路径规划——RRT-Connect算法
路径规划——RRT-Connect算法
算法原理
RRT-Connect算法是在RRT算法的基础上进行的扩展,引入了双树生长,分别以起点和目标点为树的根节点同时扩展随机树从而实现对状态空间的快速搜索。在此算法中以两棵随机树建立连接为路径规划成功的条件。并且,在搜索过程中使用了贪婪搜索的方法,在搜索的过程中,两棵树是交替扩展的,与RRT算法不同的是,RRT-Connect算法并不是每次扩展都会进行随机采样,而是第一棵树先随机采样进而扩展一个新的节点node_new,然后第二棵树利用node_new节点往相同的方向进行多次扩展直到扩展失败才会开始下一轮的交替扩展或者与另一棵树能够建立连接了从而满足路径规划完成的条件。
这种双向的RRT算法比原始RRT算法的搜索速度更快,因为除了使用双树扩展搜索,两棵树在扩展时还是朝着对方的方向进行扩展的,并不是完全随机的。
具体的算法流程可结合上述原理以及RRT算法的实现流程。
算法实现
"""
@File: rrt-connect.py
@Brief: RRT-Connect algorithm for pathplanning
@Author: Benxiaogu
@Github: https://github.com/Benxiaogu
@CSDN: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51995147?type=blog
@Date: 2024-11-13
"""
import numpy as np
import random
import math
from itertools import combinations
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import matplotlib.patches as patches
class RRTConnect:
def __init__(self,start,goal,obstacles,board_size,max_try,max_dist,goal_sample_rate,env) -> None:
self.start = self.Node(start,None,0)
self.goal = self.Node(goal,None,0)
self.obstacles = obstacles
self.board_size = board_size
self.max_try = max_try # Number of iterations
self.max_dist = max_dist # Maximum sampling distance
self.goal_sample_rate = goal_sample_rate
self.env = env
self.inflation = 1
self.searched = []
class Node:
def __init__(self,position,parent,cost) -> None:
self.position = position
self.parent = parent
self.cost = cost
def run(self):
cost,path,expand = self.plan()
self.searched = expand
self.visualize(cost,path)
def plan(self):
nodes_forward = {self.start.position: self.start}
nodes_back = {self.goal.position: self.goal}
for iter in range(self.max_try):
# Generate a random node
node_rand = self.get_random_node()
# Get the nearest neighbor node
node_near = self.get_nearest_neighbor(list(nodes_forward.values()),node_rand)
# Get the new node
node_new = self.get_new_node(node_rand,node_near)
if node_new:
nodes_forward[node_new.position] = node_new
node_near_b = self.get_nearest_neighbor(list(nodes_back.values()), node_new)
node_new_b = self.get_new_node(node_new,node_near_b)
if node_new_b:
nodes_back[node_new_b.position] = node_new_b
# Greedy extending
while True:
for node_position, node in nodes_back.items():
if node.position == node_new.position:
print("final")
cost, path = self.extractPath(node_new, nodes_back, nodes_forward)
expand = self.get_expand(list(nodes_back.values()), list(nodes_forward.values()))
print("Exploring {} nodes.".format(iter))
return cost, path, expand
node_new_b2 = self.get_new_node(node_new,node_new_b)
if node_new_b2:
nodes_back[node_new_b2.position] = node_new_b2
node_new_b = node_new_b2
else:
break
if len(nodes_back) < len(nodes_forward):
nodes_forward, nodes_back = nodes_back, nodes_forward
return 0, None, None
def get_random_node(self):
"""
Return a random node.
"""
if random.random()>self.goal_sample_rate:
node = self.Node(
(random.uniform(0,self.env.height),random.uniform(0,self.env.width)),None,0)
else:
node = self.goal
return node
def get_nearest_neighbor(self,node_list,node):
"""
Return node that is nearest to 'node' in node_list
"""
dist = [self.distance(node, n) for n in node_list]
node_near = node_list[int(np.argmin(dist))]
return node_near
def get_new_node(self,node_rand,node_near):
"""
Return node found based on node_near and node_rand.
