顺序表和链表
线性表
线性表在逻辑上是呈现线性结构,但在物理层面上不一定是连续的,常见的线性表有:顺序表,链表,栈,队列等等…
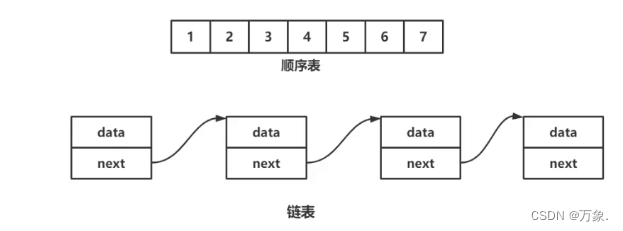
顺序表
顺序表是用一小段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储,一般可分为
静态顺序表(使用定长数组存储元素)
#define N 10
typedef int valuetype;
struct seqlist
{
valuetype arr[N];
int size;
};
动态顺序表(动态开辟的数组存储,空间不够可释放扩容)
typedef int valuetype;
struct seqlist
{
valuetype* arr;
int size;//有效数据个数
int capacity;//容量
};
静态顺序表较为不常见,我们下面来讨论动态的顺序表。
初始化
方法1:
void InitSeqlist(seqlist* psl)
{
psl->arr=NULL;
psl->size=psl->capacity=0;
}
不能只传结构体,因为函数内形参的初始化无法影响到外部的结构体,必须传地址。
方法2:
typedef int valuetype;
void InitSeqlist(seqlist* psl)
{
psl->arr=(valuetype*)malloc(sizeof(valuetype)*4);
if(psl->arr==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
psl->size=0;
psl->capacity=4;
}
销毁
void destroyseqlist(seqlist* psl)
{
psl->size=psl->capacity=0;
free(psl->arr);
psl->arr=NULL;//这里置空是可以影响到外面的结构体的,因为传参传的是指针
}
尾插
void push_back(seqlist* psl,valuetype x)
{
assert(psl!=NULL);
if(psl->size==psl->capacity)
{
(psl->capacity)*=2;//只能在使用初始化方法2时才能这样写,不然psl->capacity可能是0
free(psl->arr);
psl->arr=(valuetype*)malloc(sizeof(valuetype)*psl->capacity);//也可以用realloc
if(psl->arr==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
}
psl->arr[psl->size]=x;
psl->size++;
}
头插
void push_front(seqlist* psl,valuetype x)
{
assert(psl!=NULL);
if(psl->size==psl->capacity)
{
(psl->capacity)*=2;//只能在使用初始化方法2时才能这样写,不然psl->capacity可能是0
free(psl->arr);
psl->arr=(valuetype*)malloc(sizeof(valuetype)*psl->capacity);//也可以用realloc
if(psl->arr==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
}
for(int i=psl->size-1;i>=0;i--)
{
psl->arr[i+1]=psl->arr[i];
}
psl->arr[0]=x;
psl->size++;
}
尾删
void pop_back(seqlist* psl)
{
assert(psl!=NULL);
if(psl->size>0)
{
psl->size--;
}
}
头删
void pop_front(seqlist*psl)
{
assert(psl!=NULL);
if(psl->size>0)
{
for(int i=1;i<psl->size;i++)
{
psl->arr[i-1]=psl->arr[i];
}
psl->size--;
}
}
指定位置插入数据
void insert(seqlist* psl,int pos,valuetype x)
{
assert(pos>=0&&pos<=psl->size&&psl!=NULL);
if(psl->size==psl->capacity)
{
(psl->capacity)*=2;//只能在使用初始化方法2时才能这样写,不然psl->capacity可能是0
free(psl->arr);
psl->arr=(valuetype*)malloc(sizeof(valuetype)*psl->capacity);//也可以用realloc
if(psl->arr==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
}
for(int i=psl->size-1;i>=pos;i--)
{
psl->arr[i+1]=psl->arr[i];
}
psl->arr[pos]=x;
psl->size++;
}//可以复用在头插/尾插
指定位置删除数据
void erase(seqlist* psl,int pos)
{
assert(pos>=0&&pos<psl->size&&psl!=NULL);
//assert(psl->size>0);//可有可无,因为上面那条断言就能把为0的情况判断出来
for(int i=pos+1;i<psl->size;i++)
{
psl->arr[i-1]=psl->arr[i];
}
psl->size--;
}//可以复用在头删/尾删
查找指定数据
int find(seqlist* psl,valuetype x)
{
for(int i=0;i<psl->size;i++)
{
if(psl->arr[i]==x)
return i;
}
return -1;//没找到
}
修改指定位置数据
void modify(seqlist* psl,int pos,valuetype x)
{
assert(pos>=0&&pos<psl->size);
psl->arr[pos]=x;
}
顺序表存在的问题
1.中间/头部的插入/删除时间复杂度是O(n)。
2.增容有时候要申请新空间,拷贝旧数据和释放旧空间,消耗大。
3.增容是以2倍或者1.5倍增长,势必会造成空间浪费。
链表
顺序表存在的问题,链表可以很好的解决。
