // 4
cout << (i3++).get_value() << endl; // 4
cout << i3.get_value() << endl; // 5
return 0;
}
2.4 特殊运算符重载
2.4.1 赋值运算符重载
如果程序员不手动在类中编写赋值运算符重载函数,编译器会为这个类自动添加一个默认的赋值运算符重载函数,以便于实现同类型对象的赋值操作。
赋值运算符重载函数只能通过成员函数实现,因为需要this指针。
需要注意的是,如果出现了浅拷贝,也要修改赋值运算符重载函数的逻辑。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
* @brief The Integer class 整数类
*/
class Integer
{
private:
int value;
public:
Integer(int v):value(v){}
int get_value() const
{
return value;
}
// 默认的赋值运算符重载函数
Integer& operator =(const Integer& i)
{
this->value = i.value;
return *this;
}
};
int main() {
Integer i1(1);
Integer i2(2);
i1 = i2; // 赋值运算
cout << i1.get_value() << endl; // 2
return 0;
}
【思考】截止到目前,如果一个成员手写了一个空类,编译器会自动添加哪些内容:
- 构造函数
- 析构函数
- 拷贝构造函数
- 赋值运算符重载函数
2.4.2 类型转换运算符重载
类型转换运算符重载函数也必须使用成员函数重载,格式比较特殊
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
* @brief The Integer class 整数类
*/
class Integer
{
private:
int value;
public:
Integer(int v):value(v){}
int get_value() const
{
return value;
}
// 类型转换函数
operator int()
{
return value;
}
};
int main() {
// int → Integer
Integer i1 = 1; // 编译器自动调用构造函数
cout << i1.get_value() << endl; // 1
// Integer → int
int i2 = i1;
cout << i2 << endl; // 1
return 0;
}
2.5 注意事项
- 运算符重载只能限制在C++已有的范围内,不能创建的新的运算符。
- 运算符重载不能改变运算符的优先级和结合性。
- 运算符重载不能改变运算符的操作数和语法结构。
- 运算符重载的操作数一定包含自定义类型。
- 运算符重载的功能应该与原有功能相似,避免滥用。
- 运算符重载不能设置参数默认值。
- 通常单目运算符优先考虑成员函数,双目运算符优先考虑友元函数。
3. 字符串类型 string
之前对string的学习比较基础,实际上string有诸多字符串处理函数。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s; // 创建一个空字符串
cout << s.empty() << endl; // 判断内容是否为空
// 构造函数,参数const char*
string s1 = "Thursday";
string s2("Thursday");
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
// 拷贝构造函数
string s3 = s1;
string s4(s3);
cout << s3 << " " << s4 << endl;
// 参数1:const char* 原字符串
// 参数2:保留前几个字符
string s5("ABCDEFG",2);
cout << s5 << endl; // AB
s = "ABCDEFG";
// 参数1:string 原字符串
// 参数2:不保留前几个字符
string s6(s,2);
cout << s6 << endl; // CDEFG
// 参数1:数量
// 参数2:字符元素
string s7(5,'A');
cout << s7 << endl; // AAAAA
swap(s6,s7); // 交换
cout << s6 << endl;
cout << s7 << endl;
// 连接
cout << s6 + s7 << endl;
// 尾插单字符
s6.push_back('B');
cout << s6 << endl;
// 尾插string,支持链式调用
s6.append("CC").append("DDD");
cout << s6 << endl;
// 在第二个位置插入内容"111"
s6.insert(1,"111");
cout << s6 << endl;
// 参数1:替换的起始位置
// 参数2:替换的字符数
// 参数3:替换的新内容
s6.replace(0,3,"*****");
cout << s6 << endl;
s6.pop_back(); // 删除最后一个字符
cout << s6 << endl;
s6 = "1234567890";
// 参数1:删除的起始位置
// 参数2:删除的字符数
s6.erase(3,4);
cout << s6 << endl;
s6.clear(); // 清空
cout << s6.size() << endl; // 0
s6 = "ABCDEFGHIJK";
char c[20];
// 参数1:拷贝的目标
// 参数2:拷贝的字符数量
// 参数3:拷贝的起始位置
s6.copy(c,5,2);
cout << c << endl;
// C++ string→C string
strcpy(c,s6.c_str());
cout << c << endl;
return 0;
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Xiaomo1536/article/details/143806605
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
