JS - 事件处理:鼠标移动监听事件、div块跟随鼠标移动事件、事件的绑定、实现拖拽效果
在DOM中,每个HTML元素都可以绑定各种事件,例如点击事件(click)、鼠标移入事件(mouseover)、键盘按下事件(keydown)等。当事件发生时,可以触发相应的事件处理程序(事件监听器),执行特定的操作。
常见的事件处理方式包括:
- HTML事件处理程序:直接在HTML元素上使用事件属性(比如onclick、onmouseover)来指定事件处理函数。
<button onclick="myFunction()">Click me</button> - DOM属性事件处理程序:通过JavaScript代码为DOM元素的事件属性赋值来指定事件处理函数。
document.getElementById("myButton").onclick = function() { // 事件处理逻辑 }; - DOM方法事件处理程序:使用addEventListener()方法或attachEvent()方法(在IE中)来为元素添加事件监听器。
document.getElementById("myButton").addEventListener("click", function() { // 事件处理逻辑 }); - 事件委托:将事件处理程序绑定在父元素上,通过事件冒泡的机制来处理子元素的事件,提高性能和代码简洁度。
document.getElementById("parentElement").addEventListener("click", function(event) { if (event.target.tagName === 'BUTTON') { // 处理按钮点击事件 } }); - 第三方库或框架:许多JavaScript库和框架(如jQuery、React、Vue等)提供了自己的事件绑定机制,简化了事件处理的操作。
事件处理程序通常是一个JavaScript函数,可以在事件发生时被调用执行。事件对象(Event Object)会被传递给事件处理程序,包含了关于事件的详细信息,比如事件类型、触发的元素等。
鼠标移动监听事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
#areaDiv
{
border: 1px solid black;
width: 300px;
height: 50px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
#showMsg
{
border: 1px solid black;
width: 300px;
height: 50px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function()
{
//当鼠标在areaDiv中移动时,在showMsg中来显示鼠标的坐标
//来获取两个div
var areaDiv=document.getElementById("areaDiv");
var showMsg=document.getElementById("showMsg");
//onmousemove
//该事件将会在鼠标元素移动中被触发
//事件对象
//当事件的响应函数触发时,浏览器每次都会将一个事件对象作为实参传递进响应函数
//在事件对象当中封装了当前事件相关的一切信息,比如,鼠标的坐标,键盘哪个键本按下,鼠标滚轮滚动的方向
areaDiv.onmousemove=function(event)
{
//IE8中,响应函数处罚时,浏览器不会传递事件对象
//在IE8及以下的浏览器中,是将事件对象作为window对象的属性保存的
//即window.event.clientX和window.event.client
//console.log(event);
//在showMsg中显示鼠标移动的坐标
//clientX返回当前事件触发时,鼠标指针的水平坐标
//clientY返回当前事件触发时,鼠标指针的垂直坐标
var x=event.clientX;
var y=event.clientY;
//console.log("x="+x+",y="+y);
showMsg.innerHTML="x="+x+",y="+y;
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="areaDiv"></div>
<div id="showMsg"></div>
</body>
</html>

div块跟随鼠标移动事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1
{
width:30px;
height: 30px;
background-color: red;
/*开启绝对定位*/
position:absolute;
}
html{
cursor: url('https://npm.elemecdn.com/akilar-candyassets/cur/arrow.cur'),auto !important;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function()
{
//使div可以跟随鼠标移动
//获取box1
var box1=document.getElementById("box1");
//锁定鼠标移动事件
document.onmousemove=function(event)
{
//获取鼠标的坐标
//鼠标坐标定位是相对于当前浏览器框的定位
//clientX和clientY是相当于浏览器框的定位
//pageX和pageY是相对于页面的定位
//var left=event.clientX;
//var top=event.clientY;
var left=event.pageX;
var top=event.pageY;
//pageX和page这两个属性在IE8中不支持,所以如果需要兼容IE8,就不能使用
//设置div的偏移量
box1.style.left=left+"px";
box1.style.top=top+"px";
};
//获取box2
var box2=document.getElementById("box2");
box2.onmousemove=function(event)
{
event.cancelBubble=true;
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body style="height: 1000px;width: 2000px;">
<div id="box2" style="width: 500px;height: 500px;background-color: #bfa;"></div>
<div id="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>
事件的冒泡
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1
{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
#s1
{
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function()
{
//事件的冒泡
//所谓的冒泡指的就是事件上的向上传导,当后代元素上的事件被触发时,其祖先元素的相同事件也会被触发
//在开发中大部分情况冒泡都是有用的,如果不希望发生事件冒泡,可以通过事件对象取消冒泡
//为s1绑定一个单击响应函数
var s1=document.getElementById("s1");
s1.onclick=function(event)
{
console.log("我是span的单击响应函数");
//取消冒泡
//可以将事件对象的cancelBubble设置为true,即可取消
event.cancelBubble=true;
};
//为box1绑定一个单击响应函数
