list 的使用详解
C++ 的 list 是双向带头循环链表。由于链表的特殊性,所以其迭代器不能进行 +、- 操作,只支持 ++、-- 操作,同时其也不再支持下标访问操作。
迭代器、构造函数和拷贝构造
迭代器依旧是正向迭代器、反向迭代器、const正向、反向迭代器等。

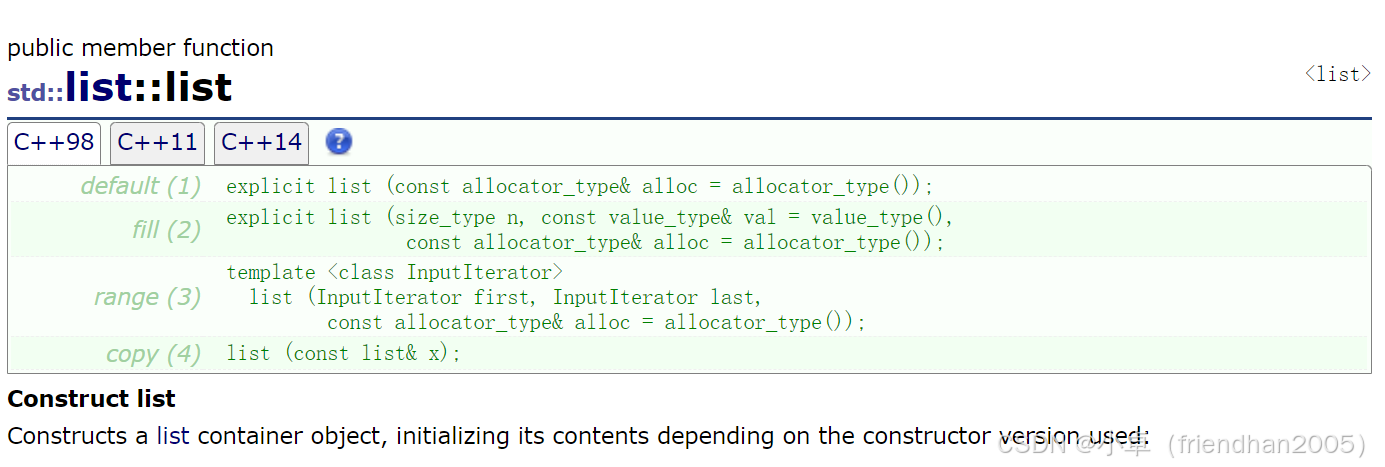
list<int> lt;
//用n个val初始化
list<int> lt1(10, 1);
list<int>::iterator it = lt1.begin();
while (it != lt1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
//迭代器区间初始化
list<int> lt2(lt1.begin(), lt1.end());
//拷贝构造
list<int> lt3(lt2);析构函数
析构函数会自动调用。

赋值重载函数(operator=( ))
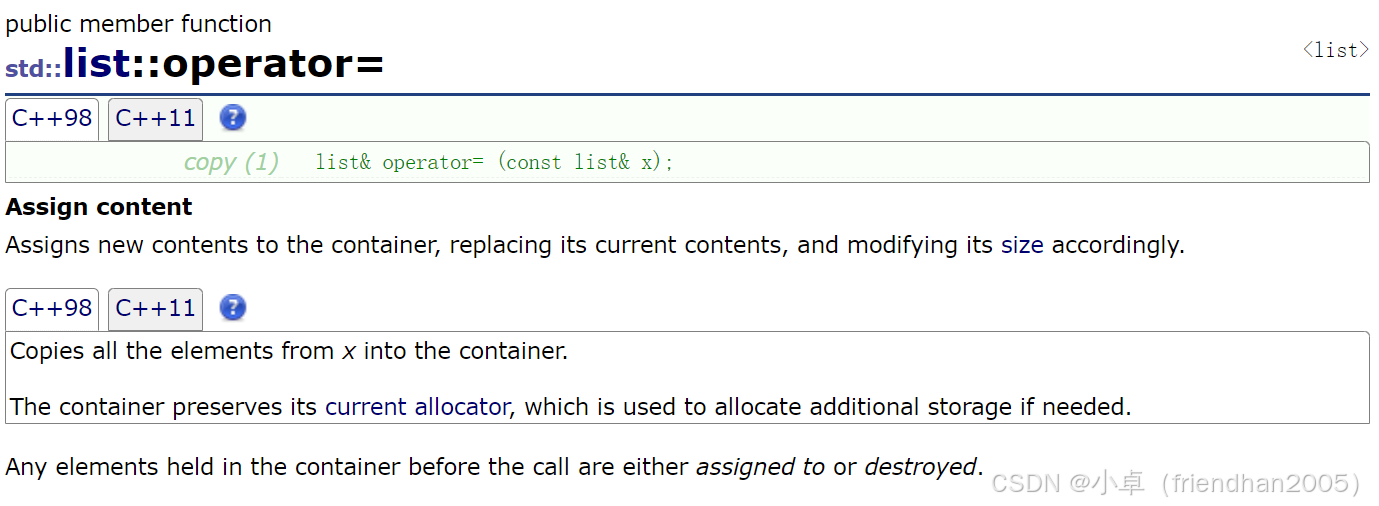
//用n个val初始化
list<int> lt1(10, 1);
//赋值重载
lt = lt1;
list<int>::iterator it1 = lt.begin();
while (it1 != lt.end())
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
it1++;
}
cout << endl;size( )
得到链表的长度。
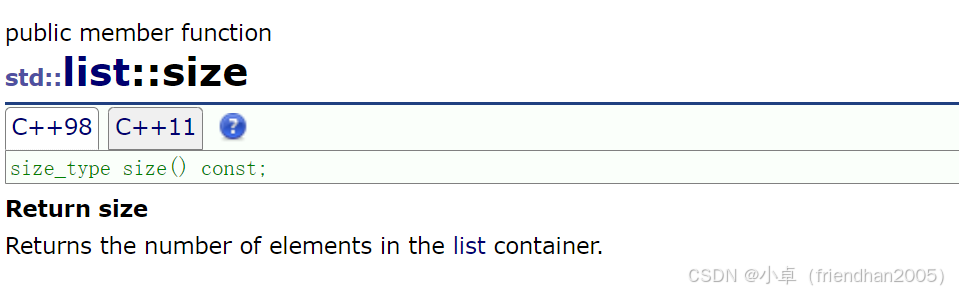
cout << lt.size() << endl;front( ) 和 back( )
取链表第一个元素和最后一个元素。
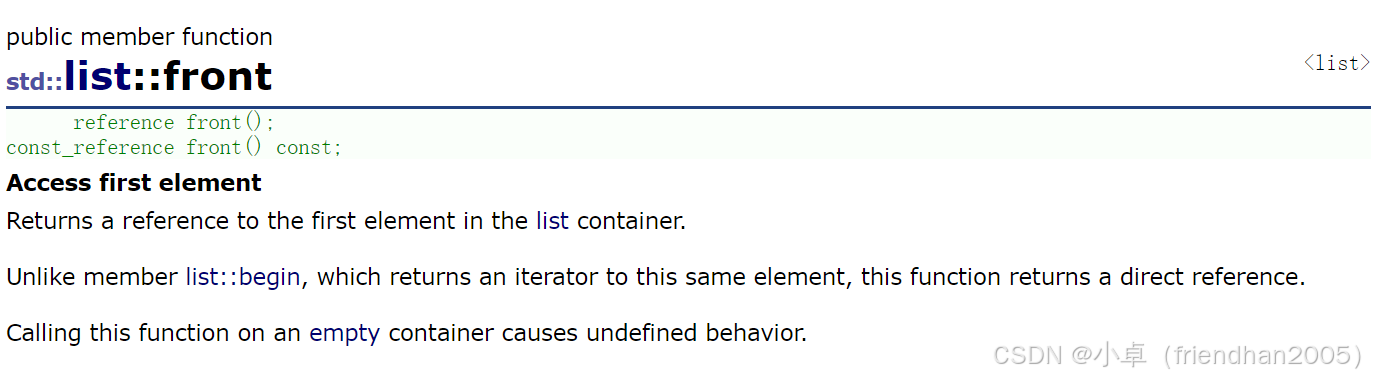
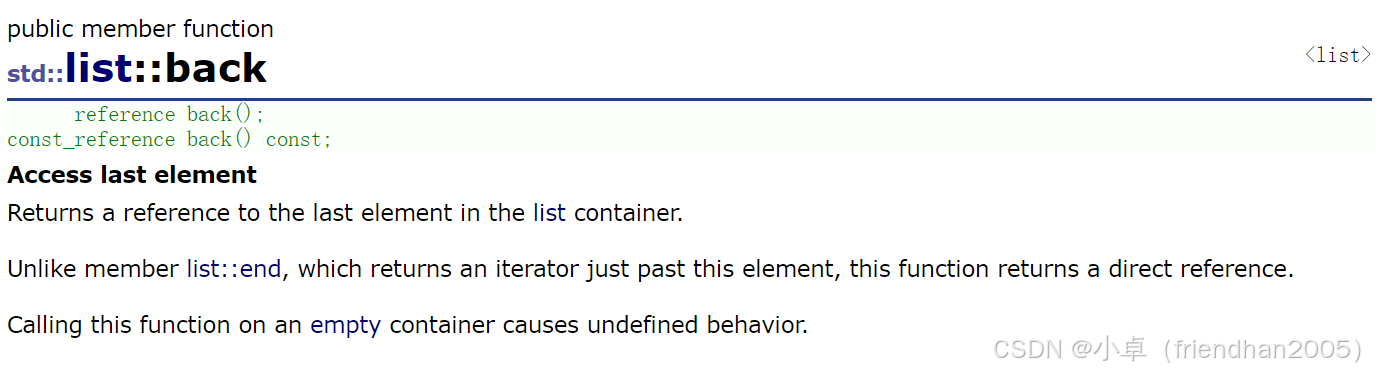
cout << lt.front() << endl;
cout << lt.back() << endl;push_back( )
向链表后追加一个数据。
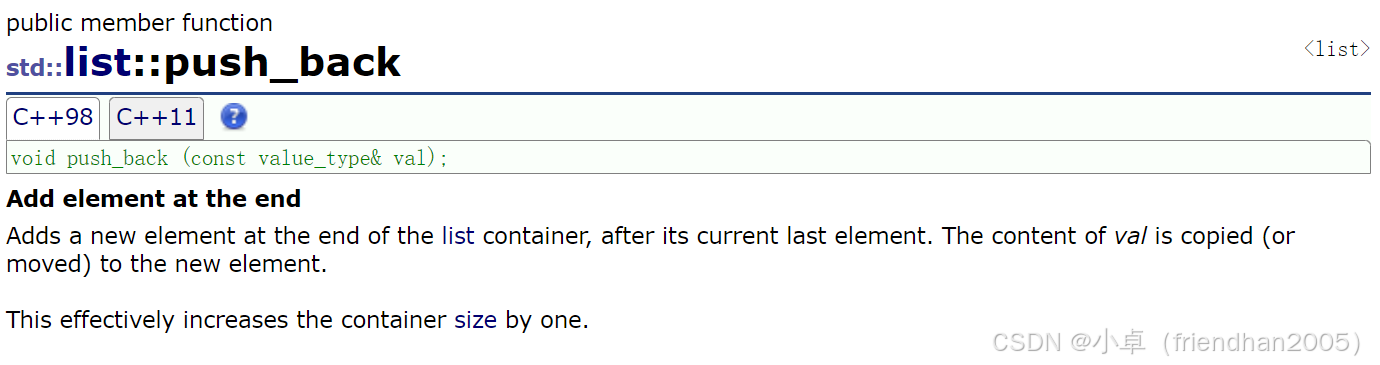
lt.push_back(6);pop_back( )
在链表尾部删除一个数据。

lt.pop_back();push_front( )
向链表头部插入一个数据。
