一、flask入门和视图
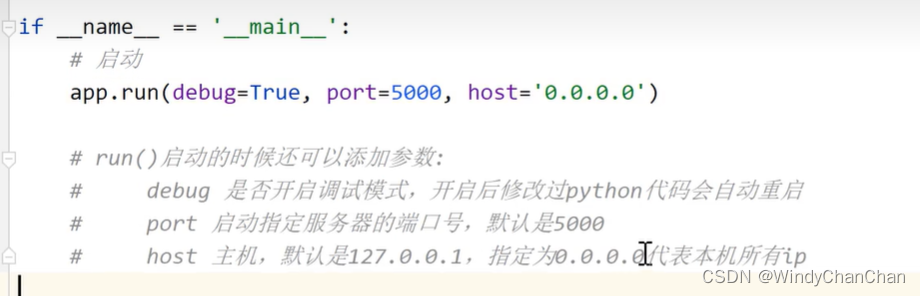
run启动参数
模板渲染
- 后端给前端页面传参

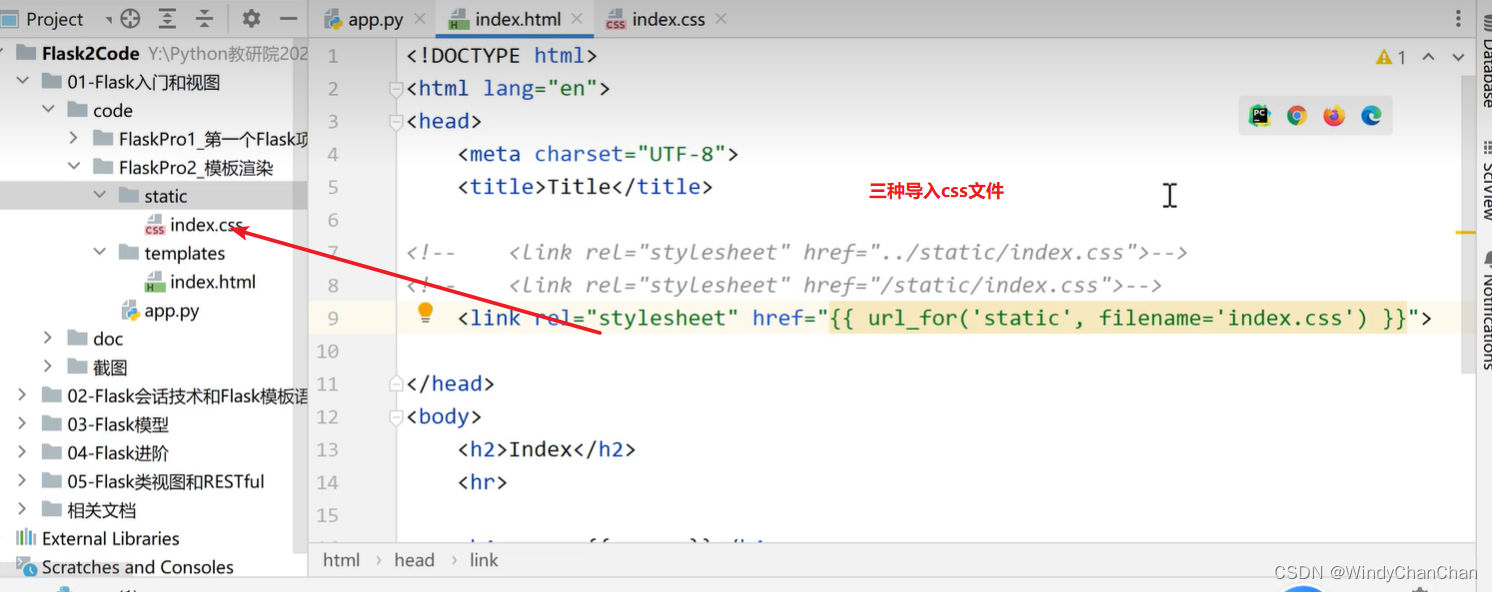
- 前端页面设置css
from flask import Flask, render_template,jsonify
# 创建flask对象
app = Flask(__name__)
# 视图函数 + 路由route
@app.route("/")
def hello_world():
# 响应,返回给前端的数据
return "hello world"
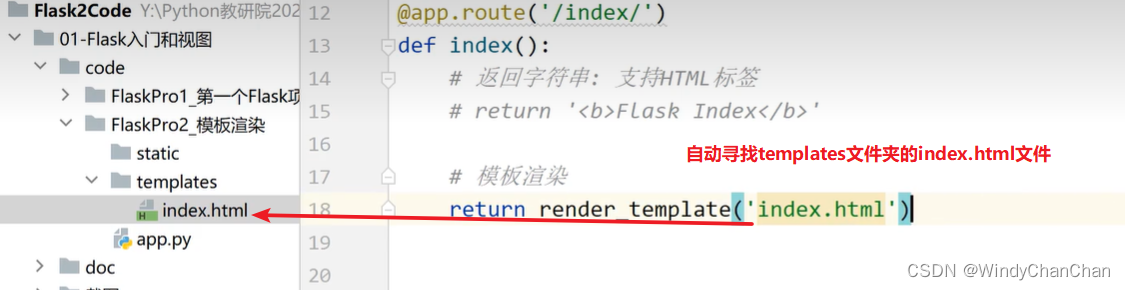
# 模板渲染 templates名字固定,存放html静态文件;static名字固定,存放css和js文件
@app.route("/index")
def index():
# 会自动寻找templates文件夹下的内容
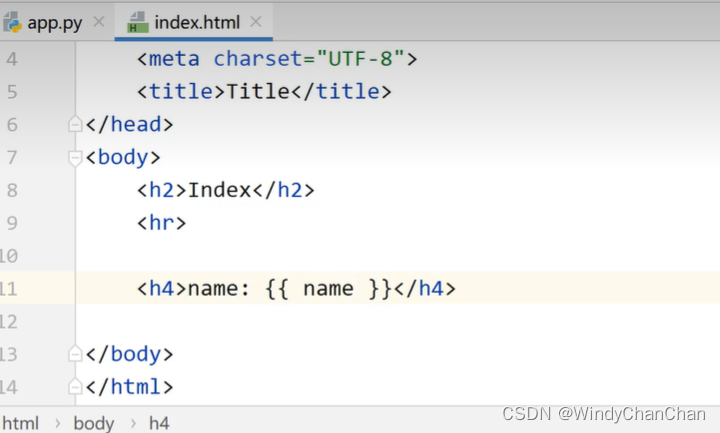
return render_template("index.html",name="zhangsan ")
# 返回json
# return jsonify({"name":"jj","age":12}) 序列化
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
路由参数
- 路由:将从客户端发送过来的请求分发到指定函数上。
路由参数:
string 接收任何没有斜杠('/')的字符串(默认)
int接收整型
float接收浮点型
path接收路径,可接收斜线('/')
uuid只接受uuid字符串,唯一码,一种生成规则
any可以同时指定多种路径,进行限定
# views.py: 路由 + 视图函数
from flask import Blueprint
from .models import *
# 蓝图
# 第一个参数:蓝图名称,第二个参数:模块名称
blue = Blueprint('user', __name__) # 使用蓝图可以模块化管理路由
@blue.route('/') # 不能使用@app.route 因为@app依赖app = Flask(__name__)
def index():
return 'index'
# 路由参数
# string 接收任何没有斜杠('/')的字符串(默认)
# int接收整型
# float接收浮点型
# path接收路径,可接收斜线('/')
# uuid只接受uuid字符串,唯一码,一种生成规则
# any可以同时指定多种路径,进行限定
# string: 重点
# @blue.route('/string/<string:username>/')
@blue.route('/string/<username>/')
def get_string(username): # 路由的参数必须由函数的参数接收且参数名一致
print(type(username)) # <class 'str'>
return username
# int 类型:参数名
@blue.route('/int/<int:id>/')
def get_int(id):
print(type(id)) # <class 'int'>
return str(id) # 返回值类型只能是string,dict,list,tuple或者WISG callable
# float
@blue.route('/float/<float:money>/')
def get_float(money):
print(type(money)) # <class 'float'>
return str(money)
# path: 支持/的字符串
# localhost:5000/path/he/llo/ 返回:he/llo
@blue.route('/path/<path:name>/')
def get_path(name):
print(type(name)) # <class 'str'>
return str(name)
