链表(单向不带头非循环)
声明
链表题考的都是单向不带头非循环,所以在本专栏中只介绍这一种结构,实际中链表的结构非常多样,组合起来就有8种链表结构。
链表的实现
创建一个链表
注意:此处简单粗暴创建的链表只是为了初学者好上手。
public class MySingleLinkedList {
static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public void createList() {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(56);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;
this.head = node1;
}
}
核心代码
1、前一个节点与后一个节点如何关联起来
node1.next=node2;
2、什么时候遍历完所有的节点
head==null
3、怎么从前一个节点走到后一个节点
head=head.next;
打印一个链表
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}获取链表的长度
public int size() {
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}头插
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = head;
head = node;
}尾插
1、先要判断是否为空链表,不然会有空指针异常。
2、如果是空链表则将节点赋给头节点,还应当用return语句结束。
3、再找到链表的尾巴节点cur.next==null
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}在任意位置插入
1、先要判断插入位置是否合法
2、在头节点插入-头插(index==0),在尾节点插入-尾插(index==size)
3、找到要插入位置的前一个结点,只需要cur走index-1步
4、连接的时候注意先绑后头
public class IndexNotLegalException extends RuntimeException {
public IndexNotLegalException() {
}
public IndexNotLegalException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
//第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
try {
checkIndex(index);
} catch (IndexNotLegalException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findIndexSubOne(index);
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
private void checkIndex(int index) throws IndexNotLegalException {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexNotLegalException("index不合法!");
}
}
private ListNode findIndexSubOne(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}查找是否包含某个值
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}删除第一次为某值的节点
1、如果是空链表则不可删,直接return
2、如果删掉的是头节点,head=head.next;
3、找到所要删除节点的前一个cur.next.val==key
public void remove(int key) {
if (head == null)
return;
if (head.val == key) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == key) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
return;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
}删除所有为某值的节点
1、同样,头节点不可删
2、cur代表当前需要删除的节点,prev代表当前需要删除节点cur的前驱节点
3、最后还要处理头节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if (head == null) return;
ListNode prev = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
} else {
prev = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (head.val == key)
head = head.next;
}清空链表
public void clear() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curN = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = curN;
}
head = null;
}链表的使用
1. LinkedList实现了List接口
2. LinkedList的底层使用了双向链表 3. LinkedList没有实现RandomAccess接口,因此LinkedList不支持随机访问 4. LinkedList的任意位置插入和删除元素时效率比较高5. LinkedList比较适合任意位置插入的场景
LinkedList的构造
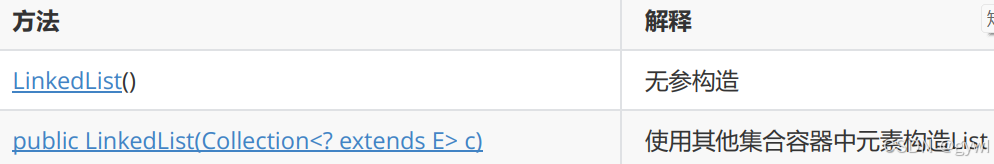
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> list2 = new LinkedList<>();
list2.add(1);
list2.add(2);
List<Integer> ret1 = new LinkedList<>(list2);
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList=new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> ret2=new LinkedList<>(arrayList);
}
}
LinkedList的其他常用方法介绍
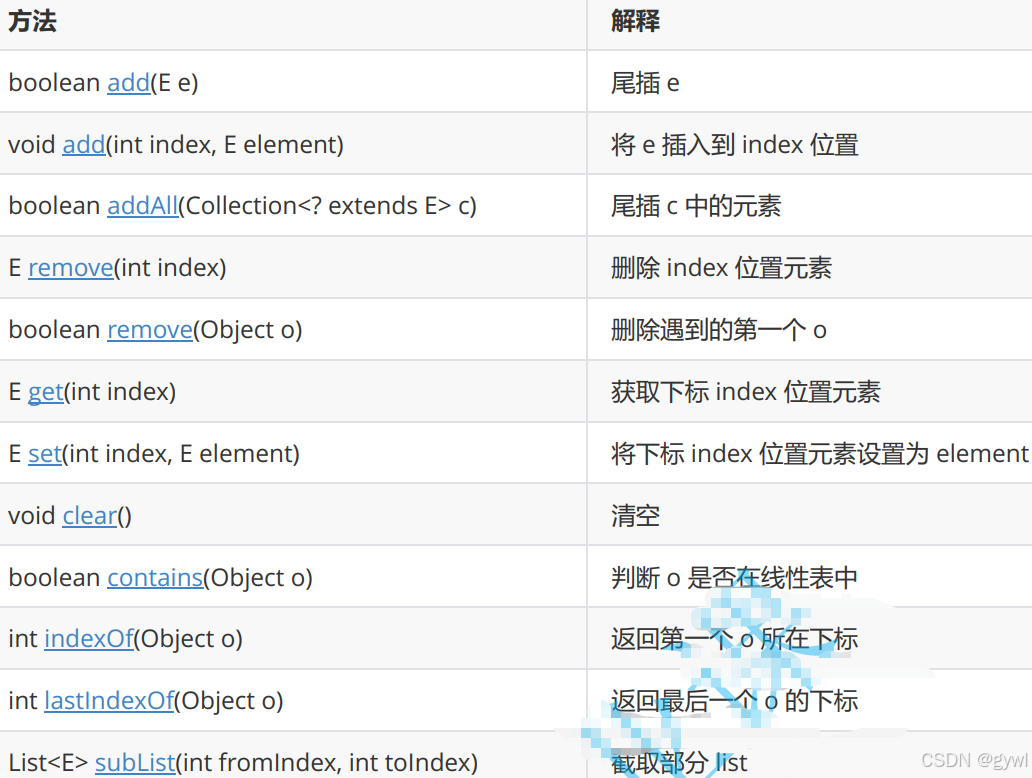
LinkedList的遍历
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
System.out.println(list.size());
// foreach遍历
for (int e : list) {
System.out.print(e + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size());
while (rit.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.print(rit.previous() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
ArrayList和LinkedList的区别

原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_80141037/article/details/142422175
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
