Web接口自动化测试之Get与Post请求
关于HTTP协议,我考虑了一下觉得没必要再花一节内容来介绍,因为网上关于HTTP协议的介绍非常详细。本着以尽量避免介绍一空洞了概念与理论来介绍接口测试,我这里仍然会给出具体实例。
在此之前先简单的介绍一下基本概念:我们想要打开一个网站,首先是需要往浏览器的地址的URL输入框架中输入网地址。当我敲下回车后,通过HTTP协议,将网址传送到域名解析服务器,域名解析服务器根据网址找到对应的IP主机(系统服务器)。这个过程叫request,即请求;当IP主机拿到请求后,将相应的资源返回给用户浏览器。这个过程叫response,即响应。
当用户浏览器向系统服务器请求时,有几种方法,最常用的就是GET和POST两种方法。
在此我们来开发这样一个可以接收GET和POST请求的web应用。当然,这里就要求读者具备一定的web开发基础了。但不编程语言与web框架不是我们讨论的重点。
以flask框架的代码为例。
GET请求
pyfl/
|---- /hello.py
|----/templates/
|----|-----------/index.html
|----|-----------/user.html
hello.py
from flask import Flask,render_template
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def index():
return render_template("index.html")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)index.html
<h1> This is index page <h1>
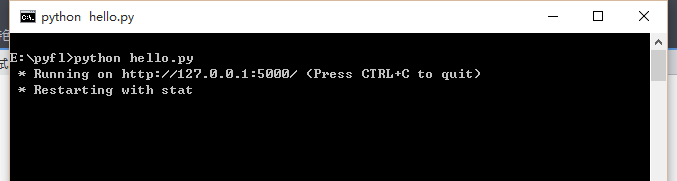
启动flask容器:
通过firebug查看GET请求信息:
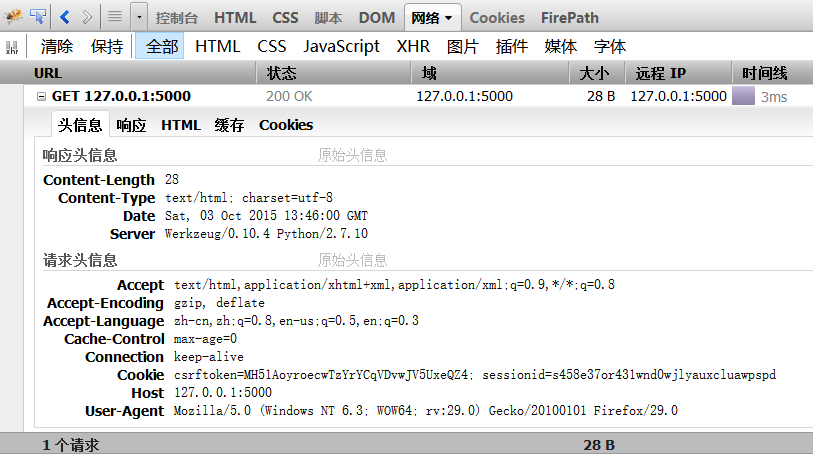
当然,这个返回只是一个静态的页面,并且不需要任何参数,我们只需要判断返回是否为200即可。
扩充hello.py如下:
from flask import Flask,render_template
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def index():
return render_template("index.html")
@app.route("/user/<name>")
def user(name):
return render_template("user.html",name=name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)user.html
<h1> Hell, {{name}} !<h1>
访问:http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/aaa
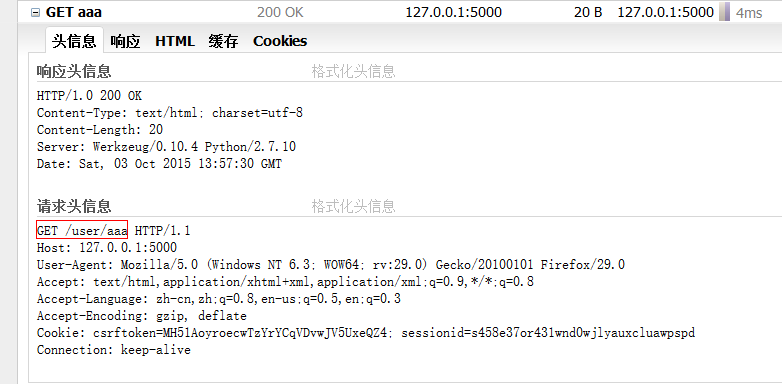
相比较来说,这个GET请求就复杂了一些,在请求的时候跟了一些参数(aaa),后台(hello.py)对参数了进行了接收,并且将其反回到了user.html页面中。
这个时候,我们就可以对这个参数做一些简单的测试,比较参数为空,字符,数字,脚本,sql 之类的。其实,安全测试的sql注入也是通过输参中带入sql语句入手的。
POST请求
pyfl/
|---- /hello.py
|----/templates/
|----|-----------/index.html
hello.py
from flask import Flask,render_template,request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def index():
return render_template("index.html")
@app.route("/login",methods = ['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == "POST":
username = request.form.get('username')
password = request.form.get('password')
if username=="zhangsan" and password=="123":
return "<h1>welcome, %s !</h1>" %username
else:
return "<h1>login Failure !</h1>"
else:
return "<h1>login Failure !</h1>"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)index.html
<form action="/login" method="post">
username: <input type="text" name="username">
password: <input type="password" name="password">
<input type="submit" id="submit">
</form>
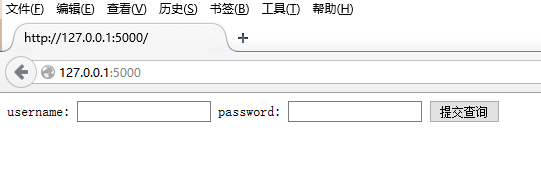
输入用户名,密码登录(后台hello.py判定,用户名为“zhangsan”,密码为“123”登录成功,其它帐号失败。)
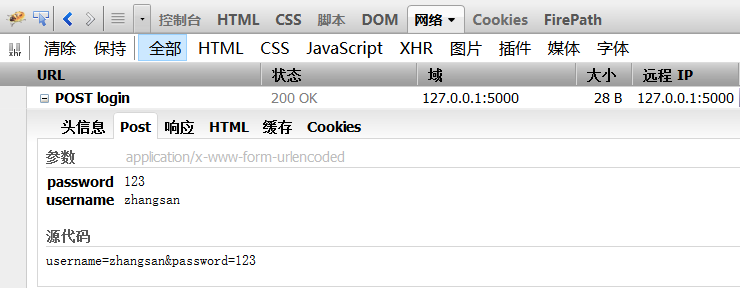
Python的有一个requests库,可以很方便的模拟测试POST请求。
#coding=utf-8
import requests
s = requests
data={"username":"zhangsan","password":"123",}
r = s.post('http://127.0.0.1:5000/login', data)
print r.status_code
print r.headers['content-type']
print r.encoding
print r.text执行结果:
200 text/html; charset=utf-8 utf-8 <h1>welcome, zhangsan !</h1>
POST接口的测试也一样,通过不输入为空,或错误的用户名密码,检查返回的内容。
===================
本文算是入门,可讨论的问题还有很多,例如接口返回的是json格式的数据,例如接口为了安全加了数字签名。从测试的角度,有哪个工作可以模拟这些请求,如何组织和运行测试用例。后面有时间再讨论。
2024最新Jmeter接口测试从入门到精通(全套项目实战教程)
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/dad22211/article/details/135608733
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
