NIO基础
一、三大组件
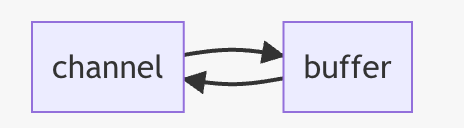
1.1 Channel
channel 有一点类似于 stream,它就是读写数据的双向通道,可以从 channel 将数据读入 buffer,也可以将 buffer 的数据写入 channel。
而之前的 stream 要么是输入,要么是输出,channel 比 stream 更为底层
常见的 Channel 有
- FileChannel
- DatagramChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
1.2 Buffer
buffer 则用来缓冲读写数据。
常见的 buffer 有:
- ByteBuffer
- MappedByteBuffer
- DirectByteBuffer
- HeapByteBuffer
- ShortBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
- CharBuffer
1.3 Selector
selector 可以理解为:事件触发后,对应处理方式的选择器。
单从字面意思不好理解,需要结合服务器的设计演化来理解它的用途。
1、多线程版设计

缺点:
- 内存占用高
- 线程上下文切换成本高
- 只适合连接数少的场景
2、线程池版设计

缺点:
- 阻塞模式下,线程仅能处理一个 socket 连接
- 仅适合短连接场景
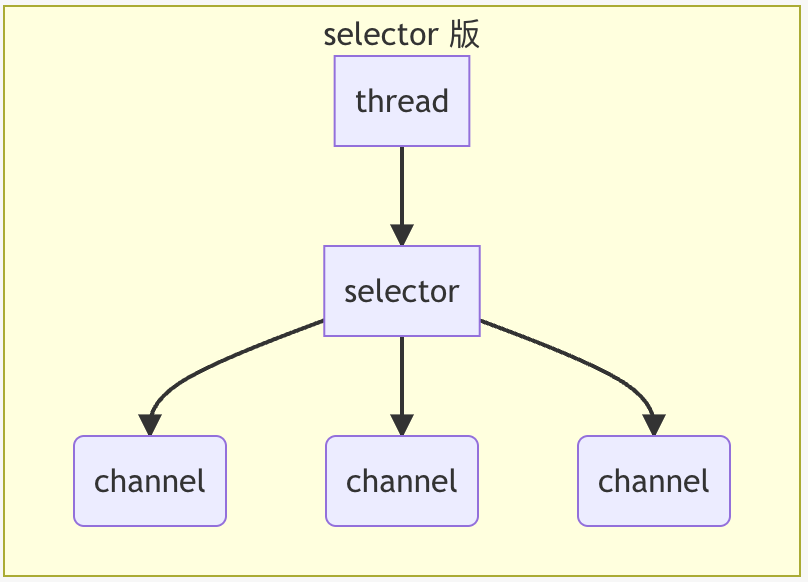
3、selector 版设计
selector 的作用就是配合一个线程来管理多个 channel,获取这些 channel 上发生的事件。
这些 channel 工作在非阻塞模式下,不会让线程吊死在一个 channel 上。
适合连接数特别多,但流量低的场景(low traffic)。

调用 selector 的 select() 会阻塞直到 channel 发生了读写就绪事件。
这些事件发生,select 方法就会返回这些事件交给 thread 来处理。
二、 ByteBuffer
有一普通文本文件 data.txt,内容为
1234567890abcd使用 FileChannel 来读取文件内容
public class ChannelDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("helloword/data.txt", "rw")) {
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
do {
// 向 buffer 写入
int len = channel.read(buffer);
log.debug("读到字节数:{}", len);
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
// 切换 buffer 读模式
buffer.flip();
while(buffer.hasRemaining()) {
log.debug("{}", (char)buffer.get());
}
// 切换 buffer 写模式
buffer.clear();
} while (true);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}输出:
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 读到字节数:10
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 1
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 2
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 3
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 4
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 5
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 6
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 7
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 8
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 9
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 0
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 读到字节数:4
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - a
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - b
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - c
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - d
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 读到字节数:-12.1 ByteBuffer 使用方式
- 向 buffer 写入数据,例如调用 channel.read(buffer)
- 调用 flip() 切换至读模式
- 从 buffer 读取数据,例如调用 buffer.get()
- 调用 clear() 或 compact() 切换至写模式
- 重复 1~4 步骤
2.2 ByteBuffer 结构
ByteBuffer 有以下重要属性
- capacity
- position
- limit
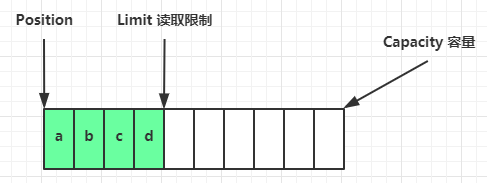
一开始,初始状态:

写模式下,position 是写入位置,limit 等于容量,下图表示写入了 4 个字节后的状态

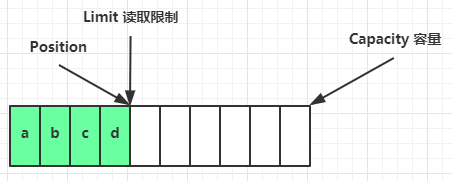
flip 动作发生后,position 切换为读取位置,limit 切换为读取限制
读取 4 个字节后,状态
clear 动作发生后,内容清空,切换成写模式

compact 方法,是把未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式

2.3 ByteBuffer 常见方法
分配空间:
可以使用 allocate 方法为 ByteBuffer 分配空间,其它 buffer 类也有该方法
Bytebuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);向 buffer 写入数据:
有两种办法
- 调用 channel 的 read 方法
- 调用 buffer 自己的 put 方法
int readBytes = channel.read(buf);
//或
buf.put((byte)127);从 buffer 读取数据:
同样有两种办法
- 调用 channel 的 write 方法
- 调用 buffer 自己的 get 方法
int writeBytes = channel.write(buf);
//或
byte b = buf.get();get 方法会让 position 读指针向后走,如果想重复读取数据
- 可以调用 rewind 方法将 position 重新置为 0
- 或者调用 get(int i) 方法获取索引 i 的内容,它不会移动读指针
mark 和 reset:
mark 是在读取时,做一个标记,即使 position 改变,只要调用 reset 就能回到 mark 的位置
注意 rewind 和 flip 都会清除 mark 位置
字符串与 ByteBuffer 互转:
ByteBuffer buffer1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("你好");
ByteBuffer buffer2 = Charset.forName("utf-8").encode("你好");
CharBuffer buffer3 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1);
System.out.println(buffer3.getClass());
System.out.println(buffer3.toString());注意:Buffer 是非线程安全的
2.4 散射读取
Scattering Reads,分散读取,有一个文本文件 3parts.txt
onetwothree使用如下方式读取,可以将数据填充至多个 buffer
try (RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("helloword/3parts.txt", "rw")) {
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
ByteBuffer a = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer c = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{a, b, c});
a.flip();
b.flip();
c.flip();
debug(a);
debug(b);
debug(c);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}2.5 聚集写入
Gathering Writes,聚集写入。使用如下方式写入,可以将多个 buffer 的数据填充至 channel
try (RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("helloword/3parts.txt", "rw")) {
ByteBuffer d = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
ByteBuffer e = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
d.put(new byte[]{'f', 'o', 'u', 'r'});
e.put(new byte[]{'f', 'i', 'v', 'e'});
d.flip();
e.flip();
//从11处开始写
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
channel.position(11);
channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{d, e});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}写入后文件内容
onetwothreefourfive2.6 练习
网络上有多条数据发送给服务端,数据之间使用 \n 进行分隔。
但由于某种原因这些数据在接收时,被进行了重新组合,例如原始数据有3条为
- Hello,world\n
- I'm zhangsan\n
- How are you?\n
变成了下面的两个 byteBuffer (黏包,半包)
- Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo
- w are you?\n
编写程序,将错乱的数据恢复成原始的按 \n 分隔的数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer source = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
source.put("Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo".getBytes());
split(source);
source.put("w are you?\nhaha!\n".getBytes());
split(source);
}
private static void split(ByteBuffer source) {
source.flip();
int oldLimit = source.limit();
for (int i = 0; i < oldLimit; i++) {
if (source.get(i) == '\n') {
System.out.println(i);
ByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(i + 1 - source.position());
// 0 ~ limit
source.limit(i + 1);
// 读之后,position也变了
target.put(source);
debugAll(target);
source.limit(oldLimit);
}
}
source.compact();
}三、文件编程
3.1 FileChannel
FileChannel 工作模式
FileChannel 只能工作在阻塞模式下
获取
不能直接打开 FileChannel,必须通过 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 来获取 FileChannel,它们都有 getChannel 方法
- 通过 FileInputStream 获取的 channel 只能读
- 通过 FileOutputStream 获取的 channel 只能写
- 通过 RandomAccessFile 是否能读写根据构造 RandomAccessFile 时的读写模式决定
读取
会从 channel 读取数据填充 ByteBuffer,返回值表示读到了多少字节,-1 表示到达了文件的末尾
int readBytes = channel.read(buffer);写入
写入的正确姿势如下
ByteBuffer buffer = ...;
buffer.put(...); // 存入数据
buffer.flip(); // 切换读模式
while(buffer.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(buffer);
}在 while 中调用 channel.write 是因为 write 方法并不能保证一次将 buffer 中的内容全部写入 channel
关闭
channel 必须关闭,不过调用了 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 的 close 方法会间接地调用 channel 的 close 方法
位置
获取当前位置
long pos = channel.position();设置当前位置
long newPos = ...;
channel.position(newPos);设置当前位置时,如果设置为文件的末尾
- 这时读取会返回 -1
- 这时写入,会追加内容,但要注意如果 position 超过了文件末尾,再写入时在新内容和原末尾之间会有空洞(00)
大小
使用 size 方法获取文件的大小
强制写入
操作系统出于性能的考虑,会将数据缓存,不是立刻写入磁盘。
可以调用 force(true) 方法将文件内容和元数据(文件的权限等信息)立刻写入磁盘
3.2 两个 Channel 传输数据
超过 2g 大小的文件传输
public class TestFileChannelTransferTo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
FileChannel from = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream("to.txt").getChannel();
) {
//数据量大时,一次拷贝完成不了
long size = from.size();
for (long left = size; left > 0; ) {
System.out.println("position:" + (size - left) + " left:" + left);
left -= from.transferTo((size - left), left, to);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}实际传输一个超大文件
position:0 left:7769948160
position:2147483647 left:5622464513
position:4294967294 left:3474980866
position:6442450941 left:13274972193.3 Path
jdk7 引入了 Path 和 Paths 类
- Path 用来表示文件路径
- Paths 是工具类,用来获取 Path 实例
Path source = Paths.get("1.txt"); // 相对路径 使用 user.dir 环境变量来定位 1.txt