链表的结构
typedef struct listnode
{
valuetype data;//数据
struct listnode* next;//结构体地址
}node;
链表的种类
可以对单向与双向,带头与不带头,循环或者非循环一起组成8种链表
无头单向非循环链表
结构简单,一般不会用来存储数据,而是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶,图的邻接表等

无向单向非循环链表增删查改的实现
注意
malloc出来的节点需要free,否则会产生内存泄露,在函数里malloc产生的节点是不会释放的,只有free才能释放。
链表结构
typedef struct node
{
valuetype data;
struct node* next;
}node;
头插
void pushfront(node** pphead,valuetype x)
{
assert(pphead);
node* newnode=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
if(newnode==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->next=NULL;
newnode->data=x;
newnode->next=*pphead;
*pphead=newnode;
}
尾插
void pushback(node**pphead,valuetype x)
{
assert(pphead);
node* newnode=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
if(newnode==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->next=NULL;
newnode->data=x;
if(*pphead==NULL)
{
*pphead=newnode;
}
else
{
node* ptail=*pphead;
while(ptail->next!=NULL)
{
ptail=ptail->next;
}
ptail->next=newnode;
}
}
头删
void popfront(node** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead!=NULL);
node* fphead=*pphead;
*pphead=fphead->next;
free(fphead);
}
尾删
法1:
void popback(node** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead!=NULL);
if((*pphead)->next==NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead=NULL;
}
else
{
node* phead=*pphead;
while(phead->next->next!=NULL)
{
phead=phead->next;
}
node* tmp=phead->next;
free(tmp);
tmp=NULL//写程序的好习惯
phead->next=NULL;
}
法2:
void popback(node** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);//无节点的情况
node* phead=*pphead;
if((*pphead)->next==NULL)//节点仅有一个的情况
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead=NULL;
}
while(phead->next->next!=NULL)//节点数大于1的情况
{
phead=phead->next;
}
free(phead->next);
phead->next=NULL;
}
查找
法1:
node* find(node** pphead,valuetype x)
{
assert(pphead);
node* tmp=*pphead;
while(tmp)
{
if(tmp->data==x)
return tmp;
tmp=tmp->next;
}
return NULL;
}
法2:
node* find(node* phead,valuetype x)
{
node* tmp=phead;
while(tmp!=NULL)
{
if(tmp->data==x)
return tmp;
tmp=tmp->next;
}
return NULL;
}
在pos位置插入
void insert(node**pphead,node* pos,valuetype x)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
if(pos==*pphead)
{
newnode->next=*pphead;
*pphead=newnode;
}
else
{
node* newnode=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
if(newnode==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data=x;
node* tmp=*pphead;
while(tmp->next!=pos)
{
tmp=tmp->next;
}
newnode->next=pos;
tmp->next=newnode;
}
}
删除pos位置的节点
void erase(node** pphead,node* pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
if(pos==*pphead)
{
node* temp=*pphead;
*pphead=temp->next;
free(temp);
temp=NULL;
}
else
{
node* tmp=*pphead;
while(tmp->next!=pos)
{
tmp=tmp->next;
}
tmp->next=pos->next;
free(pos);
pos=NULL;
}
}
释放链表
void destroy(node** pphead)//也可以用一级指针,但要把头结点在外边置空,不然会造成野指针
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
