聊聊jvm中内存模型的坑
jvm线程的内存模型
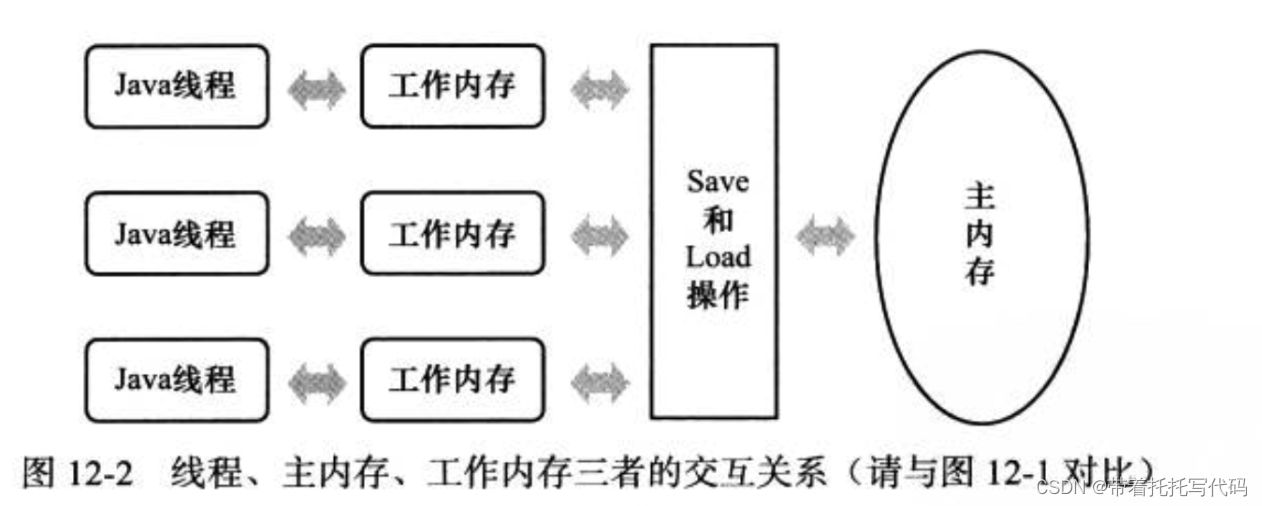
看图,简单来说线程中操作的变量是副本。在并发情况下,如果数据发生变更,副本的数据就变为脏数据。这个时候就会有并发问题。
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/yeyang/p/12580682.html
怎么解决并发问题
解决的方案有两种:
1. 加排它锁,将并发的操作变成串行的操作。
2. 无锁方案:通过cas操作,并保证如果变量发生变更,其它的线程需要立即知道。(java的原子操作类使用的就是这种方案:cas+volatile)
volatile关键字实战
先说结论, 从实战效果上看,whlie循环中的变量是无法感知到其它线程对变量的修改的,但是再加上volatile关键字修饰之后可以感知到。而for循环中即使不加关键字volatile修饰,也是可以感知到变化的。这点在写代码时特别要注意。
测试代码如下:
//结论: while循环的写法,可以反应出变量的可见性问题,for循环的写法不能反应可见性问题
public class Demo {
static AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0);
public static int a = 0;
//public volatile static int a = 0;
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
test03();
}
//while循环在变量不加volatile关键字修饰时,无法感知到变量变化。
public static void test02() throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread01 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("test01:"+a);
while (true) {
if (a >= 2) {
System.out.println("我变了");
}
}
}
});
thread01.start();
Thread thread02 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
a++;
System.out.println("test02:" + a);
}
}
});
thread02.start();
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
//for循环即使不加volatile关键字修饰,也可以感知到变量变化。
public static void test03() throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread01 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("test01:"+a);
for(int i=0; i<10000; i++){
if (i==0) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
if (a >= 2) {
System.out.println("我变了");
}
}
}
});
thread01.start();
Thread thread02 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
a++;
System.out.println("test02:" + a);
}
}
});
thread02.start();
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/langsiming/article/details/137741931
免责声明:本站文章内容转载自网络资源,如本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。更多内容请关注自学内容网(zxcms.com)!
