C++ 笛卡尔树
一、性质
-
堆性质: 笛卡尔树是一种满足堆性质的树。每个节点包含两个值:键值(key)和优先级值(priority)。在笛卡尔树中,根节点的优先级值最大,且每个节点的优先级值大于其子节点的优先级值。
-
中序遍历: 笛卡尔树的中序遍历结果与原始数组的顺序一致。这意味着,如果你将笛卡尔树按中序遍历的顺序输出,就会得到原始数组的顺序。
-
唯一性: 对于给定的键值数组,存在唯一的笛卡尔树与之对应。
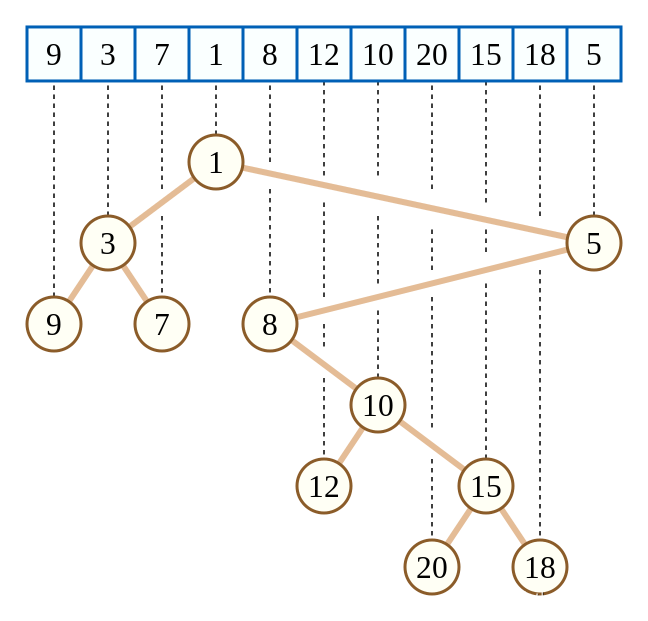 (备注:图源于 维基百科)
(备注:图源于 维基百科)
二、构建笛卡尔树
- 笛卡尔树通常是通过一个数组构建的,数组中的元素按照顺序表示树中节点的键值,另一个数组表示节点的优先级值。
- 通过递归的方式构建笛卡尔树:在给定数组范围内,找到优先级值最大的元素作为根节点,然后递归构建左子树和右子树。
三、应用
-
最小公共祖先(LCA): 通过构建笛卡尔树,可以在O(1)时间内找到任意两个节点的最小公共祖先。
-
区间最小值/最大值查询: 通过构建笛卡尔树,可以在O(log n)时间内查询给定区间的最小值或最大值。
四、源码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
int priority;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int k, int p) : key(k), priority(p), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};
Node* buildCartesianTree(vector<int>& arr, vector<int>& priority, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return nullptr;
}
int maxIndex = start;
for (int i = start + 1; i <= end; i++) {
if (priority[i] > priority[maxIndex]) {
maxIndex = i;
}
}
Node* root = new Node(arr[maxIndex], priority[maxIndex]);
root->left = buildCartesianTree(arr, priority, start, maxIndex - 1);
root->right = buildCartesianTree(arr, priority, maxIndex + 1, end);
return root;
}
void inOrderTraversal(Node* root) {
if (root) {
inOrderTraversal(root->left);
cout << "(" << root->key << ", " << root->priority << ") ";
inOrderTraversal(root->right);
}
}
int main() {
vector<int> arr = { 9,3,7,1,8,12,10,20,15,18,5 };
vector<int> priority = { 8,10,8,11,8,4,5,2,4,2,10 };
Node* root = buildCartesianTree(arr, priority, 0, arr.size() - 1);
cout << "Inorder traversal of Cartesian Tree: ";
inOrderTraversal(root);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Doctor__Chen/article/details/136791742
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
