博客系统(Servlet实现)
目录
如果想要源码可以私信作者
1.准备工作
1.1创建web项目
1.2创建目录结构
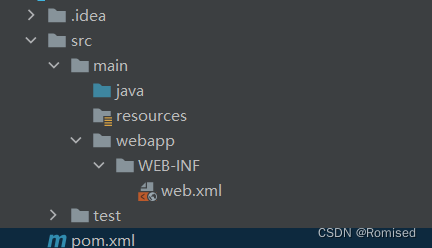
1.3配置pom.xml和web.xml
pom.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>messageWall</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet/javax.servlet-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.fasterxml.jackson.core/jackson-databind -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.14.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.16</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>web.xml:
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
</web-app>2.数据库设计
2.1表设计
当前需要设计两张表, 文章表和用户表
文章表:
create table blog (
blogId int primary key auto_increment,
-- 博客的标题
title varchar(256),
-- 博客的正文
content varchar(4096),
-- 博客的作者
userId int,
-- 博客的发布时间
postTime datetime
);用户表:
create table user (
userId int primary key auto_increment,
-- 用户名, 约定用户名不能重复.
username varchar(64) unique,
-- 密码
password varchar(64)
-- user 里还可以增加很多别的属性. github 链接, 头像链接.....
);完整SQL文件
-- 编写 SQL 完成建库建表操作.
create database if not exists blog_system charset utf8;
use blog_system;
drop table if exists user;
drop table if exists blog;
create table blog (
blogId int primary key auto_increment,
-- 博客的标题
title varchar(256),
-- 博客的正文
content varchar(4096),
-- 博客的作者
userId int,
-- 博客的发布时间
postTime datetime
);
create table user (
userId int primary key auto_increment,
-- 用户名, 约定用户名不能重复.
username varchar(64) unique,
-- 密码
password varchar(64)
-- user 里还可以增加很多别的属性. github 链接, 头像链接.....
);
-- 构造一些初始数据, 方便后续的测试.
insert into user values(1, 'zhangsan', '123'), (2, 'lisi', '123');
insert into blog values(1, '这是我的第一篇博客', '从今天开始我要好好敲代码', 1, '2023-09-23 19:00:00');
insert into blog values(2, '这是我的第二篇博客', '从昨天开始我要好好敲代码', 1, '2023-09-24 19:00:00');
insert into blog values(3, '这是我的第三篇博客', '从前天开始我要好好敲代码', 1, '2023-09-25 19:00:00');2.2封装数据库操作代码
创建DBUtil类,通过单例模式来获取数据库连接
// 通过这个类, 把数据库建立连接的逻辑进行封装.
public class DBUtil {
private static volatile DataSource dataSource = null;
private static DataSource getDataSource() {
if (dataSource == null) {
synchronized (DBUtil.class) {
if (dataSource == null) {
dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUrl("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/blog_system?useSSL=false&characterEncoding=utf8");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("123456");
}
}
}
return dataSource;
}
// 提供一个方法, 和数据库建立连接
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
return getDataSource().getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// 提供一个方法, 和数据库断开连接.
public static void close(Connection connection, PreparedStatement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
// 如果把 3 个 close 都放到同一个 try 中, 一旦前面的 close 出现异常, 就会导致后续的 close 执行不到了.
// 相比之下, 还是分开写 try 比较好.
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.3创建 Blog 类 和 User 类
Blog表示一篇博客,此处省略get、set和toString方法
public class Blog {
private int blogId;
private String title;
private String content;
private int userId;
// SQL 里有 timestamp 类型, 还有 datetime 类型.
// 使用 SQL 时, 推荐使用 datetime, 因为 timestamp 只有 4 字节, 2038 年就不够用了.
// 但是 Java 代码中的 Timestamp 是可以使用的.
private Timestamp postTime;
}User表示一个用户,此处省略get、set和toString方法
public class User {
private int userId;
private String username;
private String password;
}2.4创建 BlogDao 类和 UserDao 类
理解 DAO
DAO 全称为 "data access object",主要的功能就是对于某个数据库表进行增删改查. 一般每张数据库表会对应一个 DAO 类. 这是一种给类命名的习惯做法, 并不是强制要求.