var box1=document.getElementById("box1");
box1.onclick=function(event)
{
console.log("我是box1的单击响应函数");
//取消冒泡
event.cancelBubble=true;
};
//为body绑定一个单击响应函数
document.body.onclick=function()
{
console.log("我是body的单击响应函数");
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box1">
我是box1
<span id="s1">我是span</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
事件的委托
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function()
{
//点击按钮以后添加超链接
var btn01=document.getElementById("btn01");
var u1=document.getElementById("u1");
btn01.onclick=function()
{
//console.log("添加一个超链接");
//创建一个li
var li=document.createElement("li");
li.innerHTML="<a href='javascript:;'>新建的超链接class='link'</a>";
//将li添加到ul中
u1.appendChild(li);
};
//为每一个超链接都绑定一个单击响应函数
//为每一个超链接都绑定一个单击响应函数,这种操作比较麻烦
//而且这些操作只能为已有的超链接设置事件,而新添加的超链接必须重新绑定
/*
//获取所有的a
var allA=document.getElementsByTagName("a");
//遍历
for(var i=0;i<allA.length;i++)
{
console.log(allA[i]);
allA[i].οnclick=function()
{
console.log("我是a的单击响应函数");
};
}
*/
//我们希望只绑定一次事件,即可应用到所有的元素上.即时元素时后面添加的
//我们可以尝试将其绑定给元素的共同的祖先元素
//事件的委派
//指将事件统一绑定给元素的共同的祖先元素,这样当后台元素上的事件被触发时,会一直冒泡祖先元素
//从而通过祖先元素的响应函数来处理事件
//事件委培利用了冒泡,通过委派可以减少事件绑定的次数,提高程序的性能
//给ul绑定一个单击响应函数
//这样ul的子元素全都有单击响应函数
u1.onclick=function(event)
{
//这样绑定存在一个缺点,UI存在的区域全是判定区域,随便点击都能触发事件
//所以需要定一个标准,如果触发事件的对象睡我们期望的元素,则继续执行,否则不执行
//console.log("我是a的单击响应函数");
//先检查一下target属性
//event中的targe表示的触发事件的对象
//确定target是被点击的对象
if(event.target.className == "link")
{
console.log("我是ul的单击响应函数");
}
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn01">添加超链接</button>
<br>
<ul id="u1">
<li>我是li文档</li>
<li><a href="javascript:;" class="link">超链接一</a></li>
<li><a href="javascript:;" class="link">超链接二</a></li>
<li><a href="javascript:;" class="link">超链接三</a></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
事件的绑定
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function()
{
//点击按钮以后弹出一个内容
var btn01=document.getElementById("btn01");
//使用 对象.事件=函数的形式绑定响应函数
//他只能同时为一个元素的一个事件绑定一个响应函数,不能绑定多个,不然会出现覆盖
/*
btn01.οnclick=function()
{
console.log("1");
}
//为btn01绑定第二个单击响应函数,这样会造成函数覆盖
btn01.οnclick=function()
{
console.log("2");
}
*/
//addEventListener()
//通过这个方法也可以为元素绑定响应函数
//参数: 1.事件的字符串,要把on舍去 2.回调函数,当事件触发时,该函数会被调用
// 3.是否在捕获阶段触发事件,需要一个布尔值,一般都传false
//使用它可以同时为一个元素的相同事件同时绑定多个响应函数
//当事件被触发时,响应函数将会按照函数的绑定顺序执行
btn01.addEventListener("click",function()
{
console.log(123);
},false);
btn01.addEventListener("click",function()
{
console.log(456);
},false);
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn01">点我一下</button>
</body>
</html>
事件的传播
事件传播是指当事件发生在DOM元素上时,该事件如何在DOM树中传播到其他元素的过程。事件传播分为三个阶段:捕获阶段(capturing phase)、目标阶段(target phase)和冒泡阶段(bubbling phase)。这三个阶段统称为事件流(event flow)。
-
捕获阶段:事件从最外层的祖先元素向目标元素传播的阶段。在捕获阶段中,事件会依次经过祖先元素,直到达到目标元素。
-
目标阶段:事件达到目标元素后,在目标元素上触发相应的事件处理程序。
-
冒泡阶段:事件从目标元素开始,沿着DOM树向外传播的阶段。在冒泡阶段中,事件会依次经过目标元素的祖先元素,直到达到最外层的祖先元素。
在事件传播过程中,可以通过事件处理程序的第三个参数来控制事件的传播方式。如果第三个参数为true,则表示在捕获阶段处理事件;如果为false(默认值),则表示在冒泡阶段处理事件。
事件传播的机制使得可以在DOM树的不同层次上捕获和处理事件,同时也提供了事件委托(event delegation)的可能性。通过在祖先元素上绑定事件处理程序,可以在冒泡阶段捕获子元素上的事件,减少事件处理程序的数量,提高性能和代码简洁度。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1
{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: green;
}
#box2
{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: yellow;
}
#box3
{
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function()
{
//分别为三个div绑定单击响应函数
var box1=document.getElementById("box1");
var box2=document.getElementById("box2");
var box3=document.getElementById("box3");
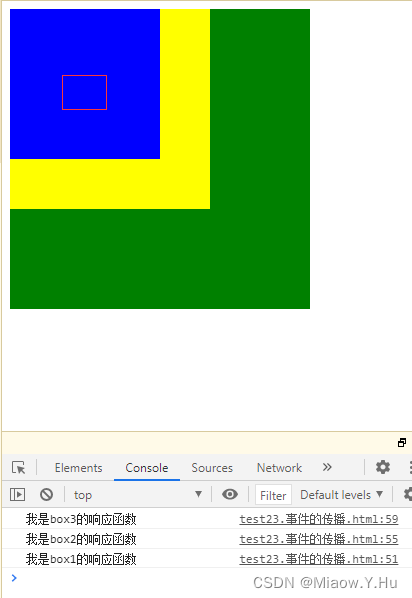
//事件的传播
//关于事件的传播网景公司和微软公司有不同的理解
//微软公司认为事件应该是由内向外传播,也就是事件触发时,先触发当前元素上的事件
