C++11 数据结构1 线性表的概念,线性表的顺序存储,实现,测试

一 线性表的概念
线性结构是一种最简单且常用的数据结构。
线性结构的基本特点是节点之间满足线性关系。
本章讨论的动态数组、链表、栈、队列都属于线性结构。
他们的共同之处,是节点中有且只有一个开始节点和终端节点。按这种关系,可以把它们的所有节点排列成一个线性序列。但是,他们分别属于几种不同的抽象数据类型实现,它们之间的区别,主要就是操作的不同。
线性表是零个或者多个数据元素的有限序列,数据元素之间是有顺序的,数据元素个数是有限的,数据元素的类型必须相同
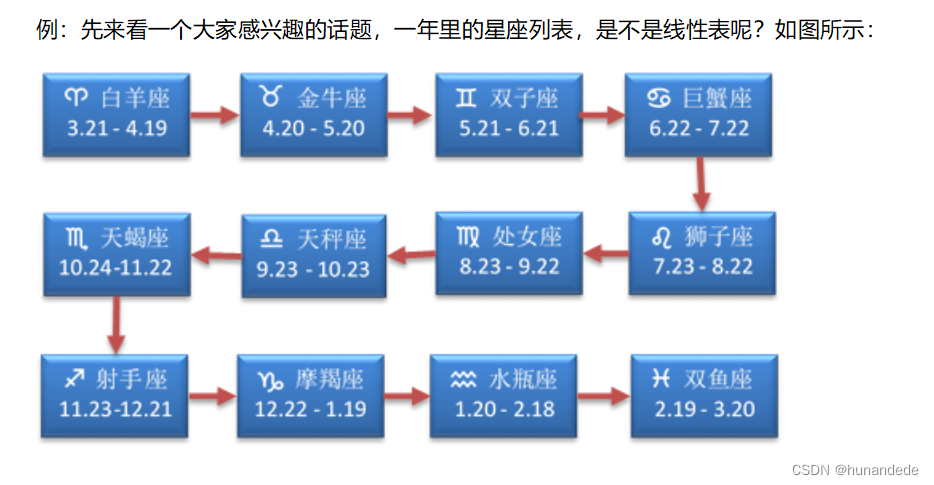
二 线性表的性质:
a)0 为性表的第一个元素,只有一个后继。
2)an 为线性表的最后一个元素,只有一个前驱。
3)除 a0 和 an 外的其它元素 ai,既有前驱,又有后继。
4)线性表能够逐项访问和顺序存取。
三 线性表顺序存储(动态数组)的设计与实现
采用顺序存储是表示线性表最简单的方法,具体做法是:将线性表中的元素一个接一个的存储在一块连续的存储区域中,这种顺序表示的线性表也成为顺序表。
1.设计底层实现
线性表的顺序存储,应该用数组的方式存储数据。
那么我们结合数组的方式想一下:应该怎么设计才合理。
数组应该有限度,例如 int arr[10],表示该数组最多能容纳10个,我们称之为数组的能力。
数组应该有实际存储的大小,例如 int arr[10],只有arr[0],arr[1]两个元素有值。该数组大小为2
数组中的元素,应该是啥?
这个数组里面每一项的内容存储啥,底层是不知道的,底层设计应该是:不管上层存储啥,都可以,那么存储的就只能是万能指针(void *),为了记忆方便:我们用 SeqListNode表示void,typedef void SeqListNode;,因此 SeqListNode* 就是一个万能指针。
那么底层的 struct 就应该出来了,注意这里,我们用
capacity 表示数组的限度,
length表示数组的实际大小,
array表示指针数组:array是一个数组,数组的每一项都是一个指针,存放上层的存储的具体类型的首地址
typedef struct _tagseqlist {
int capacity;
int length;
//int* array[];//那么这个数组应该多大才合理呢?显然,应该让使用者传递才合理,因此要换成下面的写法
int ** array;
}TSeqList;数组应该有返回值,理论上应该是底层struct 的首地址。,我们还不应该让上层知道,底层的struct 具体是啥? 因此返回给上层的应该也是void *, 为了方便,使用 SeqList表示, typedef void SeqList;因此返回值应该是 SeqList*
2.底层应该给上层提供的interface思考:
给上层创建 list 的interface,user可以自己定义想要的list的大小。
这个底层要提供的肯定有 增删改查 功能
也就是说:可以让上层存储一个具体类型的数据
删除一个具体类型的数据
查找某一个位置的具体的数据
改动某一个位置的数据(本次具体的代码中并没有实现)
3.代码实现
公用的.h文件--001seqlist.h
上层和底层公用的.h文件,这样说是因为,上层和底层有可能两个不同的公司,A公司买了B公司的产品,B是做底层的,要提供给A interface 和 动态库/静态库。因此这个interface是A和B 公用的。
#ifndef __001SEQLIST_H__
#define __001SEQLIST_H__
typedef void SeqList;
typedef void SeqListNode;
// 初始化,建立一个空的线性表
//参数capacity表示该线性表的容量。
//返回值不为NULL,表示创建成功。
//返回值为NULL,表示创建失败。
SeqList* SeqList_Create(int capacity);
//销毁该线性表
//返回值为1,表示成功。
//返回值为-1,表示失败。
int SeqList_Destory(SeqList *list);
//清空seqlist
//返回值为1,表示成功。
//返回值为-1,表示失败。
int SeqList_Clear(SeqList *list);
// 返回线性表List存在的元素个数
//返回值 >=0 表示:该list存在的元素个数
//<0 表示error
int SeqList_Length(SeqList *list);
// 返回线性表List的元素能够存储元素的能力
//返回值 >0 表示:该list能够存储元素的能力
//<0 表示error
int SeqList_Capacity(SeqList *list);
//从seqlist 中获取指定位置的数据
//参数pos:seqlist中的位置
//返回值:为存储在该位置的元素
//返回NULL 表示有问题
SeqListNode* SeqList_Get(SeqList *list, int pos);
//给seqlist中指定位置插入数据,
//参数seqlistnode为要插入的数据
//参数 pos 为要插入的位置
//如果线性表中还有空间,但是指定的pos位置是大于 现在的length
//例如 线性表capacity为100,现在存储了20了,但是pos的值是50
//我们这里做work around,就会将数据插入到21的位置
//成功返回1
//失败 返回<0
int SeqList_Insert(SeqList *list,SeqListNode *node,int pos);
//从seqlist 中删除指定位置的元素
//参数 pos
//返回值为 删除的元素
//返回NULL 表示出现了error
SeqListNode* SeqList_Delete(SeqList *list ,int pos);
#endifB公司具体的实现001seqlist.c
#include "001seqlist.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include <string.h>
//这个线性表中存储一个数组,而且数组的每一项应该都是一个地址