node* cur =*pphead;
node* after=cur->next;
while(after)
{
free(cur);
cur=after;
after=after->next;
}
free(cur);
*pphead=NULL;
}
带头双向循环链表
结构最复杂,一般用来单独存放数据,它也是实际当中最常使用的链表结构。

双向循环链表增删查改的实现
链表结构
typedef struct Dnode
{
valuetype data;
struct Dnode next;
struct Dnode prev;
}Dnode;
头结点刚开始的prev和next指针是指向自身的。
初始化
Dnode* Init(Dnode* phead)
{
phead=(Dnode*)malloc(sizeof(Dnode));
if(phead==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
phead->next=phead;
phead->prev=phead;
return phead;
}
头插
法1:
void push_front(Dnode* phead,valuetype x)
{
assert(phead);
Dnode* newnode=(Dnode*)malloc(sizeof(Dnode));
if(newnode==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data=x;
phead->next->prev=newnode;
newnode->next=phead->next;
phead->next=newnode;
newnode->prev=phead;
}
法2:
void push_front(Dnode* phead,valuetype x)
{
assert(phead);
Dnode* newnode=(Dnode*)malloc(sizeof(Dnode));
if(newnode==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
Dnode* first=phead->next;//这样就不需要关注顺序
phead->next=newnode;
newnode->prev=phead;
first->prev=newnode;
newnode->next=first;
}
尾插
void push_back(Dnode* phead,valuetype x)
{
Dnode* newnode=(Dnode*)malloc(sizeof())
if(newnode==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data=x;
Dnode* ptail=phead->prev;
newnode->next=phead;
phead->prev=newnode;
ptail->next=newnode;
newnode->prev=ptail;
}
头删
法1:
void popfront(Dnode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
Dnode* first=phead->next;
if(first==phead)
return;
first->next->prev=phead;
phead->next=first->next;
free(first);
}
法2:
void popfront(Dnode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
Dnode* first=phead->next;
Dnode* second=first->next;
if(first==phead)
return;//也可以直接用assert,尾删同理
phead->next=second;
second->prev=phead;
free(first);
}
尾删
void popback(Dnode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
Dnode* ptail=phead->prev;
if(ptail==phead)
return;
ptail->prev->next=phead;
phead->prev=ptail->prev;
free(ptail);
}
查找
Dnode* Find(Dnode* phead,valuetype x)
{
assert(phead);
Dnode* cur=phead->next;
while(cur!=phead)
{
if(cur->data==x)
return cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
在pos位置前插入
void insert(Dnode* pos,valuetype x)
{
assert(pos);
Dnode* newnode=(Dnode*)malloc(sizeof(Dnode));
if(newnode==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->data=x;
Dnode* prev=pos->prev;
prev->next=newnode;
newnode->prev=prev;
pos->prev=newnode;
newnode->next=pos;
}//可以复用到头插尾插
删除pos位置的值
void erase (Dnode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
Dnode* prev=pos->prev;
Dnode* next=pos->next;
prev->next=next;
next->prev=prev;
free(pos);
}//可以复用到头删尾删
释放
void destroy(Dnode* phead)
{
Dnode* cur=phead->next;
while(cur!=phead)
{
Dnode* next=cur->next;
free(cur);
cur=next;
}
free(phead);//在外面对链表置空
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_79127392/article/details/140159236
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