//然后再向当前元素的祖先元素上传播,事件应该在冒泡阶段执行
//网景公司认为事件应该是在由外向内传播,也就是当事件触发时,应该先触发当前元素的最外层的祖先元素的事件
//然后再向内传播给后代元素
//最后是W3C综合两个公司的方案,将事件传播分成了三个阶段
//1.捕获阶段 由最外层的祖先元素向目标元素进行事件的捕获,但默认此时不会触发事件
//2.目标阶段 事件捕获到目标元素,捕获结束开始在目标元素上触发事件
//3.冒泡阶段 事件从目标元素向他的祖先元素传递,依次触发祖先元素上的事件
//如果希望在捕获阶段触发事件,可以将addEventListener()的第三个参数设置为true
//一般情况下我们不会希望在捕获阶段触发事件,所以这个参数一般都是false
box1.addEventListener("click",function()
{
console.log("我是box1的响应函数");
},false);
box2.addEventListener("click",function()
{
console.log("我是box2的响应函数");
},false);
box3.addEventListener("click",function()
{
console.log("我是box3的响应函数");
},false);
}
/*
function bind(obj,eventStr,callback)
{
if(obj.addEventListener)
{
obj.addEventListener(event,callback,false);
}
else
{
obj.attachEvent("on"+eventStr,function()
{
callback.call(obj);
}
);
}
}
*/
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box1">
<div id="box2">
<div id="box3"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
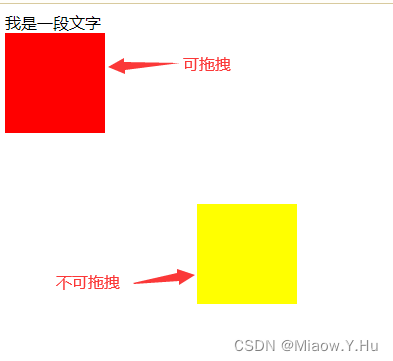
拖拽效果实现1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
}
#box2
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function()
{
//拖拽box1元素
//拖拽的流程
//1.当鼠标在被拖拽元素上按下时,开始拖拽 onmousedown
//2.当鼠标移动时被拖拽元素跟随鼠标移动 onmousemove
//3.当鼠标松开时,被拖拽元素固定在当前位置 onmouseup
//获取box1
var box1=document.getElementById("box1");
/*
var box1Style=getComputedStyle(box1,null)
console.log(box1Style.height);
console.log(box1Style.width);
*/
//为box1绑定一个鼠标按下事件
box1.onmousedown=function(event)
{
//div的水平偏移量 鼠标.clentX-元素.offsetLeft
//div的垂直偏移量 鼠标.clentY-元素.offsetTo
var ol=event.clientX - box1.offsetLeft;
var ot=event.clientY - box1.offsetTop;
//给document绑定一个onmousemove
document.onmousemove=function(event)
{
//console.log(event);
//当鼠标移动时被拖拽元素跟随鼠标移动 onmousemove
//获取鼠标的坐标
var left=event.clientX-ol;
var top=event.clientY-ot;
//修改box1的位置
box1.style.left=left+"px";//横纵坐标加一个-50,能使鼠标移动点固定在元素中间
box1.style.top=top+"px";
};
//为元素绑定一个鼠标松开事件
document.onmouseup=function()
{
//当鼠标松开时,被拖拽元素固定在当前位置 onmouseup
//取消document的onmousemove事件
document.onmousemove=null;
//取消document的onmouseup事件
document.onmouseup=null;
};
//当我们拖拽一个网页中的内容时,该浏览器会默认去搜索引擎中搜索内容
//此时会导致拖拽功能的异常,这个是浏览器的默认行为
//如果不希望发生这个行为,则可以通过return false来取消默认行为
return false;
//IE8不兼容
};
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!--谷歌浏览器Ctrl+A全选页面内容然后拖动,不会出现连带元素一起拖动的情况-->
我是一段文字
<div id="box1"></div>
<div id="box2"></div>
</body>
</html>
拖拽效果实现图片拖拽
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
}
#box2
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
}
#图一
{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
//元素拖拽代码一个一个定义过于麻烦,可以尝试进行封装
//提取一个专门用来设置拖拽的函数,拖拽英文trag
//传递一个参数:开启拖拽的元素obj
function drag(obj)
{
obj.onmousedown=function(event)
{
//div的水平偏移量 鼠标.clentX-元素.offsetLeft
//div的垂直偏移量 鼠标.clentY-元素.offsetTo
var ol=event.clientX - obj.offsetLeft;
var ot=event.clientY - obj.offsetTop;
//给document绑定一个onmousemove
document.onmousemove=function(event)
{
//console.log(event);
//当鼠标移动时被拖拽元素跟随鼠标移动 onmousemove
//获取鼠标的坐标
var left=event.clientX-ol;
var top=event.clientY-ot;
//修改box1的位置
obj.style.left=left+"px";//横纵坐标加一个-50,能使鼠标移动点固定在元素中间
obj.style.top=top+"px";
};
//为元素绑定一个鼠标松开事件
document.onmouseup=function()
{
//当鼠标松开时,被拖拽元素固定在当前位置 onmouseup
//取消document的onmousemove事件
document.onmousemove=null;
//取消document的onmouseup事件
document.onmouseup=null;
};
//当我们拖拽一个网页中的内容时,该浏览器会默认去搜索引擎中搜索内容
//此时会导致拖拽功能的异常,这个是浏览器的默认行为
//如果不希望发生这个行为,则可以通过return false来取消默认行为
return false;
//IE8不兼容
};
}
window.onload=function()
{
//拖拽的流程
//1.当鼠标在被拖拽元素上按下时,开始拖拽 onmousedown
//2.当鼠标移动时被拖拽元素跟随鼠标移动 onmousemove
//3.当鼠标松开时,被拖拽元素固定在当前位置 onmouseup
//获取box1