typedef struct _tagseqlist {
int capacity;
int length;
//int* array[];//那么这个数组应该多大才合理呢?显然,应该让使用者传递才合理,因此要换成下面的写法
int ** array;
}TSeqList;
// 初始化,建立一个空的线性表
//参数capacity表示该线性表的容量。
//返回值,表示创建成功。
//返回值null,表示创建失败。
SeqList* SeqList_Create(int capacity) {
TSeqList *tempseqlist = NULL;
tempseqlist = malloc(sizeof(TSeqList));
if (tempseqlist==NULL) {
printf("SeqList_Create error tempseqlist==NULL\n");
return NULL;
}
memset(tempseqlist,0,sizeof(TSeqList));
tempseqlist->capacity = capacity;
tempseqlist->length = 0;
tempseqlist->array = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int*) * capacity);
if (tempseqlist->array == NULL) {
printf("SeqList_Create error tempseqlist->array==NULL\n");
return NULL;
}
return tempseqlist;
}
//销毁该线性表
//返回值为1,表示成功。
//返回值为-1,表示失败。
int SeqList_Destory(SeqList *list)
{
int ret = 1;
if (list==NULL) {
printf("SeqList_Destory error list==NULL\n");
ret = -1;
return ret;
}
TSeqList *tempseqlist = NULL;
tempseqlist = (TSeqList *)list;
if (tempseqlist->array != NULL) {
free(tempseqlist->array);
tempseqlist->array = NULL;
}
if (tempseqlist!=NULL) {
free(tempseqlist);
tempseqlist = NULL;
}
return ret;
}
//清空seqlist
//返回值为1,表示成功。
//返回值为-1,表示失败。
int SeqList_Clear(SeqList *list) {
int ret = 1;
if (list == NULL) {
printf("SeqList_Clear error list==NULL\n");
ret = -1;
return ret;
}
TSeqList *tempseqlist = NULL;
tempseqlist = (TSeqList *)list;
tempseqlist->length = 0;
return ret;
}
// 返回线性表List存在的元素个数
//返回值 >=0 表示:该list存在的元素个数
//<0 表示error
int SeqList_Length(SeqList *list) {
int ret = 1;
if (list == NULL) {
printf("SeqList_Length error list==NULL\n");
ret = -1;
return ret;
}
TSeqList *tempseqlist = NULL;
tempseqlist = (TSeqList *)list;
return tempseqlist->length;
}
// 返回线性表List的元素能够存储元素的能力
//返回值 >0 表示:该list能够存储元素的能力
//<0 表示error
int SeqList_Capacity(SeqList *list) {
int ret = 1;
if (list == NULL) {
printf("SeqList_Length error list==NULL\n");
ret = -1;
return ret;
}
TSeqList *tempseqlist = NULL;
tempseqlist = (TSeqList *)list;
return tempseqlist->capacity;
}
//从seqlist 中获取指定位置的数据
//参数pos:seqlist中的位置
//返回值:为存储在该位置的元素
//返回NULL 表示有问题
SeqListNode* SeqList_Get(SeqList *list, int pos) {
SeqListNode *retSeqListNode = NULL;
if (list == NULL) {
printf("SeqList_Get error list==NULL\n");
return retSeqListNode;
}
if (pos < 0) {
printf("SeqList_Get error pos<0 pos = %d\n",pos);
return retSeqListNode;
}
TSeqList *tempseqlist = NULL;
tempseqlist = (TSeqList *)list;
if (pos > tempseqlist->length - 1 ) {
printf("SeqList_Get error pos > (tempseqlist->length - 1) pos = %d,tempseqlist->length = %d\n",
pos, tempseqlist->length);
return retSeqListNode;
}
SeqListNode *currentNode = NULL;
return tempseqlist->array[pos];
}
//给seqlist中指定位置插入数据,
//参数seqlistnode为要插入的数据
//参数 pos 为要插入的位置
