C++/Qt 小知识记录5
工作中遇到的一些小问题,总结的小知识记录:C++/Qt
小知识5
Windows下查看端口占用情况
如下为C++的调用实现
#include <Windows.h>
#include <WinSock.h>
#include <tcpmib.h>
#include <IPHlpApi.h>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
int CRetransferRequest::GetSupportPort(int nMin, int nMax)
{
for (int i = nMin; i <= nMax; i++)
{
unsigned short usPort = (unsigned short)i;
SOCKET s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_IP);
sockaddr_in addr;
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_port = htons(usPort);
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
bind(s, (LPSOCKADDR)&addr, sizeof(addr));
if (WSAGetLastError() == WSAEADDRINUSE)
{
//端口已被占用
continue;
}
else
{
return i;
}
}
return rand() % (nMax - nMin) + nMin;
}
同时在cmake中需要配置相关库依赖: ws2_32.lib、IPHlpApi.lib
# cmake下的依赖库
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}
PRIVATE
ws2_32.lib
IPHlpApi.lib
)
C++调用Python三方库
以下是一些在做C++调用Python脚本时遇到的突出问题,或者必要的记录。(如何实现就不详细解说了,网上的教程很完备)
测试库有没有被加上的测试方法
// Try to import
PyObject* pName = PyUnicode_DecodeFSDefault(strModuleName.data());
PyObject* pModule = PyImport_Import(pName);
if (pModule != NULL) {
// module exists
printf("%s library is available.\n", strModuleName.data());
// Clean up
Py_DECREF(pModule);
}
else {
// ImportError occurred
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to import %s library.\n", strModuleName.data());
}
初始化使用Python的env环境,用Py_SetPythonHome设置
Py_SetPythonHome(L"../algorithm_py_env");
Py_Initialize();
if (!Py_IsInitialized())
{
return -1;
}
GDAL相关的,需要把osgeo、rasterio的路径加入到运行环境变量
(假设Python环境在algorithm_py_env目录下)
PyRun_SimpleString("import os");
PyRun_SimpleString("os.environ['PATH'] = '../algorithm_py_env/Lib/site-packages/osgeo;../algorithm_py_env/Lib/site-packages/rasterio;'+os.environ['PATH']");
PyRun_SimpleString("os.environ['PYTHONPATH'] = '../algorithm_py_env/Lib/site-packages/osgeo;../Bin/algorithm_py_env/Lib/site-packages/rasterio;'+os.environ['PATH']");
如果调用的三方py模块,底层使用了C 扩展模块,如:rasterio,需要将ffi.dll系列库放入C++执行目录下,才能import成功。