# uuid:d12fda71-e885-444a-8cbd-5cdcbcb7c232
@blue.route('/uuid/<uuid:id>/')
def get_uuid(id):
print(type(id)) # <class 'uuid.UUID'>
return str(id)
@blue.route('/getuuid/')
def get_uuid2():
import uuid
return str(uuid.uuid4())
# any: 从列出的项目中选择一个
@blue.route('/any/<any(apple, orange, banana):fruit>/')
def get_any(fruit):
print(type(fruit)) # <class 'str'>
return str(fruit)
# methods: 请求方式
# 默认不支持POST
# 如果需要同时支持GET和POST,就设置methods
@blue.route('/methods/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def get_methods():
return 'methods'
指定请求方法
# methods: 请求方式
# 默认不支持POST
# 如果需要同时支持GET和POST,就设置methods
@blue.route('/methods/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def get_methods():
return 'methods'
请求和响应
请求
- Request请求:服务器在接收到客户端的请求后,会自动创建Request对象


from flask import Blueprint, request, render_template, \
jsonify, make_response, Response, redirect, url_for, abort
from .models import *
# 蓝图
blue = Blueprint('user', __name__)
# http一次前后端交互:先请求,后响应
# Request: 客户端向服务器发送的请求
@blue.route('/request/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def get_request():
pass
# print(request) # <Request 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/request/' [GET]>
# 重要属性
print(request.method) # 请求方式,'GET'或'POST'...
# GET请求的参数
# ImmutableMultiDict: 类字典对象,区别是可以出现重复的key
# http://127.0.0.1:5000/request/?name=lisi&name=wangwu&age=33
print(request.args) # ImmutableMultiDict([('name', 'lisi'), ('name', 'wangwu'), ('age', '33')])
# print(request.args['name'], request.args['age']) # lisi 33
# print(request.args.get('name')) # lisi
# print(request.args.getlist('name')) # ['lisi', 'wangwu']
# POST请求的参数
# res = requests.post('http://127.0.0.1:5000/request/',data={'name': 'lucy', 'age': 33})
print(request.form) # ImmutableMultiDict([('name', 'lucy'), ('age', '33')])