创建BlogDao类,针对博客表进行操作
// 通过这个类, 封装针对 blog 表的增删改查操作
public class BlogDao {
// 1. 新增一个博客
// 调用 insert 的时候, 需要先构造一个 Blog 对象.
// 作为 参数 传递给 insert. 再由 insert 内部完成数据库的插入操作.
public void insert(Blog blog) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
// 1. 和数据库建立连接.
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 2. 构造 SQL 语句.
// 此处的博客发布时间, 正好是执行 SQL 的时刻. 直接使用 SQL 里的 now() 库函数, 完成获取当前时间工作.
String sql = "insert into blog values(null, ?, ?, ?, now())";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1, blog.getTitle());
statement.setString(2, blog.getContent());
statement.setInt(3, blog.getUserId());
// 3. 执行 SQL 语句.
statement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 4. 关闭连接, 释放资源
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, null);
}
}
// 2. 查询 blog 表里所有的博客
// 正常开发中, 一般不会直接把整个表里的数据都查询出来, 一般都是要指定筛选条件/最大条数的.
// 此处咱们先不考虑这么多, 就简单粗暴全都查询就行了.
public List<Blog> getBlogs() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
List<Blog> blogs = new ArrayList<>();
try {
// 1. 和数据库建立连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 2. 构造 SQL 语句
String sql = "select * from blog order by postTime desc";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 3. 执行 SQL
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
// 4. 遍历结果集合
while (resultSet.next()) {
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setBlogId(resultSet.getInt("blogId"));
blog.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
blog.setContent(resultSet.getString("content"));
blog.setUserId(resultSet.getInt("userId"));
blog.setPostTime(resultSet.getTimestamp("postTime"));
blogs.add(blog);
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
// 如果前面的查询出现问题, blogs 就会得到空的 List
return blogs;
// return null;
}
// 3. 指定 blogId, 查询某一个博客.
public Blog getBlog(int blogId) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from blog where blogId = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1, blogId);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
// 由于此处是按照 blogId 来查询, blogId 又是主键.
// 查询到的结果要么是 1 条记录, 要么是 0 条记录. 不会有别的情况.
// 因此这里就没必要循环了, 直接条件判定即可.
if (resultSet.next()) {
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setBlogId(resultSet.getInt("blogId"));
blog.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
blog.setContent(resultSet.getString("content"));
blog.setUserId(resultSet.getInt("userId"));
blog.setPostTime(resultSet.getTimestamp("postTime"));
return blog;
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return null;
}
// 4. 指定博客进行删除
public void delete(int blogId) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "delete from blog where blogId = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1, blogId);
statement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, null);
}
}
// 像修改博客这样的操作, 此处暂时不涉及.
// 同学们如果想自己实现, 代码和上述都差不多.
}
创建 UserDao 类, 实现对于用户表的增删改查.
// 使用这个类封装针对 user 表的增删改查
public class UserDao {
// 对于新增 user, 主要就是需要实现一个 "注册" 功能. 但是当前不打算实现注册.
// 对于删除 user, 主要就是需要实现一个 "注销" 功能. 但是当前也不打算实现注销.
// 1. 根据 userId 来查询用户信息. (后续根据博客查询出作者详情)
public User getUserById(int userId) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from user where userId = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1, userId);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()) {
User user = new User();
user.setUserId(resultSet.getInt("userId"));
user.setUsername(resultSet.getString("username"));
user.setPassword(resultSet.getString("password"));
return user;
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return null;
}
// 2. 根据 username 来查询用户信息. (实现登陆效果)
public User getUserByName(String username) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from user where username = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1, username);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()) {
User user = new User();
user.setUserId(resultSet.getInt("userId"));
user.setUsername(resultSet.getString("username"));
user.setPassword(resultSet.getString("password"));
return user;
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return null;
}
}
3.读取博客列表功能
3.1约定前后端交互接口
[请求]
GET /blog
[响应]
[
{
blogId: 1,
title: "第一篇博客",
content: "博客正文",
userId: 1,
postTime: "2021-07-07 12:00:00"
},
{
blogId: 2,
title: "第二篇博客",
content: "博客正文",
userId: 1,
postTime: "2021-07-07 12:10:00"
},
...
