深入理解 OSPF NSSA “P-bit”
** 注:机翻,未校对。**
OSPF NSSA P-bit Explained
OSPF Forward Address Filtering
OSPF 转发地址过滤
In this lesson we’ll take a closer look at the OSPF NSSA “P-bit”. When we redistribute something into an OSPF NSSA area then these prefixes are flooded within the NSSA area as LSA type 7. Once these LSAs make it to an ABR, they are translated into LSA type 5 and advertised to other areas.
在本课中,我们将更深入地了解 OSPF NSSA “P-bit”。当我们将某些内容重新分发到 OSPF NSSA 区域中时,这些前缀将作为 LSA 类型 7 淹没在 NSSA 区域内。一旦这些 LSA 进入 ABR,它们就会被翻译成 LSA 类型 5 并在其他地区发布广告。
The P-bit (P stands for propagate) can be found in the options field of an LSA type 7 and it tells the ABR if the LSA type 7 should be translated into a LSA type 5 or not. Only LSAs with the P-bit will be translated and automatically this bit will be set for all prefixes that are redistributed.
P 位(P 代表传播)可以在 LSA 类型 7 的选项字段中找到,它告诉 ABR 是否应该将 LSA 类型 7 转换为 LSA 类型 5。只有具有 P 位的 LSA 才会被转换,并且将自动为所有重新分发的前缀设置此位。
Let’s take a look at this P-bit in action. First I’ll show you where you can find it and afterwards we’ll look at some examples how you prevent the translation from LSA type 7 to 5. I’ll use the following topology:
让我们来看看这个 P-bit 的实际效果。首先,我将向您展示在哪里可以找到它,然后我们将查看一些示例,如何防止从 LSA 类型 7 到 5 的翻译。我将使用以下拓扑:
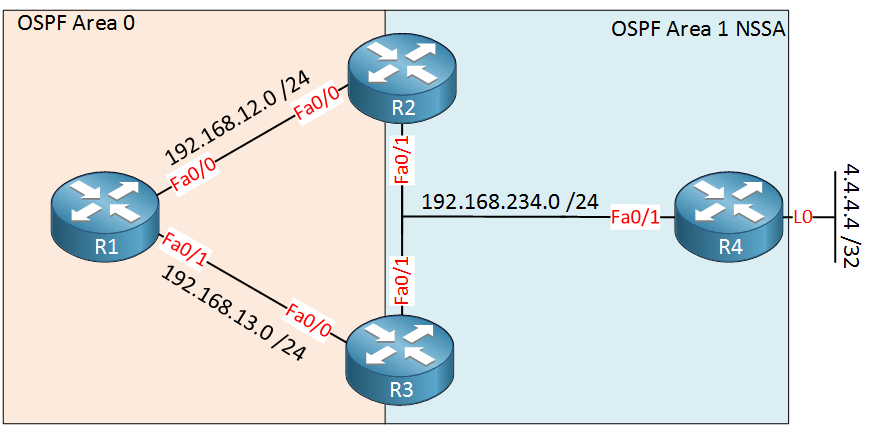
R1 is in area 0, R2 and R3 are our ABR (Area Border Routers) and R4 is within the NSSA area. It has a loopback interface that will be redistributed into OSPF.
R1 位于区域 0,R2 和 R3 是我们的 ABR(区域边界路由器),R4 位于 NSSA 区域内。它有一个环回接口,该接口将被重新分发到 OSPF 中。
Here is the OSPF configuration of all 4 routers:
以下是所有 4 个路由器的 OSPF 配置:
R1#show running-config | section ospf
router ospf 1
network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R2#show running-config | section ospf
router ospf 1
area 1 nssa
network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 192.168.234.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
R3#show running-config | section ospf
router ospf 1
area 1 nssa
network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 192.168.234.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
R4#show running-config | section ospf
router ospf 1
area 1 nssa
redistribute connected subnets
network 192.168.234.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
The OSPF configuration on all routers is pretty straight forward. I used redistribute connected subnets on R4 to redistribute the loopback interface into OSPF. Let’s start by looking at the LSDB on R4:
所有路由器上的 OSPF 配置都非常简单。我在 R4 上使用重新分配连接的子网将环回接口重新分配到 OSPF 中。让我们先看一下 R4 上的 LSDB:
R4#show ip ospf database nssa-external
OSPF Router with ID (4.4.4.4) (Process ID 1)
Type-7 AS External Link States (Area 1)
LS age: 895
Options: (No TOS-capability, Type 7/5 translation, DC)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 4.4.4.4 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 4.4.4.4
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0x78A5
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
MTID: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 192.168.234.4
External Route Tag: 0
Cisco IOS doesn’t show the P-bit as “P-bit” but you can see the OSPF options on top. The “Type 7/5 translation” part means that the P-bit has been set in this OSPF packet. Whenever this LSA reaches an ABR, it will be translated into a LSA type 5. Here’s what this LSA looks like in wireshark:
Cisco IOS 不会将 P 位显示为 “P 位”,但您可以在顶部看到 OSPF 选项。“Type 7/5 translation” 部分表示已在此 OSPF 数据包中设置了 P 位。每当此 LSA 达到 ABR 时,它将被转换为 LSA 类型 5。以下是此 LSA 在 wireshark 中的样子:
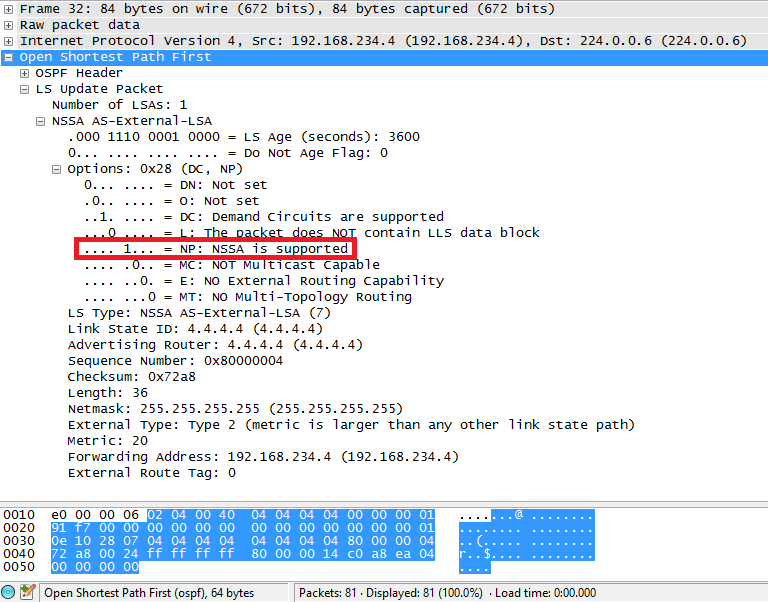
