爱上算法:每日算法(24-2月4号)
🌟坚持每日刷算法,😃将其变为习惯🤛让我们一起坚持吧💪
文章目录
232. 用栈实现队列
思路
首先应该先明确队列是先进先出,
而栈是先进后出,而如果想用栈实现队列,就可以尝试用两个栈
进栈和出栈
- 进栈模拟入队列
- 出栈模拟先出队列
画图如下

Code
Java
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stIn;
Stack<Integer> stOut;
public MyQueue() {
stIn = new Stack<>();
stOut = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stIn.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(stOut.isEmpty()){
while(!stIn.isEmpty()){
stOut.push(stIn.pop());
}
}
return stOut.pop();
}
public int peek() {
int res = this.pop();
stOut.push(res);
return res;
}
public boolean empty() {
return stOut.isEmpty()&&stIn.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
C++
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> stIn;
stack<int> stOut;
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) {
stIn.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if(stOut.empty()){
while(!stIn.empty()){
stOut.push(stIn.top());
stIn.pop();
}
}
int result = stOut.top();
stOut.pop();
return result;
}
int peek() {
int res = this->pop();
stOut.push(res);
return res;
}
bool empty() {
return stIn.empty()&&stOut.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* bool param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
复杂度
时间复杂度: push和empty为O(1), pop和peek为O(n)
空间复杂度: O(n)
225. 用队列实现栈
思路
队列是先进先出原则,
而栈是先进后出原则
因此,可以使用两个队列来实现栈
可以使用一个队列来实现栈
满足先进后出的方法就是; 入队列之后,就将这个数放到队首
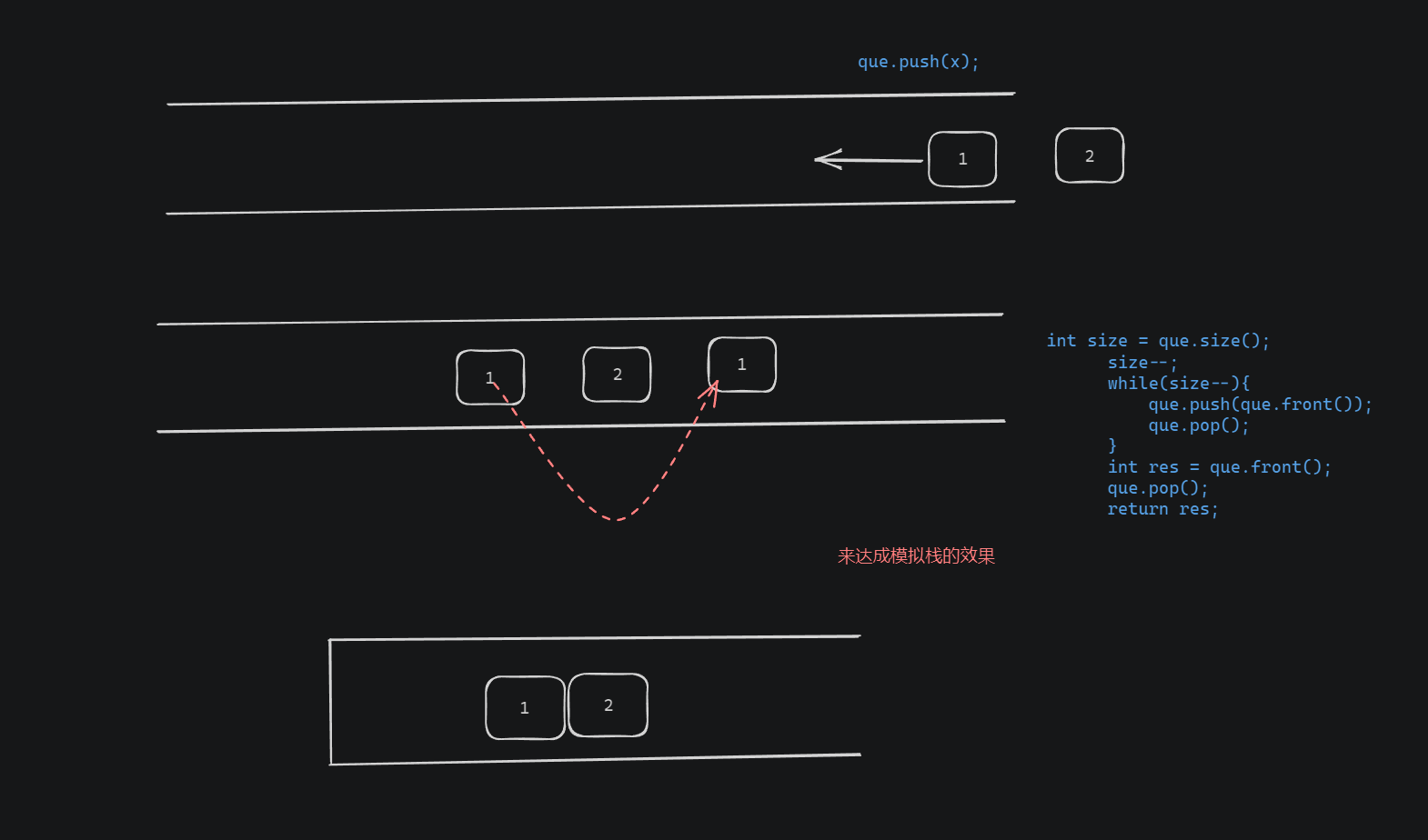
Code
C++
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que;
MyStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
que.push(x);
}
int pop() {
int size = que.size();
size--;
while(size--){
que.push(que.front());
que.pop();
}
int res = que.front();
que.pop();
return res;
}
int top() {
return que.back();
}
bool empty() {
return que.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = new MyStack();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
Java
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> que = new LinkedList<>();
public MyStack() {
}
public void push(int x) {
que.add(x);
}
public int pop() {
rePosition();
return que.poll();
}
public int top() {
rePosition();
int res = que.poll();
que.add(res);
return res;
}
public boolean empty() {
return que.isEmpty();
}
public void rePosition(){
int size = que.size();
size--; // 不包括刚刚添加的数
while(size-- > 0){
que.add(que.poll());
}
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
复杂度
- 时间复杂度: pop为O(n),其他为O(1)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_73865822/article/details/136034327
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