var box1=document.getElementById("box1");
var box2=document.getElementById("box2");
var img1=document.getElementById("图一");
drag(box1);
drag(box2);
drag(img1);
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!--谷歌浏览器Ctrl+A全选页面内容然后拖动,不会出现连带元素一起拖动的情况-->
我是一段文字
<div id="box1"></div>
<div id="box2"></div>
<img id="图一" src="./photo (1).png" style="position: absolute;">
</body>
</html>


实现滚动事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function()
{
//获取id为box1的div
var box1=document.getElementById("box1");
//为box1绑定一个鼠标滚轮滚动的事件onmousewheel
//火狐只支持DOMMouseScroll事件
box1.onmousewheel=function(event)
{
//当鼠标滚轮向下滚动时,box1变长
//当滚轮向上滚动时,box1变短
//console.log("滚了");
//判断鼠标滚轮滚动的方向
//event.wheelDelta 可以获取鼠标滚轮滚动的方向向上滚是120,向下滚是-120
//wheelDelta这个值我们不看大小,只看正负
//console.log(event.wheelDelta);
if(event.wheelDelta >0)
{
//向上滚,box1变短
//console.log("向上滚");
box1.style.height=box1.clientHeight-10+"px";
}
else
{
//向下滚,box2变长
//console.log("向下滚");
box1.style.height=box1.clientHeight+10+"px";
}
//当滚轮滚动时,如果浏览器有滚动条,那么就会随着滚动条滚动
//这是浏览器的默认行为,如果不希望发生,则可以取消该行为
return false;//但此时不能把鼠标滚轮绑定在document上
};
//另一种方法
/*
box1.addEventListener("mousewheel",function()
{
console.log("滚了");
},false);
*/
//此方法可以用event.preventDefault();来处理
//但是IE8不能支持此方法
};
</script>
</head>
<body style="height: 2000px;">
<div id="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>
实现一个键盘监听事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function()
{
//key是指键盘字符
//keyCode是指键盘字符代码
//获取input1
var input1=document.getElementById("input1");
//键盘事件
//onkeydown 按键被按下
//对于onkeydown来说 如果一直按着某个按键不松手,则事件会被一直触发
//当onkeydown连续触发时,第一次和第二次之间会间隔稍微长一点,其他的会非常快
//防止误操作的发生
//onkeyup 按键被松开 但他不会被连续触发,只能一次一次触发
//键盘事件一般都会绑定给一些可以获取到焦点的对象(也就是可以获取光标的对象)或者是document
//如何知道键盘敲击的是什么字符?需要使用event
document.onkeydown=function(event)
{
//console.log("按键被按下了");
//console.log(event.keyCode);
/*
if(event.keyCode === 89)
{
console.log("y被按下了");
}
*/
//除了keyCode,事件对象中还提供了几个属性
//altKey ctrlKey shiftKey
//这三个用来判断alt ctrl shift是否同时被按下
if(event.keyCode === 89 && event.ctrlKey)
{
//console.log("ctrl和y都被按下了");
}
};
document.onkeyup=function(event)
{
//console.log("按键被松开了");
};
//给input1绑定键盘事件
input1.onkeydown=function(event)
{
//console.log(event.keyCode);
//如果增加return false
//那么文本框将无法输入字符,但是控制台依旧会显示字符的keyCode码
//在文本框输入内容,属于onkeydown的默认行为
//如果再onkeydown中取消了默认行为,则输入的内容,不会出现在文本框中
//return false;
//如何使文本框中不能输入数字
//数字值在48-57和96-105之间
/*
if((event.keyCode>=48 && event.keyCode<=57) || (event.keyCode>=96 && event.keyCode<=105))
{
console.log("无法输入数字");
return false;
}
*/
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!--<div id="box1"></div>-->
文本框<input type="text" id="input1">
</body>
</html>
键盘控制div移动
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
//使div可以根据不同的方向键向不同的方向移动
//按左键,div向左移
//按右键,div向右移
//key是键盘字符 keyCode是键盘字符代码
window.onload=function()
{
var box1=document.getElementById("box1");
//开启一个定时器,来控制div的移动
var speed=20;
//创建一个变量表示方向
var dir;
//通过修改dir来影响移动的方向
setInterval(function()
{
switch(dir)
{
case "ArrowUp":
//console.log("向上");
box1.style.top=box1.offsetTop-speed+"px";
break;
case "ArrowRight":
//console.log("向右");
box1.style.left=box1.offsetLeft+speed+"px";
break;
case "ArrowDown":
//console.log("向下");
box1.style.top=box1.offsetTop+speed+"px";
break;
case "ArrowLeft":
//console.log("向左");
box1.style.left=box1.offsetLeft-speed+"px";
break;
}
},30);
//先给documment绑定一个按键按下事件
document.onkeydown=function(event)
{
dir=event.key;
//当用户按了ctrl时,速度加快
if(event.ctrlKey)
{
speed=50;
}
else
{
speed=20;
}
};
//当按键松开时,div不再移动
document.onkeyup=function()
{
//设置方向为0
dir=0;