//如果线性表中还有空间,但是指定的pos位置是大于 现在的length
//例如 线性表capacity为100,现在存储了20了,但是pos的值是50
//我们这里做work around,就会将数据插入到21的位置
//成功返回1
//失败 返回<0
int SeqList_Insert(SeqList *list, SeqListNode *node, int pos) {
int ret = 1;
SeqListNode *retSeqListNode = NULL;
if (list == NULL) {
ret = -1;
printf("SeqList_Insert error list==NULL ret = %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
if (node == NULL) {
ret = -2;
printf("SeqList_Insert error node==NULL ret = %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
if (pos < 0) {
ret = -3;
printf("SeqList_Insert error pos<0 pos = %d ret = %d\n", pos, ret);
return ret;
}
TSeqList *tempseqlist = NULL;
tempseqlist = (TSeqList *)list;
//如果已经满了,就没办法插入了
if (tempseqlist->capacity == tempseqlist->length) {
ret = -4;
printf("SeqList_Insert error pos<0 pos = %d ret =%d \n", pos, ret);
return ret;
}
//work around ,假设capacity为100,length这时候为20,当pos>20,小于100时,将pos变成20
//pos的值是从0开始,小于tempseqlist->capacity
if (pos > (tempseqlist->length) && pos < (tempseqlist->capacity)) {
printf("SeqList_Insert wrokaround (pos > (tempseqlist->length ) && pos < (tempseqlist->capacity)) pos = %d,tempseqlist->length = %d\n",
pos, tempseqlist->length);
pos = tempseqlist->length;
}
//正式插入数据,实际上就是将pos位置的数据往后移动,
//注意的是:i的值我们赋的是 length,这时候 array[length]是没有值的,最后一个元素是array[length-1]
//因此赋值是 tempseqlist->array[i] = tempseqlist->array[i-1];
//当i>pos的最后一次执行完毕后,i会--。这时候i的值的就是pos位置的值的了,而这时候,判断不成立
//因此这时候 i 的值就是pos的值,这时候再将 tempseqlist->array[i] = node
int i = 0;
for ( i = tempseqlist->length; i > pos;i--) {
tempseqlist->array[i] = tempseqlist->array[i-1];
}
tempseqlist->array[i] = node;
tempseqlist->length++;
return ret;
}
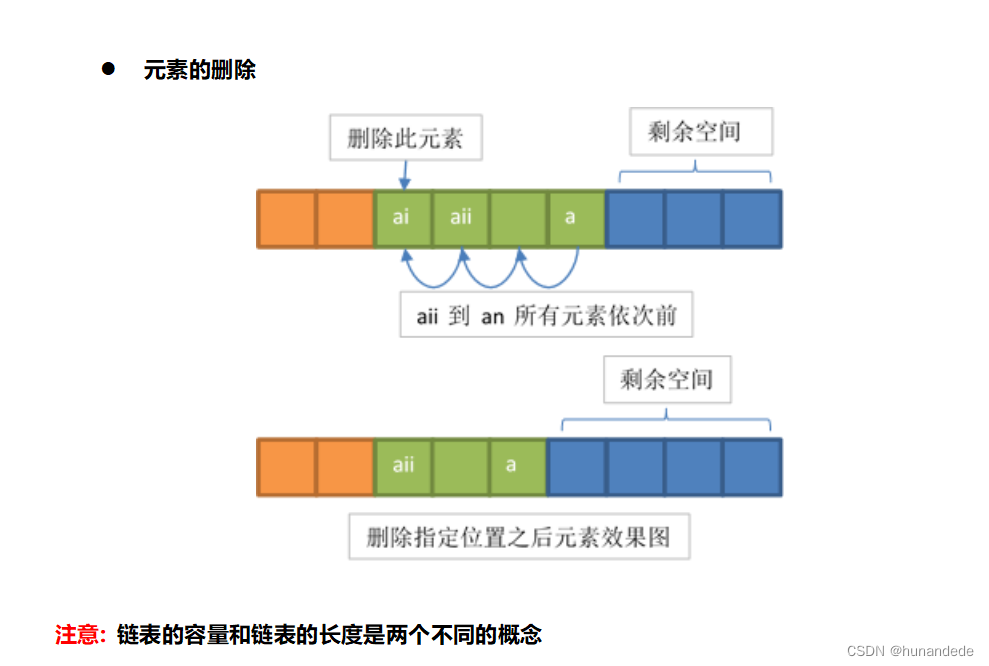
//从seqlist 中删除指定位置的元素
//参数 pos
//返回值为 删除的元素
//返回NULL 表示出现了error
SeqListNode* SeqList_Delete(SeqList *list, int pos) {
int ret = 1;
SeqListNode *retSeqListNode = NULL;
if (list == NULL) {
ret = -1;
printf("SeqList_Delete error list==NULL ret = %d\n", ret);
return retSeqListNode;
}
if (pos < 0) {
ret = -2;
printf("SeqList_Delete error pos<0 pos = %d ret = %d\n", pos, ret);
return retSeqListNode;
}
TSeqList *tempseqlist = NULL;
tempseqlist = (TSeqList *)list;
if (pos > tempseqlist->length-1) {
ret = -3;
printf("SeqList_Delete error because (pos > tempseqlist->length-1) pos = %d tempseqlist->length = %d ret =%d \n",
pos, tempseqlist->length, ret);
return retSeqListNode;
}
//先将要删除的节点缓存出来
retSeqListNode = tempseqlist->array[pos];
//
int i = 0;
for (i = pos+1; i < tempseqlist->length;++i) {
tempseqlist->array[i-1] = tempseqlist->array[i];
}
tempseqlist->length--;
return retSeqListNode;
}核心的写法图示:

C公司使用
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
extern "C" {
#include "001seqlist.h"
}
typedef struct Teacher {
int age;
char name[128];