Path source = Paths.get("d:\\1.txt"); // 绝对路径 代表了 d:\1.txt
Path source = Paths.get("d:/1.txt"); // 绝对路径 同样代表了 d:\1.txt
Path projects = Paths.get("d:\\data", "projects"); // 代表了 d:\data\projects- . 代表了当前路径
- .. 代表了上一级路径
例如目录结构如下
d:
|- data
|- projects
|- a
|- b代码
Path path = Paths.get("d:\\data\\projects\\a\\..\\b");
System.out.println(path);
System.out.println(path.normalize()); // 正常化路径会输出
d:\data\projects\a\..\b
d:\data\projects\b3.4 Files
检查文件是否存在
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
System.out.println(Files.exists(path));创建一级目录
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/d1");
Files.createDirectory(path);- 如果目录已存在,会抛异常 FileAlreadyExistsException
- 不能一次创建多级目录,否则会抛异常 NoSuchFileException
创建多级目录
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/d1/d2");
Files.createDirectories(path);拷贝文件
Path source = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/target.txt");
Files.copy(source, target);如果文件已存在,会抛异常 FileAlreadyExistsException
如果希望用 source 覆盖掉 target,需要用 StandardCopyOption 来控制
Files.copy(source, target, StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);移动文件
Path source = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Files.move(source, target, StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE);StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE 保证文件移动的原子性
删除文件
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/target.txt");
Files.delete(target);如果文件不存在,会抛异常 NoSuchFileException
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/d1");
Files.delete(target);Path target = Paths.get("helloword/d1"); Files.delete(target);
如果目录还有内容,会抛异常 DirectoryNotEmptyException
遍历目录文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk1.8.0_91");
AtomicInteger dirCount = new AtomicInteger();
AtomicInteger fileCount = new AtomicInteger();
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>(){
@Override
public FileVisitResult preVisitDirectory(Path dir, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
System.out.println(dir);
dirCount.incrementAndGet();
return super.preVisitDirectory(dir, attrs);
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
System.out.println(file);
fileCount.incrementAndGet();
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
System.out.println(dirCount); // 133
System.out.println(fileCount); // 1479
}统计 jar 的数目
Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk1.8.0_91");
AtomicInteger fileCount = new AtomicInteger();
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>(){
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
if (file.toFile().getName().endsWith(".jar")) {
fileCount.incrementAndGet();
}
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
System.out.println(fileCount); // 724删除多级目录
Path path = Paths.get("d:\\a");
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>(){
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
Files.delete(file);
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult postVisitDirectory(Path dir, IOException exc) throws IOException {
Files.delete(dir);
return super.postVisitDirectory(dir, exc);
}
});删除是危险操作,确保要递归删除的文件夹没有重要内容
拷贝多级目录
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String source = "D:\\Snipaste-1.16.2-x64";
String target = "D:\\Snipaste-1.16.2-x64aaa";
Files.walk(Paths.get(source)).forEach(path -> {
try {
String targetName = path.toString().replace(source, target);
// 是目录
if (Files.isDirectory(path)) {
Files.createDirectory(Paths.get(targetName));
}
// 是普通文件
else if (Files.isRegularFile(path)) {
Files.copy(path, Paths.get(targetName));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);四、网络编程
4.1 非阻塞 vs 阻塞
4.1.1 阻塞模式
- 阻塞模式下,相关方法都会导致线程暂停
- ServerSocketChannel.accept 会在没有连接建立时让线程暂停
- SocketChannel.read 会在没有数据可读时让线程暂停
- 阻塞的表现其实就是线程暂停了,暂停期间不会占用 cpu,但线程相当于闲置
- 单线程下,阻塞方法之间相互影响,几乎不能正常工作,需要多线程支持
- 但多线程下,有新的问题,体现在以下方面
- 32 位 jvm 一个线程 320k,64 位 jvm 一个线程 1024k,如果连接数过多,必然导致 OOM,并且线程太多,反而会因为频繁上下文切换导致性能降低
- 可以采用线程池技术来减少线程数和线程上下文切换,但治标不治本,如果有很多连接建立,但长时间 inactive,会阻塞线程池中所有线程,因此不适合长连接,只适合短连接
服务器端
// 使用 nio 来理解阻塞模式, 单线程
// 0. ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
// 1. 创建了服务器
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 2. 绑定监听端口
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 3. 连接集合
List<SocketChannel> channels = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
// 4. accept 建立与客户端连接, SocketChannel 用来与客户端之间通信
log.debug("connecting...");
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept(); // 阻塞方法,线程停止运行
log.debug("connected... {}", sc);
channels.add(sc);
for (SocketChannel channel : channels) {
// 5. 接收客户端发送的数据
log.debug("before read... {}", channel);
channel.read(buffer); // 阻塞方法,线程停止运行
buffer.flip();
debugRead(buffer);
buffer.clear();
log.debug("after read...{}", channel);
}
}客户端
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
System.out.println("waiting...");4.1.2 非阻塞
- 非阻塞模式下,相关方法都会不会让线程暂停
- 在 ServerSocketChannel.accept 在没有连接建立时,会返回 null,继续运行
- SocketChannel.read 在没有数据可读时,会返回 0,但线程不必阻塞,可以去执行其它 SocketChannel 的 read 或是去执行 ServerSocketChannel.accept
- 写数据时,线程只是等待数据写入 Channel 即可,无需等 Channel 通过网络把数据发送出去