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>
HTML实现一个俄罗斯方块
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>es6-重构俄罗斯方块(基于canvas)</title>
<style type="text/css">
#tetris{ margin: 10px 250px;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="700" height="525" id="tetris"></canvas>
<div id="text" style='color: red;font-size: 30px;'>当前分数:0</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
/**
* [一个完整的俄罗斯方块类 design by magic_xiang]
* @param {number} side [每个方块边长(px),默认35]
* @param {number} width [一行包含的方块数(个),默认20]
* @param {number} height [一列包含的方块数(个),默认15]
* @param {number} speed [方块下落移动速度(ms),默认400]
*/
class tetris{
constructor(side=35, width=20, height=15, speed=400){
this.side = side // 每个方块边长
this.width = width // 一行包含的方块数
this.height = height // 一列包含的方块数
this.speed = speed // 方块下落移动速度
this.num_blcok // 当前方块类型的数字变量
this.type_color // 当前颜色类型的字符串变量
this.ident // setInterval的标识
this.direction = 1 // 方块方向,初始化为1,默认状态
this.grade = 0 // 用来计算分数
this.over = false // 游戏是否结束
this.arr_bX = [] // 存放当前方块的X坐标
this.arr_bY = [] // 存放当前方块的Y坐标
this.arr_store_X = [] // 存放到达底部所有方块的X坐标
this.arr_store_Y = [] // 存放到达底部所有方块的Y坐标
this.arr_store_color = [] // 存放到达底部所有方块的颜色
this.paints = document.getElementById('tetris').getContext('2d')
//获取画笔
self = this
}
// 封装paints方法,让代码更简洁
paintfr(x, y, scale=1){
this.paints.fillRect(x*this.side, y*this.side, scale*this.side, scale*this.side)
}
// 游戏开始
gameStart(){
this.init()
this.run()
}
// 初始化工作
init(){
this.initBackground()
this.initBlock()
}
// 方块自动下落
run(){
this.ident = setInterval("self.down_speed_up()", this.speed)
}
// 初始化地图
initBackground(){
this.paints.beginPath()
this.paints.fillStyle='#000000' //地图填充颜色为黑色
for(let i = 0; i < this.height; i++){
for(let j = 0; j < this.width; j++){
this.paintfr(j, i)
}
}
this.paints.closePath()
}
// 初始化方块的位置和颜色
initBlock(){
this.paints.beginPath()
this.createRandom('rColor') //生成颜色字符串,
this.paints.fillStyle = this.type_color
this.createRandom('rBlock') //生成方块类型数字
this.arr_bX.forEach((item, index) => {
this.paintfr(item, this.arr_bY[index], 0.9)
})
this.paints.closePath()
}
// 利用数组画方块
drawBlock(color){
this.paints.beginPath()
this.paints.fillStyle = color
this.arr_bX.forEach((item, index) => {
this.paintfr(item, this.arr_bY[index], 0.9)
})
this.paints.closePath()
}
// 画已经在定位好的方块
drawStaticBlock(){
this.arr_store_X.forEach((item, index) => {
this.paints.beginPath()
this.paints.fillStyle = this.arr_store_color[index]
this.paintfr(item, this.arr_store_Y[index], 0.9)
this.paints.closePath()
})
}
// 生成随机数返回方块类型或颜色类型
createRandom(type){
let temp = this.width/2-1
if (type == 'rBlock'){ //如果是方块类型
this.num_blcok = Math.round(Math.random()*4+1)
switch(this.num_blcok){
case 1:
this.arr_bX.push(temp,temp-1,temp,temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(0,1,1,1)
break
case 2:
this.arr_bX.push(temp,temp-1,temp-1,temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(1,0,1,1)
break
case 3:
this.arr_bX.push(temp,temp-1,temp+1,temp+2)
this.arr_bY.push(0,0,0,0)
break
case 4:
this.arr_bX.push(temp,temp-1,temp,temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(0,0,1,1)
break
case 5:
this.arr_bX.push(temp,temp+1,temp,temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(0,0,1,1)
break
}
}
if (type == 'rColor'){ //如果是颜色类型
let num_color = Math.round(Math.random()*8+1)
switch(num_color){
case 1:
this.type_color='#3EF72A'
break
case 2:
this.type_color='yellow'
break
case 3:
this.type_color='#2FE0BF'
break
case 4:
this.type_color='red'
break
case 5:
this.type_color='gray'
break
case 6:
this.type_color='#C932C6'
break
case 7:
