1.7 JS性能优化
从输入url到页面加载完成都做了些什么
输入
URL - 资源定位符
http://www.zhaowa.com - http 协议
域名解析
https://www.zhaowa.com => ip
1. 切HOST? => 浏览器缓存映射、系统、路由、运营商、根服务器
2. 实际的静态文件存放?
大流量 => 多个IP地址、LB(负载均衡)、云服务
访问延迟 => CDN - content delivery netWork
缓存 => 各级缓存 => 浏览器缓存 - 强缓存(expire、cache-control)、协商缓存(last-modify、etag)
http 与 TCP
1. http - 应用层 < = > TCP - 传输层
2. 关联 - http基于TCP实现连接 < = > UDP
=> 握手 & 挥手 (传输速率上较UDP低) => http请求建立、发送、断开

优化点:1.0 1.1 2.0
=> 1.0 vs 1.1 —— 复用连接(持久连接 - connection: keep-alive)、队头拦截(pipelining)
=> 1.1 vs 2.0 —— 头部空间(协议层消除头部重复部分)、格式(二进制优化)、多路复用(复用通路,无并发限制)
https://www.zhaowa.com - https协议
追问:http 和 https
1. https = http + SSL(TLS) => 位于TCP协议与应用层协议之间
2. 实现原理 - 原理图
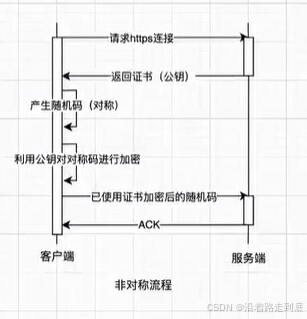
优化 —— 安全性建立导致网络请求加载时间延长
=> 合并请求 长连接
节流 防抖
* 编译 & 渲染
打包优化 => 压缩、分割、按需加载、异步加载 => 工程化
渲染 => 浏览器原理
手写并发控制
分析:
输入: max - 最大的同时处理量
存储:reqpool - 并发池
思路:执行 => 回调 => 塞入 —— 池
class LimitPromise {
constructor(max) {
// 异步“并发”上限
this._max = max || 6
// 当前正在执行的任务数量
this._count = 0
// 等待执行的任务队列
this._taskQueue = []
}
run(caller) {
// 主入口
// 输入:外部要添加的请求
// 输出:返回队列处理的promise
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 创建处理任务
const task = this._createTask(caller, resolve, reject)
// 当前的队列任务是否达到上限
if (this._count >= this._max) {
this._taskQueue.push(task)
} else {
task()
}
})
}
_createTask(caller, resolve, reject) {
return () => {
caller().then(res => {
resolve(res)
}).catch(err => {
reject(err)
}).finally(() => {
this._count--
if (this._taskQueue.length) {
const task = this._taskQueue.shift()
task()
}
})
this._count++
}
}
static instance = null
static getInstance(max) {
if (!LimitPromise.instance) {
LimitPromise.instance = new LimitPromise(max)
}
return LimitPromise.instance
}
}原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_38066007/article/details/143745795
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