是否需要显式处理 ffi.dll 取决于库的实现和其对底层资源的依赖
(并非所有的第三方库都需要直接使用 ffi.dll。使用 ffi.dll 主要是在构建和编写自定义的 C 扩展模块时,或者在 Python 中调用外部的 C 函数时才会涉及到。
许多第三方库通常是使用纯 Python 编写的,而不依赖于底层的 C 扩展。这些库在其实现中可能没有直接使用到 ffi.dll 或者其作用是被封装在库内部,因此用户在使用这些库时无需显式地处理 ffi.dll。)
- C++执行目录需要放入的python相关动态库:
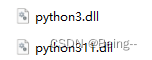
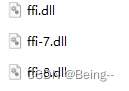
- 有依赖于C模块的py库,加入如下库(conda目录下可以找到):
如果有Qt环境,编译的时候会报错到这个地方,是和Qt的slots宏冲突了
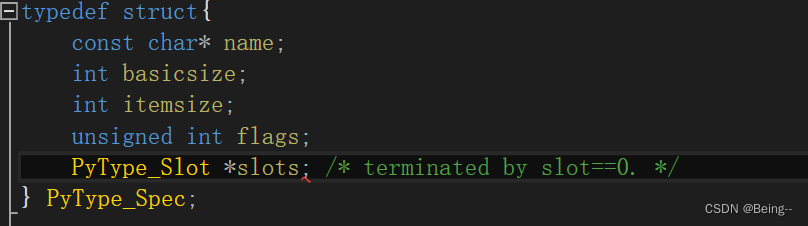
方法1. 把Python.h头文件放在最上面;
方法2. 改python的include/object.h内源码:
- 把slots宏undef后再define:
- #undef slots
- PyType_Slot *slots;
- #define slots Q_SLOTS
C++动态加载Python执行脚本
如果希望动态执行Python脚本,即每次(或者第二次以及之后)执行PyImport_ImportModule后,执行PyImport_ReloadModule来更新模块的加载。
PyObject* pModule = NULL;
PyObject* pFunc = NULL;
PyObject* pArgs = NULL;
PyObject* pRet = NULL;
pArgs = argsFunc();
std::stringstream ss;
do
{
pModule = PyImport_ImportModule(strModule.data());
if (pModule == NULL) {
ss << strModule << " module not found" << std::endl;
break;
}
if (m_bUseReload)
{
PyImport_ReloadModule(pModule); // 重新加载模块
}
pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, strFunc.data());
if (pFunc == NULL) {
ss << strFunc << " function not found" << std::endl;
break;
}
pRet = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, pArgs);
if (pRet)
{
retFunc(pRet);
}
} while (0);
//释放内存
if (NULL != pModule) Py_DECREF(pModule);
if (NULL != pFunc) Py_DECREF(pFunc);
if (NULL != pArgs) Py_DECREF(pArgs);
if (NULL != pRet) Py_DECREF(pRet);
return ss.str();
调试Python运行的小问题
[16676:0326/204323.820:ERROR:cache_util_win.cc(20)] Unable to move the cache: 拒绝访问。 (0x5)
[16676:0326/204323.820:ERROR:disk_cache.cc(205)] Unable to create cache
在windows下直接执行py文件可能报错,要用 python xxx.py 明确是用python执行
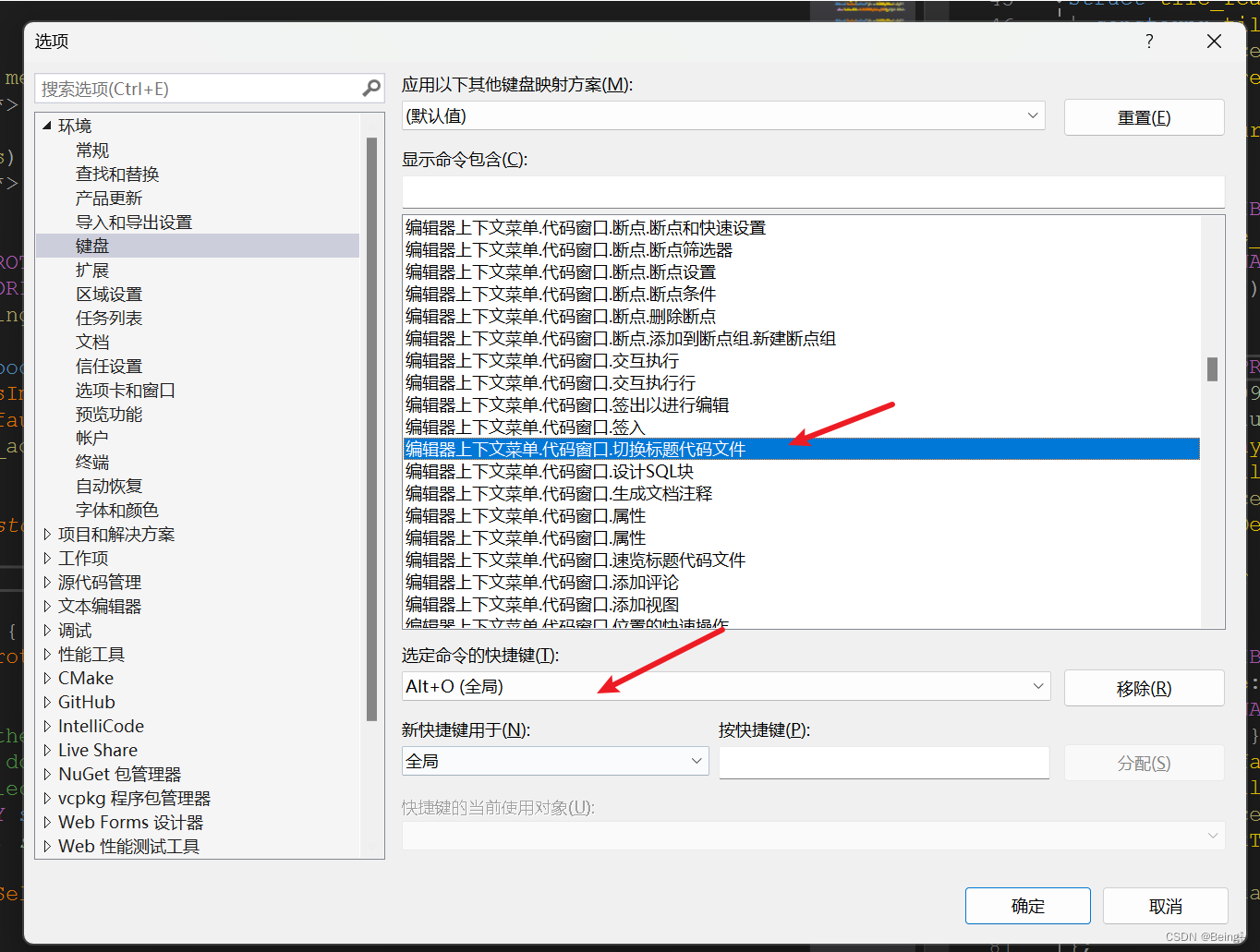
VS2022设置cpp和h的切换快捷建:Alt+o设置
个人习惯,所以特意改了
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Being__/article/details/138000064
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