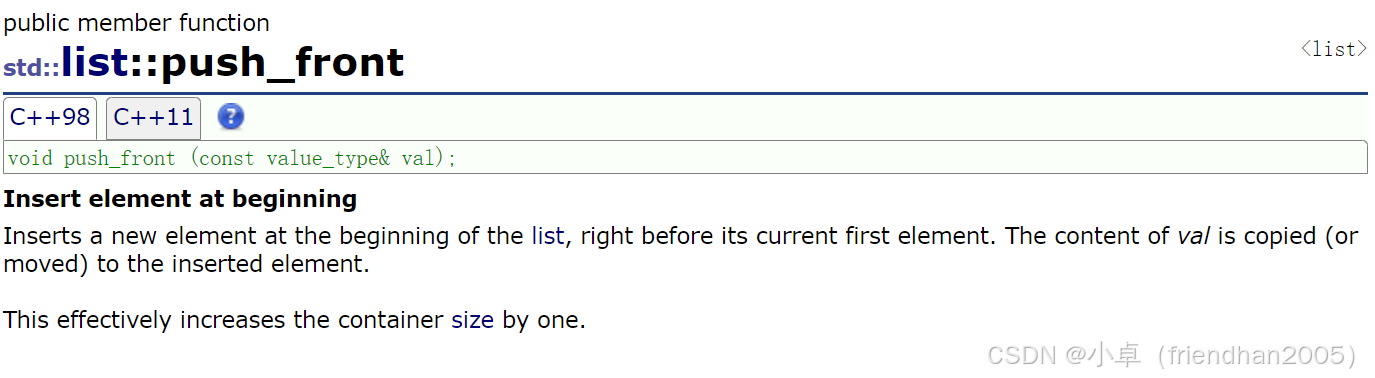
lt.push_front(6);pop_front( )
在链表开始位置删除一个数据。
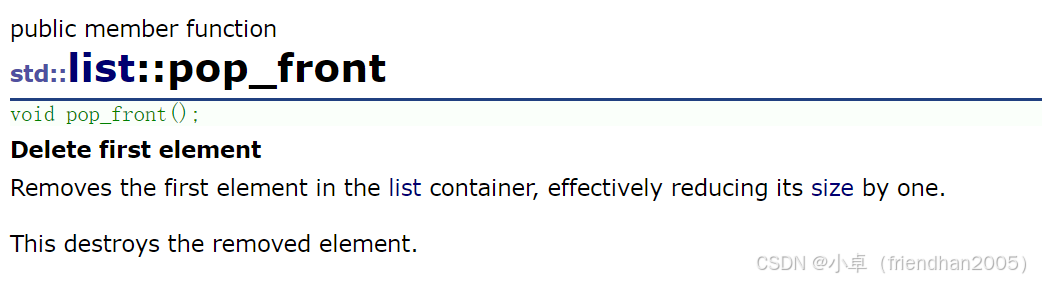
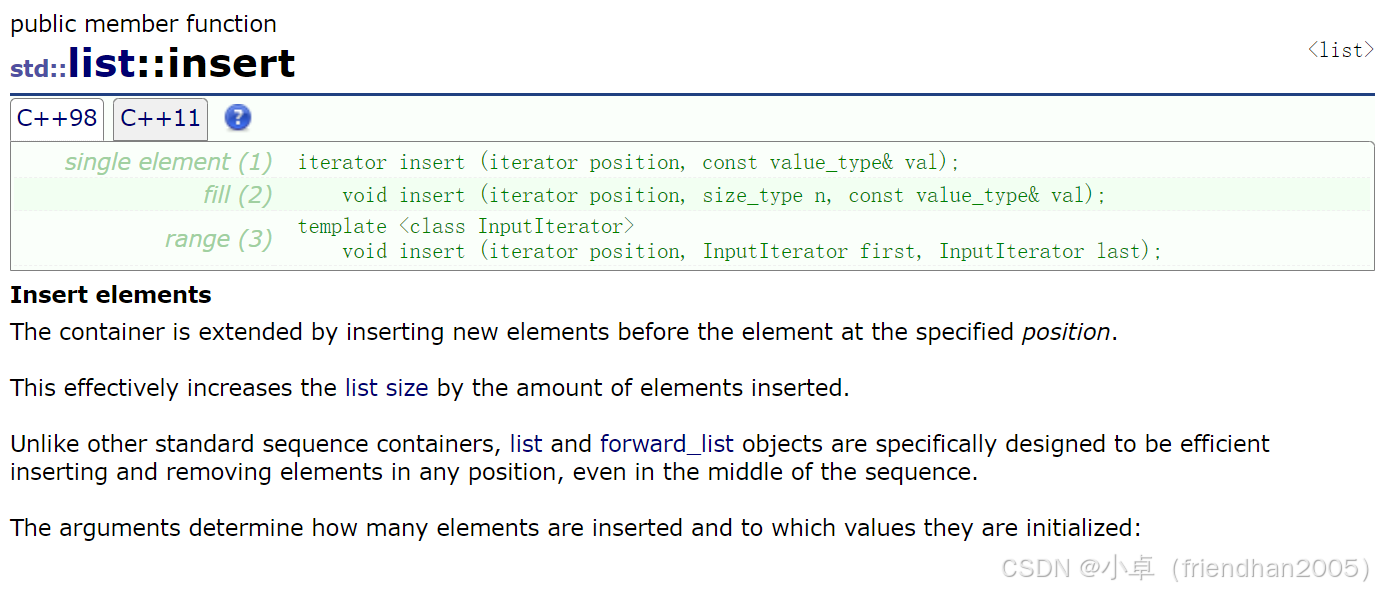
lt.pop_front();insert( )
向任意位置之前插入一个数据。
list<int> lt(10, 1);
//由于链表的特殊性,所以其迭代器不能进行 +、- 操作,只支持 ++、-- 操作
//如果要在第四个数据之前插入数据
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
int n = 3;
while (n--)
{
it++;
}
lt.insert(it, 6);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
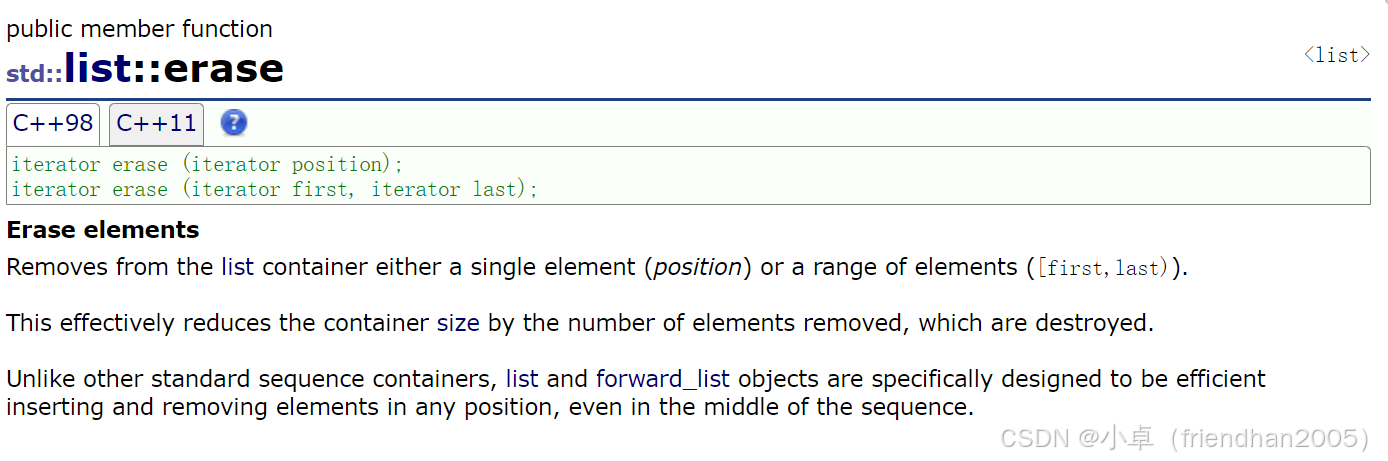
cout << endl;erase( )
删除任意一个节点。
list<int> lt(10, 1);
// 由于链表的特殊性,所以其迭代器不能进行 +、- 操作,只支持 ++、-- 操作
// 如果要删除第四个位置数据
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
int n = 3;
while (n--)
{
it++;
}
lt.erase(it);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;resize( )
调整数组的大小使其变为 n ,会改变数组的 size ,如果 n 大于当前数组长度,其会向后追加 n - size 个值为 val 的数,其默认为 0 ,如果 n 小于当前数组长度,其会将长度缩减为 n 。

lt.resize(10);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.resize(20, 9);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.resize(5);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