"""
dx = node_rand.position[0] - node_near.position[0]
dy = node_rand.position[1] - node_near.position[1]
dist = math.hypot(dx,dy)
theta = math.atan2(dy, dx)
d = min(self.max_dist,dist)
position = ((node_near.position[0]+d*math.cos(theta)),node_near.position[1]+d*math.sin(theta))
node_new = self.Node(position,node_near,node_near.cost+d)
if self.isCollision(node_new, node_near):
return None
return node_new
def isCollision(self,node1,node2):
"""
Judge collision from node1 to node2
"""
if self.isInObstacles(node1) or self.isInObstacles(node2):
return True
for rect in self.env.obs_rectangle:
if self.isInterRect(node1,node2,rect):
return True
for circle in self.env.obs_circle:
if self.isInterCircle(node1,node2,circle):
return True
return False
def distance(self,node1,node2):
dx = node2.position[0] - node1.position[0]
dy = node2.position[1] - node1.position[1]
return math.hypot(dx,dy)
def isInObstacles(self,node):
"""
Determine whether it is in obstacles or not.
"""
x,y = node.position[0],node.position[1]
for (ox,oy,w,h) in self.env.boundary:
if ox-self.inflation<x<ox+w+self.inflation and oy-self.inflation<y<oy+h+self.inflation:
return True
for (ox,oy,w,h) in self.env.obs_rectangle:
if ox-self.inflation<x<ox+w+self.inflation and oy-self.inflation<y<oy+h+self.inflation:
return True
for (ox,oy,r) in self.env.obs_circle:
if math.hypot(x-ox,y-oy)<=r+self.inflation:
return True
return False
def isInterRect(self,node1,node2,rect):
""""
Judge whether it will cross the rectangle when moving from node1 to node2
"""
ox,oy,w,h = rect
vertex = [[ox-self.inflation,oy-self.inflation],
[ox+w+self.inflation,oy-self.inflation],
[ox+w+self.inflation,oy+h+self.inflation],
[ox-self.inflation,oy+h+self.inflation]]
x1,y1 = node1.position
x2,y2 = node2.position
def cross(p1,p2,p3):
x1 = p2[0]-p1[0]
y1 = p2[1]-p1[1]
x2 = p3[0]-p1[0]
y2 = p3[1]-p1[0]
return x1*y2 - x2*y1
for v1,v2 in combinations(vertex,2):
if max(x1,x2) >= min(v1[0],v2[0]) and min(x1,x2)<=max(v1[0],v2[0]) and \
max(y1,y2) >= min(v1[1],v2[1]) and min(y1,y2) <= max(v1[1],v2[1]):
if cross(v1,v2,node1.position) * cross(v1,v2,node2.position)<=0 and \
cross(node1.position,node2.position,v1) * cross(node1.position,node2.position,v2)<=0:
return True
return False
def isInterCircle(self,node1,node2,circle):
"""
Judge whether it will cross the circle when moving from node1 to node2
"""
ox,oy,r = circle
dx = node2.position[0] - node1.position[0]
dy = node2.position[1] - node1.position[1]
# print("isInterCircle-dx:",dx)
# print("isInterCircle-dy:",dy)
d = dx * dx + dy * dy
if d==0:
return False
# Projection
t = ((ox - node1.position[0]) * dx + (oy - node1.position[1]) * dy) / d
# The projection point is on line segment AB
if 0 <= t <= 1:
closest_x = node1.position[0] + t * dx
closest_y = node1.position[1] + t * dy
# Distance from center of the circle to line segment AB
distance = math.hypot(ox-closest_x,oy-closest_y)
return distance <= r+self.inflation
return False
def extractPath(self, node_middle, nodes_back, nodes_forward):
""""
Extract the path based on the closed set.
"""
if self.start.position in nodes_back:
nodes_forward, nodes_back = nodes_back, nodes_forward
# forward
node = nodes_forward[node_middle.position]
path_forward = [node.position]
cost = node.cost
while node.position != self.start.position:
node_parent = nodes_forward[node.parent.position]
node = node_parent
path_forward.append(node.position)
# backward
node = nodes_back[node_middle.position]
path_back = []
cost += node.cost
while node.position != self.goal.position:
node_parent = nodes_back[node.parent.position]
node = node_parent
path_back.append(node.position)
path = list(reversed(path_forward))+path_back
return cost, path
def get_expand(self, nodes_back, nodes_forward):
expand = []
tree_size = max(len(nodes_forward), len(nodes_back))
for tr in range(tree_size):
if tr < len(nodes_forward):
expand.append(nodes_forward[tr])
if tr < len(nodes_back):
expand.append(nodes_back[tr])
return expand
def visualize(self, cost, path):
"""
Plot the map.
