c++234继承



#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//public 修饰的成员便俩个和方法都能使用
//protected:类的内部 在继承的子类中可使用
class Parents
{
public:
int a;//名字
protected:
int b;//密码
private:
int c;//情人
public:
void printT()
{
cout << "printT" << endl;
}
};
class Children1 :public Parents
{
public:
void useVar()
{
a = 0;
b = 0;
//c = 0;//private
}
};
//私有继承
class Children2 :private Parents
{
public:
void useVar()
{
a = 0;
b = 0;
//c = 0;//private
}
};
class Children3 :protected Parents
{
public:
void useVar()
{
a = 0;//ok
b = 0;//ok
//c = 0;
}
};
//void main01()
//{
//Parents t1, t2;
//t1.a = 10;
////t1.b = 30;//err
////t2.c = 30;//err
//
//
//return;
//}
void main02()
{
Children2 c2;
//c1.a = 10;//err
//c2.b = 30;//err
//c3.b = 20;//err
}
void main()
{
Children3 c3;
//c3.a = 10;//err
//c3.b = 30;//err
//c3.c = 20;//err
}






调用原则:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Parent
{
public:
Parent(int a, int b)
{
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
cout << "父类构造" << endl;
}
~Parent()
{
cout << "父类析构" << endl;
}
void printP(int a, int b)
{
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
cout << "father" << endl;
}
private:
int a;
int b;
};
class child :public Parent
{
public:
child(int a, int b, int c) :Parent(a, b)
{
this->c = c;
}
~child()
{
cout << "discont" << endl;
}
void printC()
{
cout << "son" << endl;
}
private:
int c;
};
void play()
{
child c1(1, 2, 3);
}
void main()
{
//Parent p(1, 2);
//child c1(1, 2, 3);
play();
return;
}
//#include <iostream>
//#include <string>
//using namespace std;
//
//class Object
//{
//public:
// Object(int a, int b) : a(a), b(b)
// {
// cout << "obj a: " << a << " b: " << b << endl;
// }
//
//protected:
// int a;
// int b;
//};
//
//class Parent : public Object
//{
//public:
// Parent(const string& p) : Object(1, 2), obj1(3, 4), obj2(5, 6), p(p)