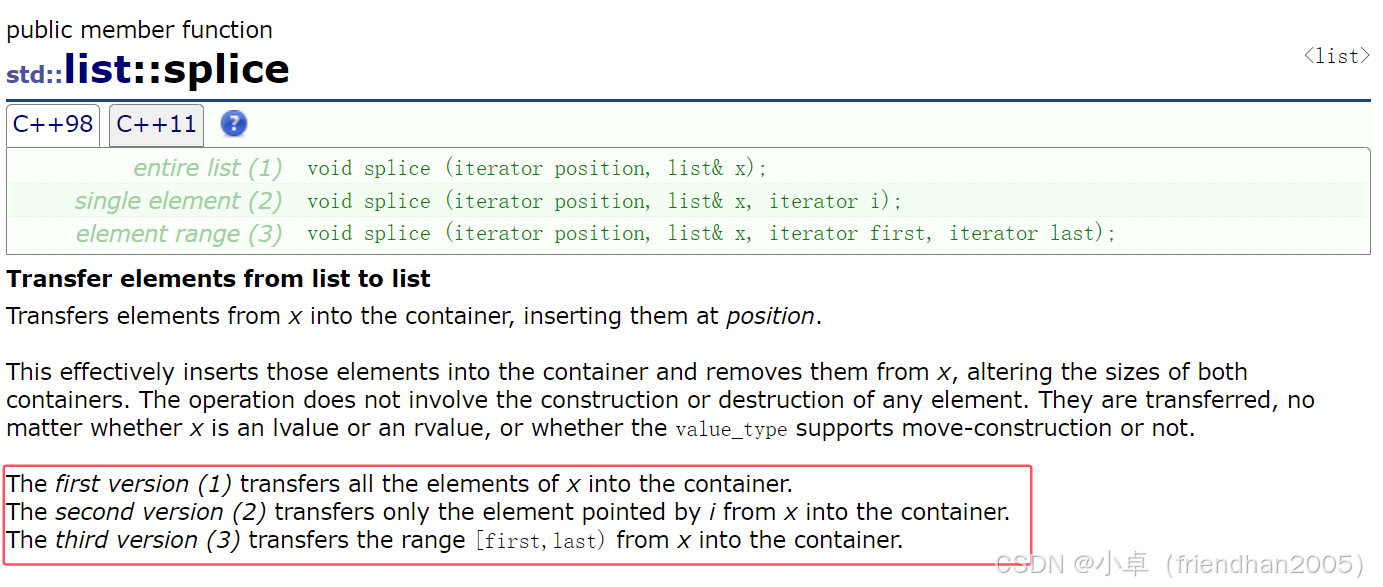
cout << endl;splice( )
用于将两个链表链接,或自身链表的移动。

list<int> lt;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
lt.push_back(i + 1);
}
list<int> lt1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
lt1.push_back(i * 10);
}
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto x : lt1)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.splice(lt.begin(), lt1);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
it++;
lt.splice(lt.begin(), lt, it);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int>::iterator it1 = lt.begin();
int n = 15;
while (n--)
{
it1++;
}
lt.splice(lt.begin(), lt, it1, lt.end());
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;list<int> lt;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
lt.push_back(i + 1);
}
list<int> lt1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
lt1.push_back(i * 10);
}
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto x : lt1)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
it++;
it++;
it++;
list<int>::iterator it1 = lt1.begin();
it1++;
it1++;
it1++;