"""
...
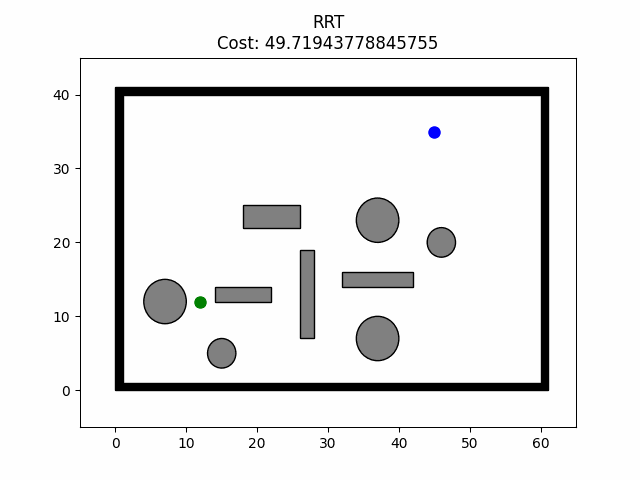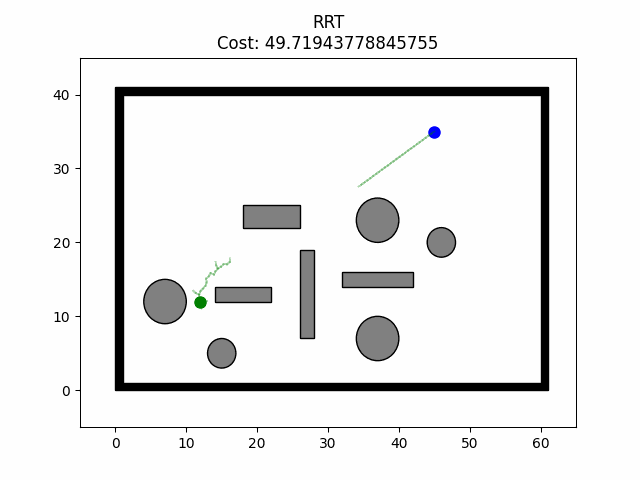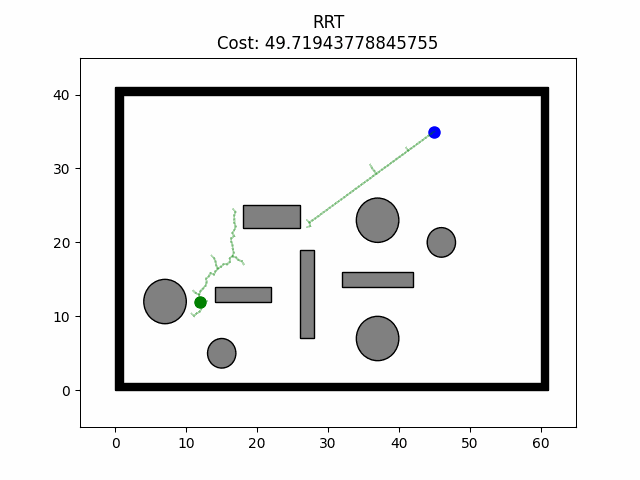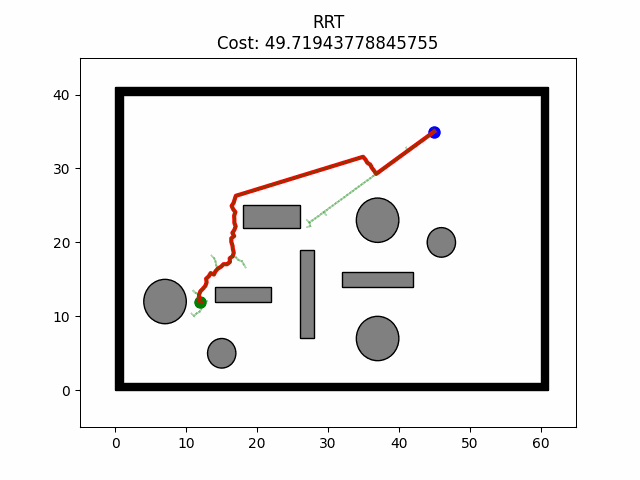
完整代码:PathPlanning
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51995147/article/details/143772185
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