- 但非阻塞模式下,即使没有连接建立,和可读数据,线程仍然在不断运行,白白浪费了 cpu
- 数据复制过程中,线程实际还是阻塞的(AIO 改进的地方)
服务器端(客户端代码不变)
// 使用 nio 来理解非阻塞模式, 单线程
// 0. ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
// 1. 创建了服务器
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false); // 非阻塞模式
// 2. 绑定监听端口
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 3. 连接集合
List<SocketChannel> channels = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
// 4. accept 建立与客户端连接, SocketChannel 用来与客户端之间通信
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept(); // 非阻塞,线程还会继续运行,如果没有连接建立,但sc是null
if (sc != null) {
log.debug("connected... {}", sc);
sc.configureBlocking(false); // 非阻塞模式
channels.add(sc);
}
for (SocketChannel channel : channels) {
// 5. 接收客户端发送的数据
int read = channel.read(buffer);// 非阻塞,线程仍然会继续运行,如果没有读到数据,read 返回 0
if (read > 0) {
buffer.flip();
debugRead(buffer);
buffer.clear();
log.debug("after read...{}", channel);
}
}
}4.1.3 多路复用
单线程可以配合 Selector 完成对多个 Channel 可读写事件的监控,这称之为多路复用
- 多路复用仅针对网络 IO、普通文件 IO 没法利用多路复用
- 如果不用 Selector 的非阻塞模式,线程大部分时间都在做无用功,而 Selector 能够保证
- 有可连接事件时才去连接
- 有可读事件才去读取
- 有可写事件才去写入: 限于网络传输能力,Channel 未必时时可写,一旦 Channel 可写,会触发 Selector 的可写事件
4.2 Selector
好处
- 一个线程配合 selector 就可以监控多个 channel 的事件,事件发生线程才去处理。避免非阻塞模式下所做无用功
- 让这个线程能够被充分利用
- 节约了线程的数量
- 减少了线程上下文切换
创建
Selector selector = Selector.open();绑定 Channel 事件
也称之为注册事件,绑定的事件 selector 才会关心
channel.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey key = channel.register(selector, 绑定事件);- channel 必须工作在非阻塞模式
- FileChannel 没有非阻塞模式,因此不能配合 selector 一起使用
- 绑定的事件类型可以有
- connect - 客户端连接成功时触发
- accept - 服务器端成功接受连接时触发
- read - 数据可读入时触发,有因为接收能力弱,数据暂不能读入的情况
- write - 数据可写出时触发,有因为发送能力弱,数据暂不能写出的情况
监听 Channel 事件
可以通过下面三种方法来监听是否有事件发生,方法的返回值代表有多少 channel 发生了事件
方法1,阻塞直到绑定事件发生
int count = selector.select();方法2,阻塞直到绑定事件发生,或是超时(时间单位为 ms)
int count = selector.select(long timeout);方法3,不会阻塞,也就是不管有没有事件,立刻返回,自己根据返回值检查是否有事件
int count = selector.selectNow();select 何时不阻塞
- 事件发生时
- 客户端发起连接请求,会触发 accept 事件
- 客户端发送数据过来,客户端正常、异常关闭时,都会触发 read 事件,另外如果发送的数据大于 buffer 缓冲区,会触发多次读取事件
- channel 可写,会触发 write 事件
- 在 linux 下 nio bug 发生时
- 调用 selector.wakeup()
- 调用 selector.close()
- selector 所在线程 interrupt
4.3 处理 accept 事件
客户端代码
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 8080)) {
System.out.println(socket);
socket.getOutputStream().write("world".getBytes());
System.in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}服务器端代码
public class ChannelDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open()) {
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
System.out.println(channel);
Selector selector = Selector.open();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
int count = selector.select();
// 获取所有事件
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
// 遍历所有事件,逐一处理
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = keys.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
// 判断事件类型
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel c = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
// 必须处理
SocketChannel sc = c.accept();
log.debug("{}", sc);
}
// 处理完毕,必须将事件移除
iter.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}事件发生后,要么处理,要么取消(cancel),不能什么都不做,否则下次该事件仍会触发,这是因为 nio 底层使用的是水平触发
4.4 处理 read 事件
4.4.1 示例
public class ChannelDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open()) {
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
System.out.println(channel);
Selector selector = Selector.open();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
int count = selector.select();
// 获取所有事件
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
// 遍历所有事件,逐一处理
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = keys.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
// 判断事件类型
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel c = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = c.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
log.debug("连接已建立: {}", sc);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
int read = sc.read(buffer);
if(read == -1) {
key.cancel();
sc.close();
} else {
buffer.flip();
debug(buffer);
}
}
iter.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}为何要 iter.remove()
select 在事件发生后,就会将相关的 key 放入 selectedKeys 集合,但不会在处理完后从 selectedKeys 集合中移除,需要我们自己编码删除。 第一次触发了 ssckey 上的 accept 事件,没有移除 ssckey. 第二次触发了 sckey 上的 read 事件,但这时 selectedKeys 中还有上次的 ssckey ,在处理时因为没有真正的 serverSocket 连上了,就会导致空指针异常
cancel 的作用
cancel 会取消注册在 selector 上的 channel,并从 keys 集合中删除 key 后续不会再监听事件
4.4.2 边界处理问题
问题示例:
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(9000);
while (true) {
Socket s = ss.accept();
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
// 这里这么写,有没有问题
byte[] arr = new byte[4];
while(true) {
int read = in.read(arr);
// 这里这么写,有没有问题
if(read == -1) {
break;
}
System.out.println(new String(arr, 0, read));
}
}
}
}客户端
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket max = new Socket("localhost", 9000);
OutputStream out = max.getOutputStream();
out.write("hello".getBytes());
out.write("world".getBytes());
out.write("你好".getBytes());
max.close();
}
}输出
hell
owor
ld�
�好处理消息的边界:

- 一种思路是固定消息长度,数据包大小一样,服务器按预定长度读取,缺点是浪费带宽
- 另一种思路是按分隔符拆分,缺点是效率低
- TLV 格式,即 Type 类型、Length 长度、Value 数据,类型和长度已知的情况下,就可以方便获取消息大小,分配合适的 buffer,缺点是 buffer 需要提前分配,如果内容过大,则影响 server 吞吐量
- Http 1.1 是 TLV 格式
- Http 2.0 是 LTV 格式
4.4.2.1 按分割符示例

服务器端
private static void split(ByteBuffer source) {
source.flip();
for (int i = 0; i < source.limit(); i++) {
// 找到一条完整消息
if (source.get(i) == '\n') {
int length = i + 1 - source.position();
// 把这条完整消息存入新的 ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(length);
// 从 source 读,向 target 写
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
target.put(source.get());
}
debugAll(target);
}
}
source.compact(); // 0123456789abcdef position 16 limit 16
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建 selector, 管理多个 channel
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
// 2. 建立 selector 和 channel 的联系(注册)
// SelectionKey 就是将来事件发生后,通过它可以知道事件和哪个channel的事件
SelectionKey sscKey = ssc.register(selector, 0, null);
// key 只关注 accept 事件
sscKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
log.debug("sscKey:{}", sscKey);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
while (true) {
// 3. select 方法, 没有事件发生,线程阻塞,有事件,线程才会恢复运行
// select 在事件未处理时,它不会阻塞, 事件发生后要么处理,要么取消,不能置之不理
selector.select();
// 4. 处理事件, selectedKeys 内部包含了所有发生的事件
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); // accept, read
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
// 处理key 时,要从 selectedKeys 集合中删除,否则下次处理就会有问题
iter.remove();
log.debug("key: {}", key);
// 5. 区分事件类型
if (key.isAcceptable()) { // 如果是 accept
ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = channel.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16); // attachment
// 将一个 byteBuffer 作为附件关联到 selectionKey 上
SelectionKey scKey = sc.register(selector, 0, buffer);
scKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
log.debug("{}", sc);
log.debug("scKey:{}", scKey);
} else if (key.isReadable()) { // 如果是 read
try {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); // 拿到触发事件的channel
// 获取 selectionKey 上关联的附件
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
int read = channel.read(buffer); // 如果是正常断开,read 的方法的返回值是 -1
if(read == -1) {
key.cancel();
} else {
split(buffer);
// 需要扩容
if (buffer.position() == buffer.limit()) {
ByteBuffer newBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(buffer.capacity() * 2);
buffer.flip();
newBuffer.put(buffer); // 0123456789abcdef3333\n
key.attach(newBuffer);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
key.cancel(); // 因为客户端断开了,因此需要将 key 取消(从 selector 的 keys 集合中真正删除 key)
}
}
}
}
}客户端
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
SocketAddress address = sc.getLocalAddress();
// sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("hello\nworld\n"));
sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("0123\n456789abcdef"));
sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("0123456789abcdef3333\n"));
System.in.read();ByteBuffer 大小分配
- 每个 channel 都需要记录可能被切分的消息,因为 ByteBuffer 不能被多个 channel 共同使用,因此需要为每个 channel 维护一个独立的 ByteBuffer
- ByteBuffer 不能太大,比如一个 ByteBuffer 1Mb 的话,要支持百万连接就要 1Tb 内存,因此需要设计大小可变的 ByteBuffer
- 一种思路是首先分配一个较小的 buffer,例如 4k,如果发现数据不够,再分配 8k 的 buffer,将 4k buffer 内容拷贝至 8k buffer,优点是消息连续容易处理,缺点是数据拷贝耗费性能,参考实现 Java Resizable Array
- 另一种思路是用多个数组组成 buffer,一个数组不够,把多出来的内容写入新的数组,与前面的区别是消息存储不连续解析复杂,优点是避免了拷贝引起的性能损耗
4.5 处理 write 事件
一次无法写完例子:
- 非阻塞模式下,无法保证把 buffer 中所有数据都写入 channel,因此需要追踪 write 方法的返回值(代表实际写入字节数)
- 用 selector 监听所有 channel 的可写事件,每个 channel 都需要一个 key 来跟踪 buffer,但这样又会导致占用内存过多,就有两阶段策略
- 当消息处理器第一次写入消息时,才将 channel 注册到 selector 上
- selector 检查 channel 上的可写事件,如果所有的数据写完了,就取消 channel 的注册
- 如果不取消,会每次可写均会触发 write 事件
public class WriteServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while(true) {
selector.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey sckey = sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 1. 向客户端发送内容
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 3000000; i++) {
sb.append("a");
}
ByteBuffer buffer = Charset.defaultCharset().encode(sb.toString());
int write = sc.write(buffer);
// 3. write 表示实际写了多少字节
System.out.println("实际写入字节:" + write);
// 4. 如果有剩余未读字节,才需要关注写事件
if (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
// read 1 write 4
// 在原有关注事件的基础上,多关注 写事件
sckey.interestOps(sckey.interestOps() + SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
// 把 buffer 作为附件加入 sckey
sckey.attach(buffer);
}
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
int write = sc.write(buffer);
System.out.println("实际写入字节:" + write);
if (!buffer.hasRemaining()) { // 写完了
key.interestOps(key.interestOps() - SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
key.attach(null);