char *othername;
char **stuname; //一个老师下面有5个学生
}Teacher;
int main001() {
_CrtSetDbgFlag(_CRTDBG_ALLOC_MEM_DF | _CRTDBG_LEAK_CHECK_DF);//程序退出时检测内存泄漏并显示到“输出”窗口
int ret = 0;
SeqList* seqlist = NULL;
// 初始化,建立一个空的线性表
//参数capacity表示该线性表的容量。
//返回值为SeqList*,表示创建成功。
//返回值NULL,表示创建失败。
seqlist = SeqList_Create(100);
if (seqlist==NULL) {
ret = -1;
printf("SeqList_Create(100) func error ret =%d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
int listcapacity = SeqList_Capacity(seqlist);
if (listcapacity < 0) {
ret = -2;
printf("SeqList_Capacity(seqlist) func error ret =%d listcapacity = %d\n", ret, listcapacity);
return ret;
}
//给seqlist中指定位置插入数据,
//参数seqlistnode为要插入的数据
//参数 pos 为要插入的位置
//如果线性表中还有空间,但是指定的pos位置是大于 现在的length
//例如 线性表capacity为100,现在存储了20了,但是pos的值是50
//我们这里做work around,就会将数据插入到21的位置
//成功返回1
//失败 返回<=0
Teacher tea1;
tea1.age = 11;
strcpy(tea1.name, (const char*)"zhangsan");
tea1.othername = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 128);
memset(tea1.othername, 0, sizeof(char)*128);
strcpy(tea1.othername, (const char*)"zhangsanothername");
tea1.stuname = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * 5);
memset(tea1.stuname, 0, sizeof(char *) * 5);
for (size_t i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
tea1.stuname[i] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 128);//每个学生名字也有128个字符
memset(tea1.stuname[i], 0, sizeof(char)*128);
sprintf(tea1.stuname[i],"zhangsanstuname%d",i+1);
}
Teacher tea2;
tea2.age = 22;
strcpy(tea2.name, (const char*)"lisi");
tea2.othername = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 128);
memset(tea2.othername, 0, sizeof(char) * 128);
strcpy(tea2.othername, (const char*)"lisiothername");
tea2.stuname = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * 5);
memset(tea2.stuname, 0, sizeof(char *) * 5);
for (size_t i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
tea2.stuname[i] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 128);//每个学生名字也有128个字符
memset(tea2.stuname[i], 0, sizeof(char) * 128);
sprintf(tea2.stuname[i], "lisistuname%d", i + 1);
}
Teacher tea3;
tea3.age = 33;
strcpy(tea3.name, (const char*)"wangwu");
tea3.othername = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 128);
memset(tea3.othername, 0, sizeof(char) * 128);
strcpy(tea3.othername, (const char*)"wagnwuothername");
tea3.stuname = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * 5);
memset(tea3.stuname, 0, sizeof(char *) * 5);
for (size_t i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
tea3.stuname[i] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 128);//每个学生名字也有128个字符
memset(tea3.stuname[i], 0, sizeof(char) * 128);
sprintf(tea3.stuname[i], "wangwustuname%d", i + 1);
}
ret = SeqList_Insert(seqlist, &tea1, 0);