this.type_color= '#FC751B'
break
case 8:
this.type_color= '#6E6EDD'
break
case 9:
this.type_color= '#F4E9E1'
break
}
}
}
// 判断方块之间是否碰撞(下),以及变形时是否越过下边界
judgeCollision_down(){
for(let i = 0; i < this.arr_bX.length; i++){
if (this.arr_bY[i] + 1 == this.height){ //变形时是否越过下边界
return false
}
if (this.arr_store_X.length != 0) { //判断方块之间是否碰撞(下)
for(let j = 0; j < this.arr_store_X.length; j++){
if (this.arr_bX[i] == this.arr_store_X[j]) {
if (this.arr_bY[i] + 1 == this.arr_store_Y[j]) {
return false
}
}
}
}
}
return true
}
//判断方块之间是否碰撞(左右),以及变形时是否越过左右边界
judgeCollision_other(num){
for(let i = 0; i < this.arr_bX.length; i++){
if (num == 1) { //变形时是否越过右边界
if (this.arr_bX[i] == this.width - 1)
return false
}
if (num == -1) { //变形时是否越过左边界
if (this.arr_bX[i] == 0)
return false
}
if (this.arr_store_X.length != 0) { //判断方块之间是否碰撞(左右)
for(let j = 0; j < this.arr_store_X.length; j++){
if (this.arr_bY[i] == this.arr_store_Y[j]) {
if (this.arr_bX[i] + num == this.arr_store_X[j]) {
return false
}
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
//方向键为下的加速函数
down_speed_up(){
let flag_all_down = true
flag_all_down = this.judgeCollision_down()
if (flag_all_down) {
this.initBackground()
for(let i = 0; i < this.arr_bY.length; i++){
this.arr_bY[i] = this.arr_bY[i] + 1
}
}
else{
for(let i=0; i < this.arr_bX.length; i++){
this.arr_store_X.push(this.arr_bX[i])
this.arr_store_Y.push(this.arr_bY[i])
this.arr_store_color.push(this.type_color)
}
this.arr_bX.splice(0,this.arr_bX.length)
this.arr_bY.splice(0,this.arr_bY.length)
this.initBlock()
}
this.clearUnderBlock()
this.drawBlock(this.type_color)
this.drawStaticBlock()
this.gameover()
}
//方向键为左右的左移动函数
move(dir_temp){
this.initBackground()
if (dir_temp == 1) { //右
let flag_all_right = true
flag_all_right = this.judgeCollision_other(1)
if (flag_all_right) {
for(let i = 0; i < this.arr_bY.length; i++){
this.arr_bX[i] = this.arr_bX[i]+1
}
}
}
else{
let flag_all_left = true
flag_all_left = this.judgeCollision_other(-1)
if (flag_all_left) {
for(let i=0; i < this.arr_bY.length; i++){
this.arr_bX[i] = this.arr_bX[i]-1
}
}
}
this.drawBlock(this.type_color)
this.drawStaticBlock()
}
//方向键为空格的变换方向函数
up_change_direction(num_blcok){
if (num_blcok == 5) {
return
}
let arr_tempX = []
let arr_tempY = []
//因为不知道是否能够变形成功,所以先存储起来
for(let i = 0;i < this.arr_bX.length; i++){
arr_tempX.push(this.arr_bX[i])
arr_tempY.push(this.arr_bY[i])
}
this.direction++
//将中心坐标提取出来,变形都以当前中心为准
let ax_temp = this.arr_bX[0]
let ay_temp = this.arr_bY[0]
this.arr_bX.splice(0, this.arr_bX.length) //将数组清空
this.arr_bY.splice(0, this.arr_bY.length)
if (num_blcok == 1) {
switch(this.direction%4){
case 1:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp-1,ax_temp,ax_temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp+1,ay_temp+1,ay_temp+1)
break
case 2:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp-1,ax_temp,ax_temp)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp,ay_temp-1,ay_temp+1)
break
case 3:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp-1,ax_temp,ax_temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp,ay_temp+1,ay_temp)
break
case 0:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp-1,ay_temp+1,ay_temp)
break
}
}
if (num_blcok == 2) {
switch(this.direction%4){
case 1:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp-1,ax_temp-1,ax_temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp,ay_temp-1,ay_temp)
break
case 2:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp-1)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp-1,ay_temp+1,ay_temp+1)
break