}
}
}
}
}
}客户端
public class WriteClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT | SelectionKey.OP_READ);
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
int count = 0;
while (true) {
selector.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isConnectable()) {
System.out.println(sc.finishConnect());
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024 * 1024);
count += sc.read(buffer);
buffer.clear();
System.out.println(count);
}
}
}
}
}write 为何要取消
只要向 channel 发送数据时,socket 缓冲可写,这个事件会频繁触发,因此应当只在 socket 缓冲区写不下时再关注可写事件,数据写完之后再取消关注
4.6 利用多线程优化
现在都是多核 cpu,设计时要充分考虑别让 cpu 的力量被白白浪费。
前面的代码只有一个选择器,没有充分利用多核 cpu,如何改进呢?
分两组选择器
- 单线程配一个选择器,专门处理 accept 事件
- 创建 cpu 核心数的线程,每个线程配一个选择器,轮流处理 read 事件
public class ChannelDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new BossEventLoop().register();
}
@Slf4j
static class BossEventLoop implements Runnable {
private Selector boss;
private WorkerEventLoop[] workers;
private volatile boolean start = false;
AtomicInteger index = new AtomicInteger();
public void register() throws IOException {
if (!start) {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
boss = Selector.open();
SelectionKey ssckey = ssc.register(boss, 0, null);
ssckey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
workers = initEventLoops();
new Thread(this, "boss").start();
log.debug("boss start...");
start = true;
}
}
public WorkerEventLoop[] initEventLoops() {
WorkerEventLoop[] workerEventLoops = new WorkerEventLoop[2];
for (int i = 0; i < workerEventLoops.length; i++) {
workerEventLoops[i] = new WorkerEventLoop(i);
}
return workerEventLoops;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
boss.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = boss.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel c = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = c.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
log.debug("{} connected", sc.getRemoteAddress());
workers[index.getAndIncrement() % workers.length].register(sc);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Slf4j
static class WorkerEventLoop implements Runnable {
private Selector worker;
private volatile boolean start = false;
private int index;
private final ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Runnable> tasks = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
public WorkerEventLoop(int index) {
this.index = index;
}
public void register(SocketChannel sc) throws IOException {
if (!start) {
worker = Selector.open();
new Thread(this, "worker-" + index).start();
start = true;
}
tasks.add(() -> {
try {
SelectionKey sckey = sc.register(worker, 0, null);
sckey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
worker.selectNow();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
worker.wakeup();
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
worker.select();
Runnable task = tasks.poll();
if (task != null) {
task.run();
}
Set<SelectionKey> keys = worker.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = keys.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
try {
int read = sc.read(buffer);
if (read == -1) {
key.cancel();
sc.close();
} else {
buffer.flip();
log.debug("{} message:", sc.getRemoteAddress());
debugAll(buffer);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
key.cancel();
sc.close();
}
}
iter.remove();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}4.7 UDP
- UDP 是无连接的,client 发送数据不会管 server 是否开启
- server 这边的 receive 方法会将接收到的数据存入 byte buffer,但如果数据报文超过 buffer 大小,多出来的数据会被默默抛弃
服务器端
public class UdpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (DatagramChannel channel = DatagramChannel.open()) {
channel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
System.out.println("waiting...");
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
channel.receive(buffer);
buffer.flip();
debug(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}输出
waiting...
客户端
public class UdpClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (DatagramChannel channel = DatagramChannel.open()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9999);
channel.send(buffer, address);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}服务器端输出
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f |hello |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+五、NIO vs BIO
5.1 stream vs channel
- stream 不会自动缓冲数据,channel 会利用系统提供的发送缓冲区、接收缓冲区(更为底层)
- stream 仅支持阻塞 API,channel 同时支持阻塞、非阻塞 API,网络 channel 可配合 selector 实现多路复用
- 二者均为全双工,即读写可以同时进行
5.2 IO 模型
同步阻塞、同步非阻塞、同步多路复用、异步阻塞(没有此情况)、异步非阻塞
- 同步:线程自己去获取结果(一个线程)
- 异步:线程自己不去获取结果,而是由其它线程送结果(至少两个线程)
当调用一次 channel.read 或 stream.read 后,会切换至操作系统内核态来完成真正数据读取,而读取又分为两个阶段,分别为:
- 等待数据阶段
- 复制数据阶段