// {
// cout << p << endl;
// cout << "父类构造" << endl;
// }
//
// ~Parent()
// {
// cout << "父类析构" << endl;
// }
//
// void printP(int a, int b)
// {
// cout << "father" << endl;
// }
//
//protected:
// string p;
// Object obj1;
// Object obj2;
//};
//
//class child : public Parent
//{
//public:
// child(const string& p) : Parent(p), obj1(3, 4), obj2(5, 6), myp(p)
// {
//
// }
//
// ~child()
// {
// cout << "discont " << myp << endl;
// }
//
// void printC()
// {
// cout << "son " << myp << endl;
// }
//
//private:
// string myp;
// Object obj1;
// Object obj2;
//};
//
//int main()
//{
// child c1("继承");
// c1.printC();
// return 0;
//}
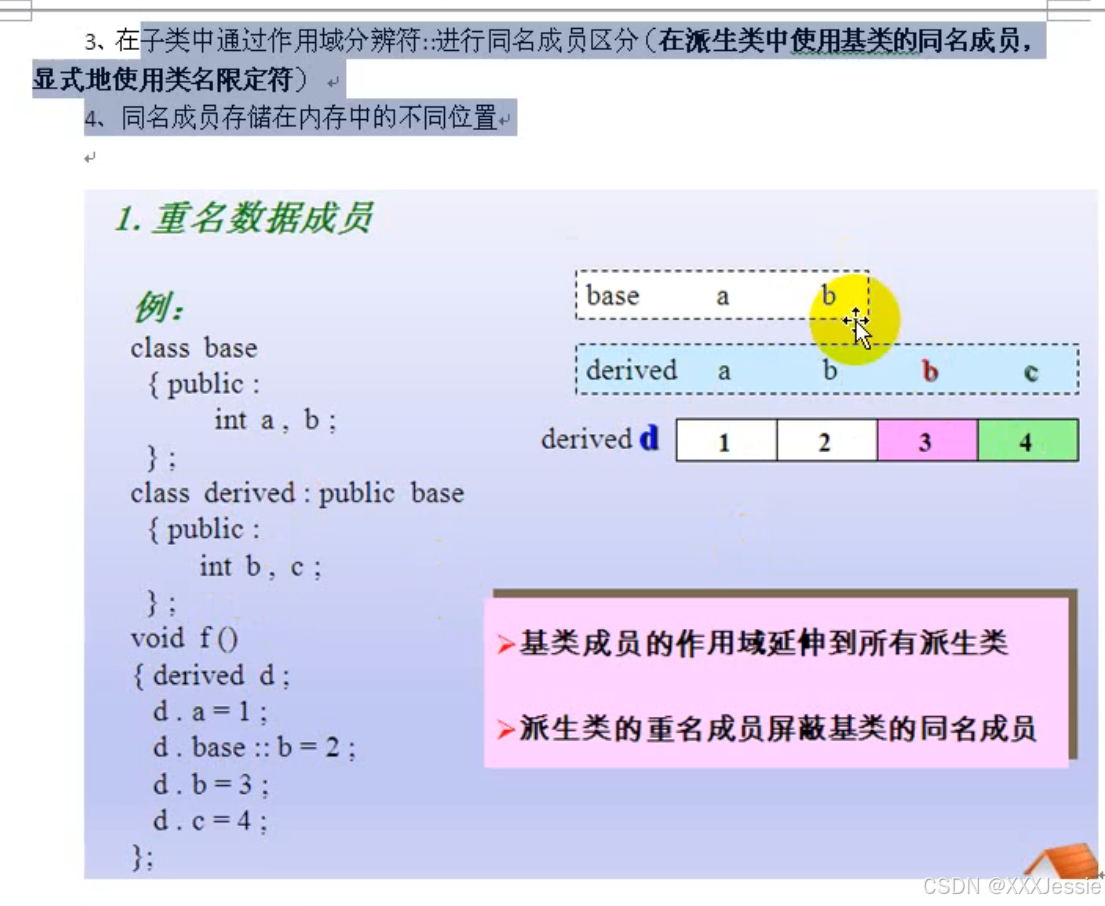
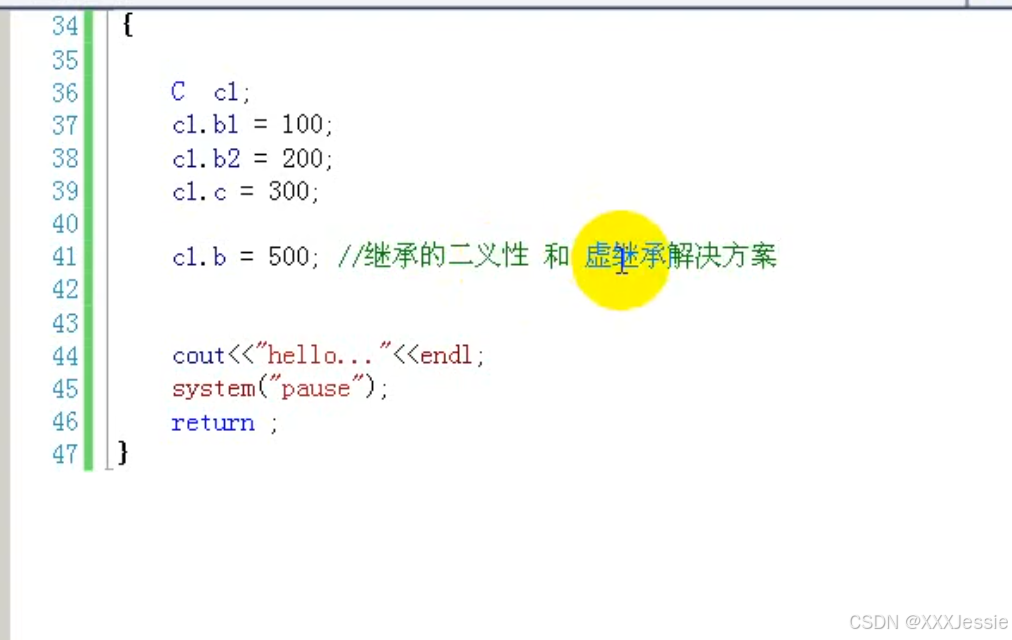
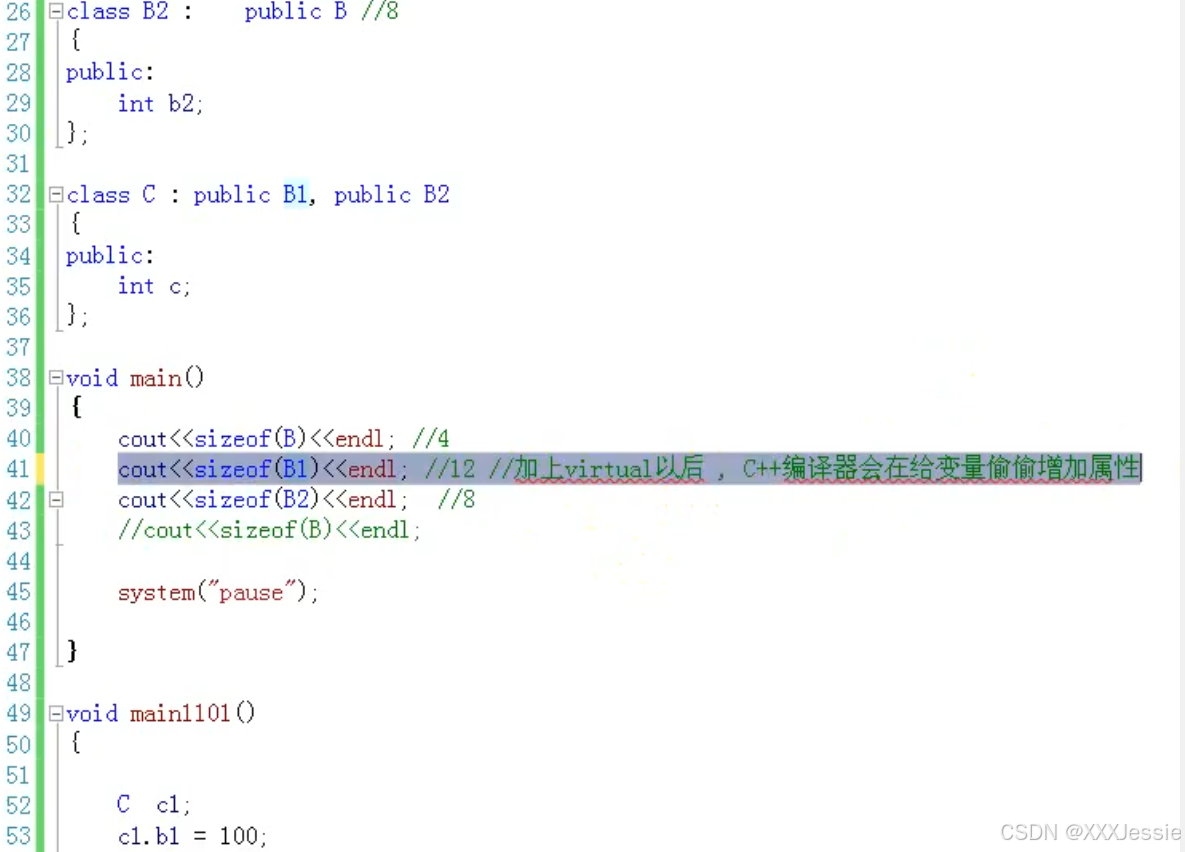
继承二义性
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_74340589/article/details/142282484
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