case 3:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp-1,ax_temp+1,ax_temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp,ay_temp,ay_temp+1)
break
case 0:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp-1,ay_temp+1,ay_temp-1)
break
}
}
if (num_blcok == 3) {
switch(this.direction%4){
case 1:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp-1,ax_temp+1,ax_temp+2)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp,ay_temp,ay_temp)
break
case 2:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp-1,ay_temp+1,ay_temp+2)
break
case 3:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp-1,ax_temp+1,ax_temp+2)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp,ay_temp,ay_temp)
break
case 0:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp-1,ay_temp+1,ay_temp+2)
break
}
}
if (num_blcok == 4) {
switch(this.direction%4){
case 1:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp-1,ax_temp,ax_temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp,ay_temp+1,ay_temp+1)
break
case 2:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp+1,ax_temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp+1,ay_temp,ay_temp-1)
break
case 3:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp-1,ax_temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp-1,ay_temp,ay_temp-1)
break
case 0:
this.arr_bX.push(ax_temp,ax_temp,ax_temp+1,ax_temp+1)
this.arr_bY.push(ay_temp,ay_temp-1,ay_temp,ay_temp+1)
break
}
}
if (! (this.judgeCollision_other(-1) && this.judgeCollision_down() && this.judgeCollision_other(1) )) { //如果变形不成功则执行下面代码
this.arr_bX.splice(0, this.arr_bX.length)
this.arr_bY.splice(0, this.arr_bY.length)
for(let i=0; i< arr_tempX.length; i++){
this.arr_bX.push(arr_tempX[i])
this.arr_bY.push(arr_tempY[i])
}
}
this.drawStaticBlock()
}
//一行满了清空方块,上面方块Y坐标+1
clearUnderBlock(){
//删除低层方块
let arr_row=[]
let line_num
if (this.arr_store_X.length != 0) {
for(let j = this.height-1; j >= 0; j--){
for(let i = 0; i < this.arr_store_color.length; i++){
if (this.arr_store_Y[i] == j) {
arr_row.push(i)
}
}
if (arr_row.length == this.width) {
line_num = j
break
}else{
arr_row.splice(0, arr_row.length)
}
}
}
if (arr_row.length == this.width) {
//计算成绩grade
this.grade++
document.getElementById('text').innerHTML = '当前成绩:'+this.grade
for(let i = 0; i < arr_row.length; i++){
this.arr_store_X.splice(arr_row[i]-i, 1)
this.arr_store_Y.splice(arr_row[i]-i, 1)
this.arr_store_color.splice(arr_row[i]-i, 1)
}
//让上面的方块往下掉一格
for(let i = 0; i < this.arr_store_color.length; i++){
if (this.arr_store_Y[i] < line_num) {
this.arr_store_Y[i] = this.arr_store_Y[i]+1
}
}
}
}
//判断游戏结束
gameover(){
for(let i=0; i < this.arr_store_X.length; i++){
if (this.arr_store_Y[i] == 0) {
clearInterval(this.ident)
this.over = true
}
}
}
}
let tetrisObj = new tetris()
tetrisObj.gameStart()
//方向键功能函数
document.onkeydown = (e) => {
if (tetrisObj.over)
return
switch(e.keyCode){
case 40: // 方向为下
tetrisObj.down_speed_up()
break
case 32: // 空格换方向
tetrisObj.initBackground() //重画地图
tetrisObj.up_change_direction(tetrisObj.num_blcok)
tetrisObj.drawBlock(tetrisObj.type_color)
break
case 37: // 方向为左
tetrisObj.initBackground()
tetrisObj.move(-1)
tetrisObj.drawBlock(tetrisObj.type_color)
break
case 39: // 方向为右
tetrisObj.initBackground()
tetrisObj.move(1)
tetrisObj.drawBlock(tetrisObj.type_color)
break
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
HTML实现一个贪吃蛇
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>html5实现贪吃蛇小游戏</title>
<style>
#myCanvas {
box-shadow: 0 0 6px #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<br/><br/><br/>