Here you can see the NP bit. This bit position has two roles:
在这里你可以看到 NP 位。此位位置有两个角色:
- N-bit: this one is used in hello packets for OSPF NSSA routers. When the N-bit is not supported, the routers won’t become neighbors.
N-bit:此位用于 OSPF NSSA 路由器的 hello 数据包。当 N 位不受支持时,路由器不会成为邻居。 - P-bit: this one is only used in the NSSA external LSA header.
P-bit:此仅在 NSSA 外部 LSA 标头中使用。
Since the N and P bit are never used at the same time, this bit position can be used for both roles.
由于 N 位和 P 位从不同时使用,因此此位位置可用于两个角色。
Let’s take a look at this LSA on R2 and R3 (our ABRs):
让我们看一下 R2 和 R3(我们的 ABR)上的这个 LSA:
R2#show ip ospf database nssa-external
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.234.2) (Process ID 1)
Type-7 AS External Link States (Area 1)
LS age: 1233
Options: (No TOS-capability, Type 7/5 translation, DC)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 4.4.4.4 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 4.4.4.4
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0x78A5
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
MTID: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 192.168.234.4
External Route Tag: 0
R3#show ip ospf database nssa-external
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.234.3) (Process ID 1)
Type-7 AS External Link States (Area 1)
Routing Bit Set on this LSA in topology Base with MTID 0
LS age: 1237
Options: (No TOS-capability, Type 7/5 translation, DC)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 4.4.4.4 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 4.4.4.4
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0x78A5
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
MTID: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 192.168.234.4
External Route Tag: 0
Both routers have the LSA in their LSDB. Let’s check R1:
两台路由器的 LSDB 中都有 LSA。让我们检查一下 R1:
R1#show ip ospf database external
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.13.1) (Process ID 1)
Type-5 AS External Link States
Routing Bit Set on this LSA in topology Base with MTID 0
LS age: 1346
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 4.4.4.4 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 192.168.234.3
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0xFAE5
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
MTID: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 192.168.234.4
External Route Tag: 0
R1 has a LSA type 5 for this network and you can see that R3 (192.168.234.3) has translated this LSA. The forward address to reach this network is R4 (192.168.234.4). OSPF separates the advertising router and the address to reach this particular network (forward address). When R1 wants to reach this network it can use both paths since the cost is equal:
R1 具有此网络的 LSA 类型 5,您可以看到 R3 (192.168.234.3) 已转换此 LSA。到达此网络的转发地址是 R4 (192.168.234.4)。OSPF 将广告路由器和到达此特定网络的地址(转发地址)分开。当 R1 想要访问此网络时,它可以使用两条路径,因为成本相等:
R1#show ip route ospf | begin 4.4.4.4
O E2 4.4.4.4 [110/20] via 192.168.13.3, 00:38:49, FastEthernet0/1
[110/20] via 192.168.12.2, 00:38:49, FastEthernet0/0
So why did R3 do the translation of LSA type 7 into 5? We have two ABRs after all. Since OSPF uses a forward address, there is no need for both R2 and R3 to translate our LSA type 7 into a LSA type 5. Only one router has to do it.
那么,为什么 R3 要将 LSA 类型 7 翻译成 5 型呢?毕竟,我们有两个 ABR。由于 OSPF 使用转发地址,因此 R2 和 R3 无需将 LSA 类型 7 转换为 LSA 类型 5。只有一个路由器必须这样做。
via:
-
OSPF NSSA P-bit Explained
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/u013669912/article/details/140669968
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