]我们约定, 浏览器给服务器发送一个 GET /blog 这样的 HTTP 请求, 服务器给浏览器返回了一个 JSON 格式的数据.
3.2实现服务器代码
创建 BlogServlet 、实现 doGet, 完成读取博客列表的功能.如果blogId为空则显示博客列表页面,如果点击了查看详情,则就会有blogId,则显示博客详情
@WebServlet("/blog")
public class BlogServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 查询数据库, 获取到数据之后, 构造成要求的 json 格式并返回.
// 先尝试获取下 blogId 这个参数, 看看能不能获取到.
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
String blogId = req.getParameter("blogId");
if (blogId == null) {
// 此时说明是获取博客列表. 没有 blogId 参数
List<Blog> blogs = blogDao.getBlogs();
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(blogs);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
} else {
// 此时说明是获取博客详情. 有 blogId 参数.
Blog blog = blogDao.getBlog(Integer.parseInt(blogId));
if (blog == null) {
// 返回一个 id 为 0 的 blog 对象. 前端再根据这里进行判定.
blog = new Blog();
}
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(blog);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
}
}
3.3实现客户端代码
使用 ajax 给服务器发送 HTTP 请求.
服务器返回的响应是一个 JSON 格式的数据, 根据这个响应数据使用 DOM API 构造页面内容.
响应中的 postTime 字段为 ms级时间戳, 需要转成格式化日期.
列表页中拿到的 "content" 字段其实是已经裁剪过的摘要.
跳转到博客详情页的 url 形如 blog_content.html?blogId=1这样就可以让博客详情页知道当前是要访问哪篇博客.
function getBlogs() {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'blog',
success: function (body) {
// 就需要根据响应的内容, 构造出 html 片段, 展示到页面上.
// 由于服务器响应中已经设置了 Content-Type 为 application/json, 此时
// jQuery 就能够自动的把此处响应的内容解析成 js 对象数组.
let containter = document.querySelector('.container-right');
for (let blog of body) {
// 根据当前这个 blog 构造出一个 html 片段.
let blogDiv = document.createElement('div');
blogDiv.className = 'blog';
// 构造标题
let titleDiv = document.createElement('div');
titleDiv.className = 'title';
titleDiv.innerHTML = blog.title;
blogDiv.appendChild(titleDiv);
// 构造发布时间
let dateDiv = document.createElement('div');
dateDiv.className = 'date';
dateDiv.innerHTML = blog.postTime;
blogDiv.appendChild(dateDiv);
// 构造摘要信息
let descDiv = document.createElement('div');
descDiv.className = 'desc';
descDiv.innerHTML = blog.content;
blogDiv.appendChild(descDiv);
// 构造 "查看全文" 按钮
let a = document.createElement("a");
a.href = 'blog_detail.html?blogId=' + blog.blogId;
a.innerHTML = '查看全文 >>';
blogDiv.appendChild(a);
// 最后把拼好的 blogDiv 添加到 container 的后面
containter.appendChild(blogDiv);
}
}
});
}运行结果:博客列表成功显示

理解数据交互过程
在刚才的页面访问过程中, 涉及两次 HTTP 请求-响应的交互. (不考虑从服务器下载 css, js, 图片等)
![]()
第一次请求: 浏览器从服务器下载 blog_list.html 页面.
第二次请求: blog_list.html 中触发了 ajax 请求, 获得到 博客列表 数据.
在前后端分离的模式中, 往往一个页面的显示需要多次 HTTP 交互过程.
4.实现博客详情
目前点击博客列表页的 "查看全文" , 能进入博客详情页, 但是这个博客详情页是写死的内容. 我们期望能够根据当前的 博客 id 从服务器动态获取博客内容.