lt.splice(it, lt1, it1);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;remove( )
去除所有值为 val 的元素。其与 erase 不同,erase 还要先找出值为 val 的位置,才能进行删除,并且只能删除一个。

list<int> lt(10, 1);
int count = 0;
for (auto& x : lt)
{
if (count % 2 == 0)
{
x = x + 1;
}
count++;
}
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.remove(1);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;sort( )
对链表中的元素进行排序。

int arr[] = { 3,9,5,4,2,0,8,16,99,1 };
list<int> lt(arr, arr + 10);
lt.sort();
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
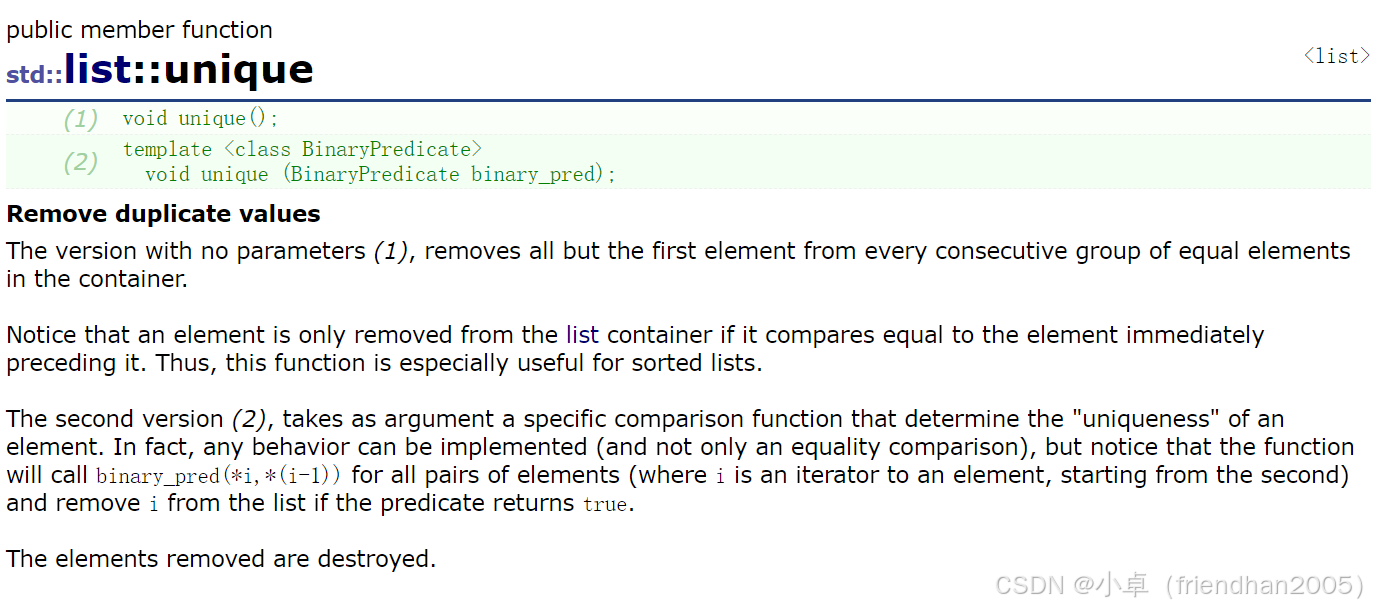
cout << endl;unique( )
去除链表中重复的元素,只保留第一个,但前提是其必须是有序的,因为其会比较一个元素与前一个元素的值是否相等,如果相等,就删除该元素。因此,此函数对于排序列表特别有用。否则其不能完全删除重复值。
int arr[] = { 1,2,7,12,3,12,3,7,15,2 };
list<int> lt(arr, arr + 10);
lt.sort();
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.unique();
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
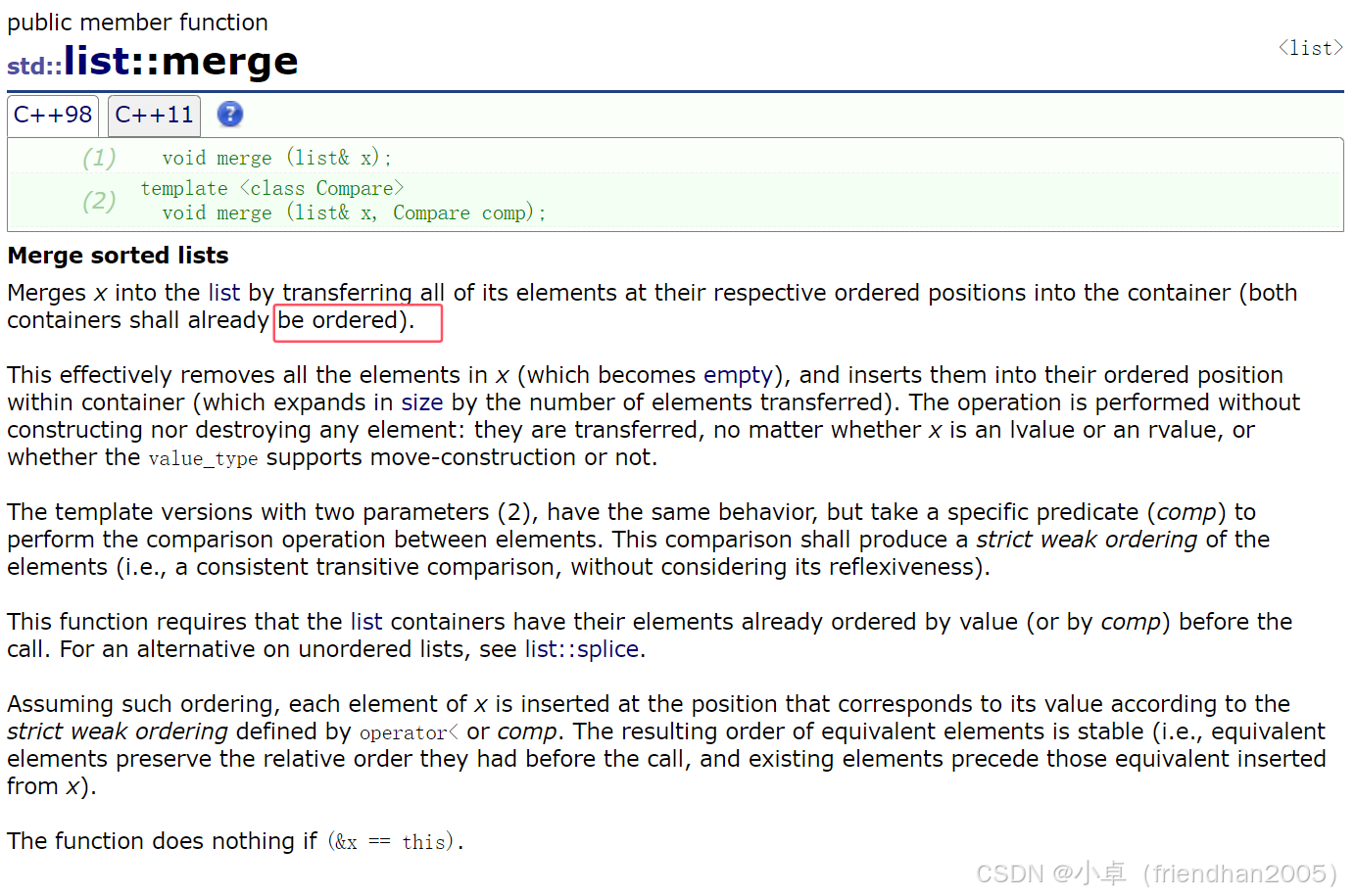
cout << endl;merge( )
归并两个链表的数据。但前提是要归并的两个链表的数据是有序的。
list<int> lt1;
list<int> lt2;
lt1.push_back(8);
lt1.push_back(3);
lt1.push_back(2);
lt1.push_back(9);