<input type="button" value="开始游戏" onclick="beginGame();"><br/><br/><br/>
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="450" height="450"></canvas>
<script>
var canvas = document.getElementById("myCanvas");
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
var w = 15; //格子宽、高
var snaLen = 6; //初始长度
var snake = []; //身体长度
for (var i = 0; i < snaLen; i++) {
snake[i] = new cell(i, 0, 39);
}
var head = snake[snaLen - 1]; //头部
//初始食物
var foodx = Math.ceil(Math.random() * 28 + 1);
var foody = Math.ceil(Math.random() * 28 + 1);
var food = new Food(foodx, foody);
//食物
function Food(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
return this;
}
//身体
function cell(x, y, d) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.d = d;
return this;
}
//动作
function draw() {
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, 450, 450);
//画布局
// for(var i = 0; i < 30; i++){
// ctx.strokeStyle = "#ccc";//线条颜色
// ctx.beginPath();
// ctx.moveTo(0,i*w);
// ctx.lineTo(450,i*w);
// ctx.moveTo(i*w,0);
// ctx.lineTo(i*w,450);
// ctx.closePath();
// ctx.stroke();
// }
//画蛇身
for (var j = 0; j < snake.length; j++) {
ctx.fillStyle = "green";
if (j == snake.length - 1) {
ctx.fillStyle = "red";
}
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.rect(snake[j].x * w, snake[j].y * w, w, w);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fill();
ctx.stroke();
}
//出现食物
drawFood();
//吃到食物
if (head.x == food.x && head.y == food.y) {
initFood();
food = new Food(foodx, foody);
//重新出现食物
drawFood();
//增加蛇的长度 有些小瑕疵,蛇身增长时应该是身体增长,而不是在蛇头上增长
var newCell = new cell(head.x, head.y, head.d);
switch (head.d) {
case 40:
newCell.y++;
break; //下
case 39:
newCell.x++;
break; //右
case 38:
newCell.y--;
break; //上
case 37:
newCell.x--;
break; //左
}
snake[snake.length] = newCell;
head = newCell;
//head =
}
}
//随机初始化食物
function initFood() {
foodx = Math.ceil(Math.random() * 28 + 1);
foody = Math.ceil(Math.random() * 28 + 1);
for (var i = 0; i < snake.length; i++) {
if (snake[i].x == foodx && snake[i].y == foody) {
initFood();
}
}
}
//画食物
function drawFood() {
//绘制食物
ctx.fillStyle = "orange";
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.rect(food.x * w, food.y * w, w, w);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fill();
}
draw();
//监听键盘事件
document.onkeydown = function(e) {
//下40 , 右边39,左边37,上38 键盘事件
var keyCode = e.keyCode;
if (head.d - keyCode != 2 && head.d - keyCode != -2 && keyCode >= 37 && keyCode <= 40) {
moveSnake(keyCode);
}
}
//控制蛇移动方向
function moveSnake(keyCode) {
var newSnake = [];
var newCell = new cell(head.x, head.y, head.d); //头
//身体
for (var i = 1; i < snake.length; i++) {
newSnake[i - 1] = snake[i];
}
newSnake[snake.length - 1] = newCell;
newCell.d = keyCode;
switch (keyCode) {
case 40:
newCell.y++;
break; //下
case 39:
newCell.x++;
break; //右
case 38:
newCell.y--;
break; //上
case 37:
newCell.x--;
break; //左
}
snake = newSnake;
head = snake[snake.length - 1];
checkDeath();
draw();
}
//游戏规则
function checkDeath() {
//超出边框
if (head.x >= 30 || head.y >= 30 || head.x < 0 || head.y < 0) {
alert("Game over!");
window.location.reload();
}
//咬到自己
for (var i = 0; i < snake.length - 1; i++) {
if (head.x == snake[i].x && head.y == snake[i].y) {
alert("Game over!");
window.location.reload();
}
}
}
//蛇自动走
function moveClock() {
moveSnake(head.d);
}
var isMove = false;
function beginGame() {
!isMove && setInterval(moveClock, 300);
isMove = true;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45922256/article/details/137833683
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