4.1约定前后端交互接口
[请求]
GET /blog?blogId=1
[响应] {
blogId: 1,
title: "第一篇博客",
content: "博客正文",
userId: 1,
postTime: "2021-07-07 12:00:00"
},相比于博客列表页, 博客详情页的请求中多了一个 blogId 参数, 响应中只获取到一个博客的内容.
4.2实现服务器代码
在之前BlogServlet中,设置了参数blogId,如果是输入网站的话blogId就为空,点击博客列表中的查看详情,就会带一个blogId参数给当前页面,并放到Querystring中,
@WebServlet("/blog")
public class BlogServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 查询数据库, 获取到数据之后, 构造成要求的 json 格式并返回.
// 先尝试获取下 blogId 这个参数, 看看能不能获取到.
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
String blogId = req.getParameter("blogId");
if (blogId == null) {
// 此时说明是获取博客列表. 没有 blogId 参数
List<Blog> blogs = blogDao.getBlogs();
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(blogs);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
} else {
// 此时说明是获取博客详情. 有 blogId 参数.
Blog blog = blogDao.getBlog(Integer.parseInt(blogId));
if (blog == null) {
// 返回一个 id 为 0 的 blog 对象. 前端再根据这里进行判定.
blog = new Blog();
}
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(blog);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
}
}
4.3实现客户端代码
其中blog_list.html中有跳转到详情页的代码:
当用户点击这个按钮后会携带blogId参数进入blog_detail.html

修改 blog_detail.html:
其中要引入editor_md的依赖
function getBlog() {
$.ajax({
url: 'blog' + location.search,
type: 'get',
success: function (body) {
// 根据拿到的响应数据, 构造页面内容.
let h3 = document.querySelector('.container-right h3');
h3.innerHTML = body.title;
let dateDiv = document.querySelector('.container-right .date');
dateDiv.innerHTML = body.postTime;
editormd.markdownToHTML('content', {markdown: body.content});
}
});
}
getBlog();
运行结果:
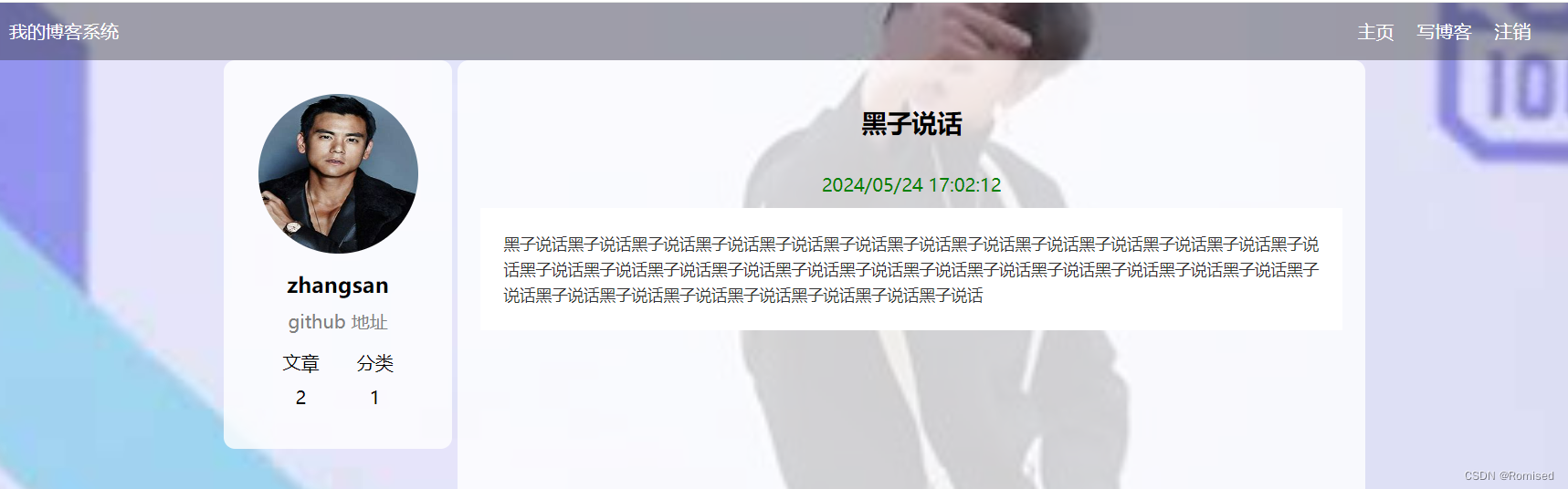
5.实现登录功能
登陆页面提供一个 form 表单, 通过 form 的方式把用户名密码提交给服务器.
