pytorch Neural Networks学习笔记
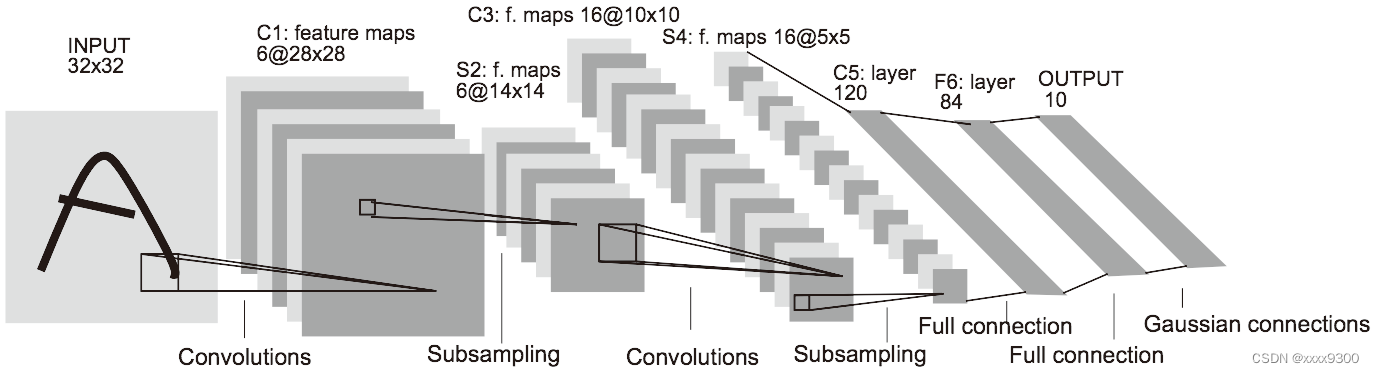
(1)输入图像,1×32×32,通道数1,高32,宽32
(2)卷积层1,滤波器的shape为6×1×5×5,滤波器个数6,通道数1,高5,宽5。卷积层1的输出为6×28×28。
(3)relu层,输出和输入的shape相同
(4)池化层,滤波器的大小为2×2,stride为2×2,输出为6×14×14。
(5)卷积层2,滤波器的shape为16×6×5×5,滤波器个数16,通道数6,高5,宽5。卷积层2的输出为16×10×10。
(6)relu层,输出和输入的shape相同
(7)池化层,滤波器的大小为2×2,stride为2×2,输出为16×5×5。reshape为1×400后输入到全连接层1。
(8)全连接层1,权重的shape为400×120,输出为1×120
(9)relu层,输出和输入的shape相同
(10)全连接层2,权重的shape为120×84,输出为1×84
(11)relu层,输出和输入的shape相同
(12)全连接层3,权重的shape为84×10,输出为1×10
这个网络的结构如下:
input -> conv2d -> relu -> maxpool2d -> conv2d -> relu -> maxpool2d
-> flatten -> linear -> relu -> linear -> relu -> linear
-> MSELoss
-> loss
Let’s define this network:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# 1 input image channel, 6 output channels, 5x5 square convolution
# kernel
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
# an affine operation: y = Wx + b
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120) # 5*5 from image dimension
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# Max pooling over a (2, 2) window
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
# If the size is a square, you can specify with a single number
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1) # flatten all dimensions except the batch dimension
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
net = Net()
print(net)
Net(
(conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(fc1): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=120, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True)
(fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
这里写代码测试一下flatten函数的用法:
>>> data=[[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]], [[7,8,9],[10,11,12]]]
>>> x_data = torch.tensor(data)
>>> print(f"x_data: \n {x_data} \n")
x_data:
tensor([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]],
[[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]]])
>>> print(f"Shape of x_data: {x_data.shape}")
Shape of x_data: torch.Size([2, 2, 3])
>>> x_data = torch.flatten(x_data, 1)
>>> print(f"x_data: \n {x_data} \n")
x_data:
tensor([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[ 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]])
>>> print(f"Shape of x_data: {x_data.shape}")
Shape of x_data: torch.Size([2, 6])
该网络有2个卷积层和3个全连接层,有5个权重参数和5个偏置参数,共10个参数。
params = list(net.parameters())
print(len(params))
for i in range(len(params)):
print(params[i].size())
以上代码打印了每个参数的shape,如下:
10
torch.Size([6, 1, 5, 5])
torch.Size([6])
torch.Size([16, 6, 5, 5])
torch.Size([16])
torch.Size([120, 400])
torch.Size([120])
torch.Size([84, 120])
torch.Size([84])
torch.Size([10, 84])
torch.Size([10])
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21603315/article/details/137722622
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