for (auto x : lt1)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt2.push_back(3);
lt2.push_back(7);
lt2.push_back(1);
lt2.push_back(4);
for (auto x : lt2)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt1.sort();
for (auto x : lt1)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt2.sort();
for (auto x : lt2)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt1.merge(lt2);
for (auto x : lt1)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;完整代码
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
void test()
{
list<int> lt;
//用n个val初始化
list<int> lt1(10, 1);
list<int>::iterator it = lt1.begin();
while (it != lt1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
//迭代器区间初始化
list<int> lt2(lt1.begin(), lt1.end());
//拷贝构造
list<int> lt3(lt2);
//赋值重载
lt = lt1;
list<int>::iterator it1 = lt.begin();
while (it1 != lt.end())
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << lt.size() << endl;
cout << lt.front() << endl;
cout << lt.back() << endl;
lt.push_back(6);
lt.push_back(6);
lt.push_back(6);
lt.pop_back();
lt.push_front(6);
lt.push_front(6);
lt.push_front(6);
lt.pop_front();
}
void test1()
{
list<int> lt(10, 1);
//由于链表的特殊性,所以其迭代器不能进行 +、- 操作,只支持 ++、-- 操作
//如果要在第四个数据之前插入数据
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
int n = 3;
while (n--)
{
it++;
}
it = lt.insert(it, 6);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.erase(it);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test2()
{
list<int> lt(10, 1);
// 由于链表的特殊性,所以其迭代器不能进行 +、- 操作,只支持 ++、-- 操作
// 如果要删除第四个位置数据
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
int n = 3;
while (n--)
{
it++;
}
lt.erase(it);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.resize(10);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.resize(20, 9);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.resize(5);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test3()
{
list<int> lt;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
lt.push_back(i + 1);
}
list<int> lt1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
lt1.push_back(i * 10);
}
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto x : lt1)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.splice(lt.begin(), lt1);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