服务器端验证用户名密码是否正确.
如果密码正确, 则在服务器端创建 Session ,并把 sessionId 通过 Cookie 返回给浏览器.
5.1约定前后端交互接口
[请求]
POST /login
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
username=test&password=123
[响应]
HTTP/1.1 302
Location: blog_list.html5.2实现服务器代码
创建 LoginServlet
@WebServlet("/login")
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1. 获取请求中的用户名和密码
// 给请求对象设置字符集, 保证说请求中的 username 或者 password 是中文, 也能正确处理.
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf8");
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
if (username == null || password == null || "".equals(username) || "".equals(password)) {
// 当前提交的用户名密码有误!
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("当前传过来的 username 或者 password 为空");
return;
}
// 2. 和数据库进行验证. 看当前这样的用户名和密码是否匹配.
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
User user = userDao.getUserByName(username);
if (user == null) {
// 当前提交的用户名密码有误!
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("您的用户名或者密码错误!");
return;
}
if (!password.equals(user.getPassword())) {
// 当前提交的用户名密码有误!
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("您的用户名或者密码错误!");
return;
}
// 3. 创建会话
HttpSession session = req.getSession(true);
// 把当前登录的用户信息保存到 session 中, 方便后续进行获取.
session.setAttribute("user", user);
// 4. 跳转到博客列表页.
resp.sendRedirect("blog_list.html");
}5.3实现客户端代码
修改login.html:
<div class="login-container">
<!-- 登录对话框 -->
<div class="login-dialog">
<h3>登录</h3>
<!-- 使用 form 包裹一下下列内容, 便于后续给服务器提交数据 -->
<form action="login" method="post">
<div class="row">
<span>用户名</span>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username">
</div>
<div class="row">
<span>密码</span>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password">
</div>
<div class="row">
<input type="submit" id="submit" value="登录">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>部署程序验证效果:

6.实现强制要求登陆
当用户访问 博客列表页 和 博客详情页 时, 如果用户当前尚未登陆, 就自动跳转到登陆页面.
6.1实现服务器代码
修改LoginServlet代码:添加方法检测登录状态
// 通过这个方法, 来检测当前的登录状态.
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 会话不存在, 就认为是未登录.
HttpSession session = req.getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
// 未登录
resp.setStatus(403);
return;
}
// 不仅仅是看 session 对象本身, 还需要看 user 对象存在. (为了后面实现 "退出登录" 功能)
User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
if (user == null) {
resp.setStatus(403);
return;
}
// 返回 200 表示已经登陆.
resp.setStatus(200);
}6.2实现服务器代码
单独编写一个js文件,在每个页面中都加上登录检查机制
function checkLogin() {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'login',
success: function(body) {
},
error: function(body) {
location.assign('login.html');
}
});
}7.实现显示用户信息
目前页面的用户信息部分是写死的. 形如:

我们期望这个信息可以随着用户登陆而发生改变.
如果当前页面是博客列表页, 则显示当前登陆用户的信息.
如果当前页面是博客详情页, 则显示该博客的作者用户信息.
7.1约定前后端交互接口
在博客列表页, 获取当前登陆的用户的用户信息.
[请求]
GET /user
[响应] {
userId: 1,
username: test
}在博客详情页, 获取当前文章作者的用户信息
[请求]
GET /user?blogId=1
[响应] {
userId: 1,
username: test
}7.2实现服务器代码
创建UserServlet:
@WebServlet("/user")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String blogId = req.getParameter("blogId");
if (blogId == null) {
// 博客列表页
// 从 session 中拿到 user 对象.
HttpSession session = req.getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
User user = new User();
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
return;
}
User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
if (user == null) {
user = new User();
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
return;
}
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
} else {
// 博客详情页
// 需要查询数据库了.