# print(request.form.get('name')) # lucy
# cookie
# res = requests.post('http://127.0.0.1:5000/request/',data={'name': 'lucy', 'age': 33},cookies={'name': 'hello'})
print(request.cookies) # ImmutableMultiDict([('name', 'hello')])
# 路径
print(request.path) # /request/
print(request.url) # http://127.0.0.1:5000/request/?name=lisi&name=wangwu&age=33
print(request.base_url) # http://127.0.0.1:5000/request/
print(request.host_url) # http://127.0.0.1:5000/
print(request.remote_addr) # 127.0.0.1,客户端的ip
print(request.files) # 文件内容 ,ImmutableMultiDict([])
print(request.headers) # 请求头
print(request.user_agent) # 用户代理,包括浏览器和操作系统的信息 , python-requests/2.28.2
return 'request ok!'
响应
- Response响应:服务器返回客户端数据

from flask import Blueprint, request, render_template, \
jsonify, make_response, Response, redirect, url_for, abort
from .models import *
# 蓝图
blue = Blueprint('user', __name__)
# Response: 服务器端向客户端发送的响应
@blue.route('/response/')
def get_response():
pass
# 响应的几种方式
# 1. 返回字符串(不常用)
# return 'response OK!'
# 2. 模板渲染 (前后端不分离)
# return render_template('index.html', name='张三', age=33)
# 3. 返回json数据 (前后端分离)
data = {'name': '李四', 'age': 44}
# return data
# jsonify(): 序列化,字典=>字符串
# return jsonify(data)
# 4. 自定义Response对象
html = render_template('index.html', name='张三', age=33)
print(html, type(html)) # <class 'str'>
# res = make_response(html, 200)
res = Response(html)
return res
重定向

# Redirect: 重定向
@blue.route('/redirect/')
def make_redirect():
pass
# 重定向的几种方式
# return redirect('https://www.qq.com')
# return redirect('/response/')
# url_for():反向解析,通过视图函数名反过来找到路由
# url_for('蓝图名称.视图函数名')
# ret = url_for('user.get_response')
# print('ret:', ret) # /response/
# return redirect(ret)
# url_for传参
ret2 = url_for('user.get_request', name='王五', age=66)
return redirect(ret2)
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/u013308709/article/details/137477675
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