it++;
lt.splice(lt.begin(), lt, it);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int>::iterator it1 = lt.begin();
int n = 15;
while (n--)
{
it1++;
}
lt.splice(lt.begin(), lt, it1, lt.end());
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test4()
{
list<int> lt;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
lt.push_back(i + 1);
}
list<int> lt1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
lt1.push_back(i * 10);
}
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto x : lt1)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
it++;
it++;
it++;
list<int>::iterator it1 = lt1.begin();
it1++;
it1++;
it1++;
lt.splice(it, lt1, it1);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test5()
{
list<int> lt(10, 1);
int count = 0;
for (auto& x : lt)
{
if (count % 2 == 0)
{
x = x + 1;
}
count++;
}
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.remove(1);
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test6()
{
int arr[] = { 3,9,5,4,2,0,8,16,99,1 };
list<int> lt(arr, arr + 10);
lt.sort();
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test7()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,7,12,3,12,3,7,15,2 };
list<int> lt(arr, arr + 10);
lt.sort();
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.unique();
for (auto x : lt)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test8()
{
list<int> lt1;
list<int> lt2;
lt1.push_back(8);
lt1.push_back(3);
lt1.push_back(2);
lt1.push_back(9);
for (auto x : lt1)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt2.push_back(3);
lt2.push_back(7);
lt2.push_back(1);
lt2.push_back(4);
for (auto x : lt2)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt1.sort();
for (auto x : lt1)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt2.sort();
for (auto x : lt2)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt1.merge(lt2);
for (auto x : lt1)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test8();
return 0;
}原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/friendhan2005/article/details/142622519
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