- 阻塞 IO

- 非阻塞 IO

- 多路复用

- 异步 IO

- 阻塞 IO vs 多路复用


5.3 零拷贝
5.3.1 传统 IO 问题
传统的 IO 将一个文件通过 socket 写出
File f = new File("helloword/data.txt");
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
byte[] buf = new byte[(int)f.length()];
file.read(buf);
Socket socket = ...;
socket.getOutputStream().write(buf);内部工作流程是这样的:

- java 本身并不具备 IO 读写能力,因此 read 方法调用后,要从 java 程序的用户态切换至内核态,去调用操作系统(Kernel)的读能力,将数据读入内核缓冲区。这期间用户线程阻塞,操作系统使用 DMA(Direct Memory Access)来实现文件读,其间也不会使用 cpu
- 从内核态切换回用户态,将数据从内核缓冲区读入用户缓冲区(即 byte[] buf),这期间 cpu 会参与拷贝,无法利用 DMA
- 调用 write 方法,这时将数据从用户缓冲区(byte[] buf)写入 socket 缓冲区,cpu 会参与拷贝
- 接下来要向网卡写数据,这项能力 java 又不具备,因此又得从用户态切换至内核态,调用操作系统的写能力,使用 DMA 将 socket 缓冲区的数据写入网卡,不会使用 cpu
可以看到中间环节较多,java 的 IO 实际不是物理设备级别的读写,而是缓存的复制,底层的真正读写是操作系统来完成的
- 用户态与内核态的切换发生了 3 次,这个操作比较重量级
- 数据拷贝了共 4 次
5.3.2 NIO 优化
通过 DirectByteBuf
- ByteBuffer.allocate(10) HeapByteBuffer 使用的还是 java 内存
- ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(10) DirectByteBuffer 使用的是操作系统内存
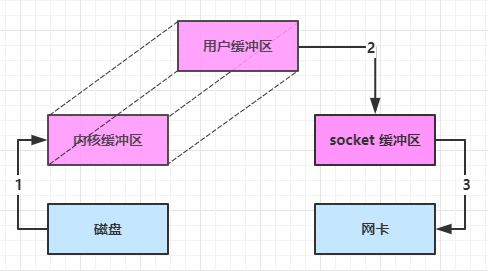
大部分步骤与优化前相同,不再赘述。唯有一点:java 可以使用 DirectByteBuf 将堆外内存映射到 jvm 内存中来直接访问使用
- 这块内存不受 jvm 垃圾回收的影响,因此内存地址固定,有助于 IO 读写
- java 中的 DirectByteBuf 对象仅维护了此内存的虚引用,内存回收分成两步
- DirectByteBuf 对象被垃圾回收,将虚引用加入引用队列
- 通过专门线程访问引用队列,根据虚引用释放堆外内存
- 减少了一次数据拷贝,用户态与内核态的切换次数没有减少
进一步优化(底层采用了 linux 2.1 后提供的 sendFile 方法),java 中对应着两个 channel 调用 transferTo/transferFrom 方法拷贝数据