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
Blog blog = blogDao.getBlog(Integer.parseInt(blogId));
if (blog == null) {
User user = new User();
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
return;
}
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
User user = userDao.getUserById(blog.getUserId());
if (user == null) {
user = new User();
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
return;
}
String respJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write(respJson);
}
}
}7.3实现客户端代码
1. 修改 blog_list.html和blog_detail.html,都要加上下列代码
function getUser() {
$.ajax({
type: 'get',
url: 'user',
success: function (body) {
// body 就是解析后的 user 对象了.
let h3 = document.querySelector('.card h3');
h3.innerHTML = body.username;
}
})
}
getUser();8.实现注销登陆
8.1约定前后端交互接口
[请求]
GET /logout
[响应]
HTTP/1.1 302
Location: login.html8.2实现服务器代码
从 session 中删除掉保存的 User 对象
响应重定向到 login.html 页面.
创建 LogoutServlet:
@WebServlet("/logout")
public class LogoutServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
// 当前就是未登录状态, 谈不上退出登录!
resp.sendRedirect("login.html");
return;
}
// 之前在登录成功后, 就会给 session 中存储 user 这样的 Attribute .
// 把这个删掉之后, 自然就会判定为 "未登录" 了.
session.removeAttribute("user");
resp.sendRedirect("login.html");
}
}
9.实现发布博客
9.1约定前后端交互接口
[请求]
POST /blog
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
title=标题&content=正文 ...
[响应]
HTTP/1.1 302
Location: blog_list.html9.2实现服务器代码
修改 BlogServlet, 新增 doPost 方法.
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 1. 获取到登录的用户
// 在博客编辑页, 已经做了登录检查了. 当用户提交的时候, 必然是已经登录的状态.
HttpSession session = req.getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("用户未登录! 无法发布博客!");
return;
}
User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
if (user == null) {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("用户未登录! 无法发布博客!");
return;
}
// 2. 获取到请求中传递过来的内容
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf8"); // 这个操作不要忘, 否则遇到中文可能会乱码
String title = req.getParameter("title");
String content = req.getParameter("content");
if (title == null || content == null || "".equals(title) || "".equals(content)) {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("标题或者正文为空");
return;
}
// 3. 构造 Blog 对象, 并且插入到数据库中.
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setTitle(title);
blog.setContent(content);
blog.setUserId(user.getUserId());
// 由于在 sql 插入数据的时候, 已经使用 sql 自带的 now 获取当前时间, 不需要此处代码中手动设置时间了.
blog.setPostTime(new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));
BlogDao blogDao = new BlogDao();
blogDao.insert(blog);
// 4. 跳转到博客列表页
resp.sendRedirect("blog_list.html");
}9.3实现客户端代码
修改 blog_edit.html 页面结构,
增加 form 标签, action 为 blog_edit , method 为 POST
给 form 指定 height: 100%; 防止编辑器高度不能正确展开. . 给标题的 input 标签加上 name 属性
把提交按钮改成 <input type="submit" value="发布文章"> •
在 <div id="editor"> 里面加上一个隐藏的 textarea
<!-- 博客编辑页的版心 -->
<div class="blog-edit-container">
<form action="blog" method="post">
<!-- 标题编辑区 -->
<div class="title">
<input type="text" id="title-input" name="title">
<input type="submit" id="submit">
</div>
<!-- 博客编辑器 -->
<!-- 把 md 编辑器放到这个 div 中 -->
<div id="editor">
<textarea name="content" style="display: none;"></textarea>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<script src="js/app.js"></script>
<script>
var editor = editormd("editor", {
// 这里的尺寸必须在这里设置. 设置样式会被 editormd 自动覆盖掉.
width: "100%",
// 设定编辑器高度
height: "calc(100% - 50px)",
// 编辑器中的初始内容
markdown: "# 在这里写下一篇博客",
// 指定 editor.md 依赖的插件路径
path: "editor.md/lib/"
});
checkLogin();
</script>原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Romised/article/details/139173177
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