if (ret<0) {
printf("SeqList_Insert(seqlist, &tea1, 0) func error ret =%d \n", ret);
return ret;
}
ret = SeqList_Insert(seqlist, &tea2, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("SeqList_Insert(seqlist, &tea1, 0) func error ret =%d \n", ret);
return ret;
}
ret = SeqList_Insert(seqlist, &tea3, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("SeqList_Insert(seqlist, &tea1, 0) func error ret =%d \n", ret);
return ret;
}
// 返回线性表List存在的元素个数
//返回值 >=0 表示:该list存在的元素个数
//<0 表示error
int seqlistlength = SeqList_Length(seqlist);
if (seqlistlength < 0) {
ret = seqlistlength;
printf("SeqList_Length(seqlist) func error ret =%d \n", ret);
return ret;
}
printf("seqlistlength = %d\n", seqlistlength);
//从seqlist 中获取指定位置的数据
//参数pos:seqlist中的位置
//返回值:为存储在该位置的元素
//返回NULL 表示有问题
for (int i = 0; i < SeqList_Length(seqlist); i++)
{
Teacher* temptea = (Teacher *)SeqList_Get(seqlist, i);
if (temptea ==NULL) {
printf("can not get find teacher from pos = %d\n",i);
}
printf("temptea->age = %d,temptea->name = %s,temptea->othername=%s\n",
temptea->age,
temptea->name,
temptea->othername);
for (size_t j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("temptea->stuname[%d] = %s, ",
j, temptea->stuname[j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//从seqlist 中删除指定位置的元素
//参数 pos
//返回值为 删除的元素
//返回NULL 表示出现了error
while (SeqList_Length(seqlist)>0) {
Teacher* deltea = (Teacher *) SeqList_Delete(seqlist, 0);
if (deltea == NULL) {
printf("delete teacher from 0 error \n");
break;
}
printf("deltea->age = %d,deltea->name = %s,deltea->othername=%s\n",
deltea->age,
deltea->name,
deltea->othername);
if(deltea->stuname!=NULL) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
if (deltea->stuname[i] != NULL) {
printf("deltea->stuname[%d] = %s, ",
i,deltea->stuname[i]);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
if (deltea->stuname != NULL) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
free(deltea->stuname[i]);
deltea->stuname[i] = NULL;
}
free(deltea->stuname);
deltea->stuname = NULL;
}
free(deltea->othername);
deltea->othername = NULL;
printf("\n");
}
//清空seqlist
//返回值为1,表示成功。
//返回值为-1,表示失败。
ret = SeqList_Clear(seqlist);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("SeqList_Clear(seqlist) func error ret =%d \n", ret);
return ret;
}
//销毁该线性表
//返回值为1,表示成功。
//返回值为-1,表示失败。
ret = SeqList_Destory(seqlist);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("SeqList_Destory(seqlist) func error ret =%d \n", ret);
return ret;
}
return 0;
}注意的点:
上层在将数据delete 后,记得要free相关数据。
底层并不知道上层是什么样子的数据结构,因此只需要将自己malloc的数据清理就好。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/hunandede/article/details/137678868
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
