rocketmq架构解析以及rabbimq对比
对比rabbitmq
为了偷懒,拿了张本人过往rabbimq老图,多了点没必要的connection细节
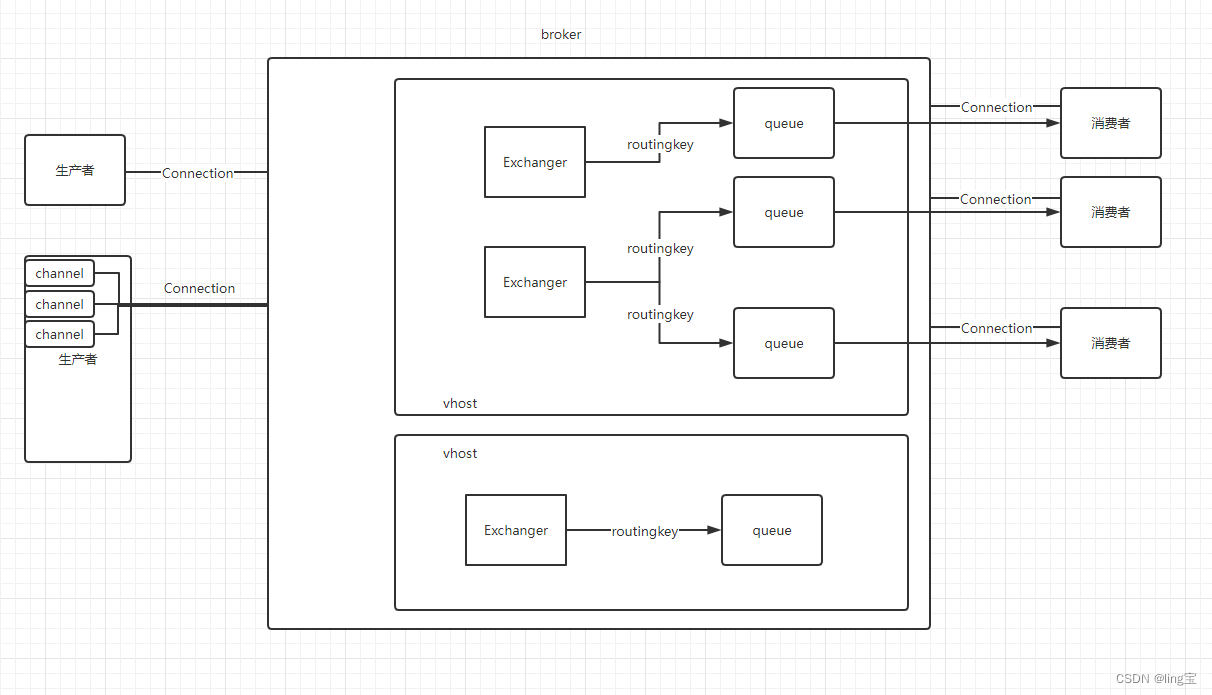

1 rocketmq的queue水平拆分了一个topic的消息,而rabbitmq最多只能做到筛选消息,queue之间并没有关联。
2 生’''产者和消费者指向的都是proxy,简化了操作者的配置。proxy可以通过负载均衡来选择消费者组将要消费的队列,从而选择消费者组所要消费的队列。rabbitmq需要手动指定生产者的exchanger和消费者的queue。
2 rocketmq有自己的存储淘汰机制以及offset机制,从而使得queue的内容可以复用。而rabbitmq更像一个buffer,阅后即删。
3 rocketmq有自己的messageGroup和messageId机制,从而保证了自己可以在消费者组多消费者消费时,依然还可以保持顺序机制。而rabbitmq的顺序机制必须指定单一消费者消费队列,来保证顺序。
4 rocketmq原生支持事务机制,可以保证在broker和生产者之间完成分布式事务。而rabbitmq虽然也可以实现分布式事务,但是是由生产者和消费者之间达成的,多了一层broker,提高了复杂度,性能还更差。
从crud感知架构
对于消费者而言,需要完成消费类型(推/拉),消费者组,消费过滤条件(tag),topic选择
@Test
public void t1() throws Exception {
final ClientServiceProvider provider = ClientServiceProvider.loadService();
String endpoints = "192.168.96.200:8081";
ClientConfiguration clientConfiguration = ClientConfiguration.newBuilder()
.setEndpoints(endpoints)
.build();
String tag = "*";
FilterExpression filterExpression = new FilterExpression(tag, FilterExpressionType.TAG);
String consumerGroup = "testGroup";
String topic = "first";
PushConsumer pushConsumer = provider.newPushConsumerBuilder()
.setClientConfiguration(clientConfiguration)
.setConsumerGroup(consumerGroup)
.setSubscriptionExpressions(Collections.singletonMap(topic, filterExpression))
.setMessageListener(messageView -> {
System.out.println(messageView.getMessageId());
ByteBuffer body = messageView.getBody();
byte[] bytes = new byte[body.remaining()];
body.get(bytes);
String content = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Received message: " + content);
return ConsumeResult.SUCCESS;
})
.build();
Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE);
// pushConsumer.close();
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Liyizhi111/article/details/140085140
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