- java 调用 transferTo 方法后,要从 java 程序的用户态切换至内核态,使用 DMA将数据读入内核缓冲区,不会使用 cpu
- 数据从内核缓冲区传输到 socket 缓冲区,cpu 会参与拷贝
- 最后使用 DMA 将 socket 缓冲区的数据写入网卡,不会使用 cpu
可以看到
- 只发生了一次用户态与内核态的切换
- 数据拷贝了 3 次
进一步优化(linux 2.4)
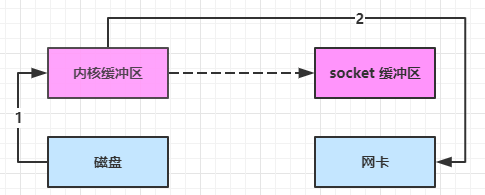
- java 调用 transferTo 方法后,要从 java 程序的用户态切换至内核态,使用 DMA将数据读入内核缓冲区,不会使用 cpu
- 只会将一些 offset 和 length 信息拷入 socket 缓冲区,几乎无消耗
- 使用 DMA 将 内核缓冲区的数据写入网卡,不会使用 cpu
整个过程仅只发生了一次用户态与内核态的切换,数据拷贝了 2 次。所谓的【零拷贝】,并不是真正无拷贝,而是在不会拷贝重复数据到 jvm 内存中,零拷贝的优点有
- 更少的用户态与内核态的切换
- 不利用 cpu 计算,减少 cpu 缓存伪共享
- 零拷贝适合小文件传输
5.3 AIO
AIO 用来解决数据复制阶段的阻塞问题
- 同步意味着,在进行读写操作时,线程需要等待结果,还是相当于闲置
- 异步意味着,在进行读写操作时,线程不必等待结果,而是将来由操作系统来通过回调方式由另外的线程来获得结果
异步模型需要底层操作系统(Kernel)提供支持 Windows 系统通过 IOCP 实现了真正的异步 IO Linux 系统异步 IO 在 2.6 版本引入,但其底层实现还是用多路复用模拟了异步 IO,性能没有优势
5.3.1 文件 AIO
先来看看 AsynchronousFileChannel
@Slf4j
public class AioDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try{
AsynchronousFileChannel s =
AsynchronousFileChannel.open(
Paths.get("1.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(2);
log.debug("begin...");
s.read(buffer, 0, null, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
log.debug("read completed...{}", result);
buffer.flip();
debug(buffer);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
log.debug("read failed...");
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("do other things...");
System.in.read();
}
}输出
13:44:56 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.aio.AioDemo1 - begin...
13:44:56 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.aio.AioDemo1 - do other things...
13:44:56 [DEBUG] [Thread-5] c.i.aio.AioDemo1 - read completed...2
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 0d |a. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+可以看到
- 响应文件读取成功的是另一个线程 Thread-5
- 主线程并没有 IO 操作阻塞
默认文件 AIO 使用的线程都是守护线程,所以最后要执行 System.in.read() 以避免守护线程意外结束
5.3.2 网络 AIO
public class AioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel ssc = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
ssc.accept(null, new AcceptHandler(ssc));
System.in.read();
}
private static void closeChannel(AsynchronousSocketChannel sc) {
try {
System.out.printf("[%s] %s close\n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), sc.getRemoteAddress());
sc.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static class ReadHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> {
private final AsynchronousSocketChannel sc;
public ReadHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel sc) {
this.sc = sc;
}
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
try {
if (result == -1) {
closeChannel(sc);
return;
}
System.out.printf("[%s] %s read\n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), sc.getRemoteAddress());
attachment.flip();
System.out.println(Charset.defaultCharset().decode(attachment));
attachment.clear();
// 处理完第一个 read 时,需要再次调用 read 方法来处理下一个 read 事件
sc.read(attachment, attachment, this);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
closeChannel(sc);
exc.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static class WriteHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> {
private final AsynchronousSocketChannel sc;
private WriteHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel sc) {
this.sc = sc;
}
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
// 如果作为附件的 buffer 还有内容,需要再次 write 写出剩余内容
if (attachment.hasRemaining()) {
sc.write(attachment);
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
closeChannel(sc);
}
}
private static class AcceptHandler implements CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object> {
private final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel ssc;
public AcceptHandler(AsynchronousServerSocketChannel ssc) {
this.ssc = ssc;
}
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel sc, Object attachment) {
try {
System.out.printf("[%s] %s connected\n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), sc.getRemoteAddress());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
// 读事件由 ReadHandler 处理
sc.read(buffer, buffer, new ReadHandler(sc));
// 写事件由 WriteHandler 处理
sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("server hello!"), ByteBuffer.allocate(16), new WriteHandler(sc));
// 处理完第一个 accpet 时,需要再次调用 accept 方法来处理下一个 accept 事件
ssc.accept(null, this);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
}
}原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/guaituo0129/article/details/140139016
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
